Pico-Motor-Driver
| ||
Overview
Raspberry Pi Pico motor driver expansion board, suitable for driving two-wheel or four-wheel robots
Features
- Onboard Raspberry Pi Pico interface, suitable for Raspberry Pi Pico series boards
- I2C controlled, supports 32 x different I2C addresses by setting the 5 address jumpers
- Onboard PCA9685 chip, can output 12-bit hardware PWM to control motor speed
- Onboard TB6612FNG dual H-bridge motor driver chip, high efficiency, not easy to heat
- Integrates 5V regulator, up to 3A output current, can be powered from the battery through VIN terminal
- Break out unused pins of Pico for easy extension
- Provides online supporting manual (demos for Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ and MicroPython)
Specification
- Operating Voltage: 6~12V (VIN terminal)
- Logic level: 3.3V
- PWM driver: PCA9685
- Motor driver: TB6612FNG
- Control interface: I2C
- Hole diameter: 3.0mm
- Dimensions: 65 × 56 (mm)
Pinout
Dimensions
Pico Getting Started
Firmware Download
Basic Introduction
MicroPython Series
Install Thonny IDE
In order to facilitate the development of Pico/Pico2 boards using MicroPython on a computer, it is recommended to download the Thonny IDE
- Download Thonny IDE and follow the steps to install, the installation packages are all Windows versions, please refer to Thonny's official website for other versions
- After installation, the language and motherboard environment need to be configured for the first use. Since we are using Pico/Pico2, pay attention to selecting the Raspberry Pi option for the motherboard environment
- Configure MicroPython environment and choose Pico/Pico2 port
- Connect Pico/Pico2 to your computer first, and in the lower right corner of Thonny left-click on the configuration environment option --> select Configture interpreter
- In the pop-up window, select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico), and choose the corresponding port
Flash Firmware
- Click OK to return to the Thonny main interface, download the corresponding firmware library and burn it to the device, and then click the Stop button to display the current environment in the Shell window
- Note: Flashing the Pico2 firmware provided by Micropython may cause the device to be unrecognized, please use the firmware below or in the package
- How to download the firmware library for Pico/Pico2 in windows: After holding down the BOOT button and connecting to the computer, release the BOOT button, a removable disk will appear on the computer, copy the firmware library into it
- How to download the firmware library for RP2040/RP2350 in windows: After connecting to the computer, press the BOOT key and the RESET key at the same time, release the RESET key first and then release the BOOT key, a removable disk will appear on the computer, copy the firmware library into it (you can also use the Pico/Pico2 method)
MicroPython Series Tutorials
【MicroPython】 machine.Pin class function details
【MicroPython】machine.PWM class function details
【MicroPython】machine.ADC class function details
【MicroPython】machine.UART class function details
【MicroPython】machine.I2C class function details
【MicroPython】machine.SPI class function details
【MicroPython】rp2.StateMachine class function details
C/C++ Series
For C/C++, it is recommended to use Pico VS Code for development. This is a Microsoft Visual Studio Code extension designed to make it easier for you to create, develop, and debug projects for the Raspberry Pi Pico series development boards. No matter if you are a beginner or an experienced professional, this tool can assist you in developing Pico with confidence and ease. Here's how to install and use the extension.
- Official website tutorial: https://www.raspberrypi.com/news/pico-vscode-extension/
- This tutorial is suitable for Raspberry Pi Pico, Pico2 and the RP2040 and RP2350 series development boards developed by Waveshare
- The development environment defaults to Windows11. For other environments, please refer to the official tutorial for installation
Install VSCode
-
First, click to download pico-vscode package, unzip and open the package, double-click to install VSCode
Note: If vscode is installed, check if the version is v1.87.0 or later
Install Extension
-
Click Extensions and select Install from VSIX
-
Select the package with the vsix suffix and click Install
-
Then vscode will automatically install raspberry-pi-pico and its dependency extensions, you can click Refresh to check the installation progress
-
The text in the right lower corner shows that the installation is complete. Close VSCode
Configure Extension
-
Open directory C:\Users\username and copy the entire .pico-sdk to that directory
-
The Copy is completed
-
Open vscode and configure the paths for the Raspberry Pi Pico extensions
The configuration is as follows:Cmake Path: ${HOME}/.pico-sdk/cmake/v3.28.6/bin/cmake.exe Git Path: ${HOME}/.pico-sdk/git/cmd/git.exe Ninja Path: ${HOME}/.pico-sdk/ninja/v1.12.1/ninja.exe Python3 Path: ${HOME}/.pico-sdk/python/3.12.1/python.exe
New Project
-
The configuration is complete, create a new project, enter the project name, select the path, and click Create to create the project
To test the official example, you can click on the Example next to the project name to select
-
The project is created successfully
-
Select the SDK version
-
Select Yes for advanced configuration
-
Choose the cross-compilation chain, 13.2.Rel1 is applicable for ARM cores, RISCV.13.3 is applicable for RISCV cores. You can select either based on your requirements
-
Select default for CMake version (the path configured earlier)
-
Select default for Ninjaversion
-
Select the development board
-
Click Complie to compile
-
The uf2 format file is successfully compiled
Import Project
- The Cmake file of the imported project cannot have Chinese (including comments), otherwise the import may fail
-
To import your own project, you need to add a line of code to the Cmake file to switch between pico and pico2 normally, otherwise even if pico2 is selected, the compiled firmware will still be suitable for pico
set(PICO_BOARD pico CACHE STRING "Board type")
Update Extension
-
The extension version in the offline package is 0.15.2, and you can also choose to update to the latest version after the installation is complete
Arduino IDE Series
Install Arduino IDE
-
First, go to Arduino official website to download the installation package of the Arduino IDE.

-
Here, you can select Just Download.

-
Once the download is complete, click Install.

Notice: During the installation process, it will prompt you to install the driver, just click Install
Arduino IDE Interface
-
After the first installation, when you open the Arduino IDE, it will be in English. You can switch to other languages in File --> Preferences, or continue using the English interface.

-
In the Language field, select the language you want to switch to, and click OK.

Install Arduino-Pico Core in Arduino IDE
-
Open the Arduino IDE, click on the file in the top left corner, and select Preferences
-
Add the following link to the attached board manager URL, and then click OK
https://github.com/earlephilhower/arduino-pico/releases/download/4.0.2/package_rp2040_index.json
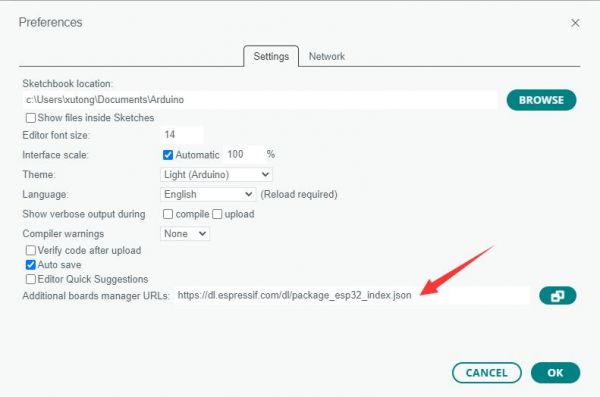
Note: If you already have an ESP32 board URL, you can use a comma to separate the URLs as follows:https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json,https://github.com/earlephilhower/arduino-pico/releases/download/4.0.2/package_rp2040_index.json
-
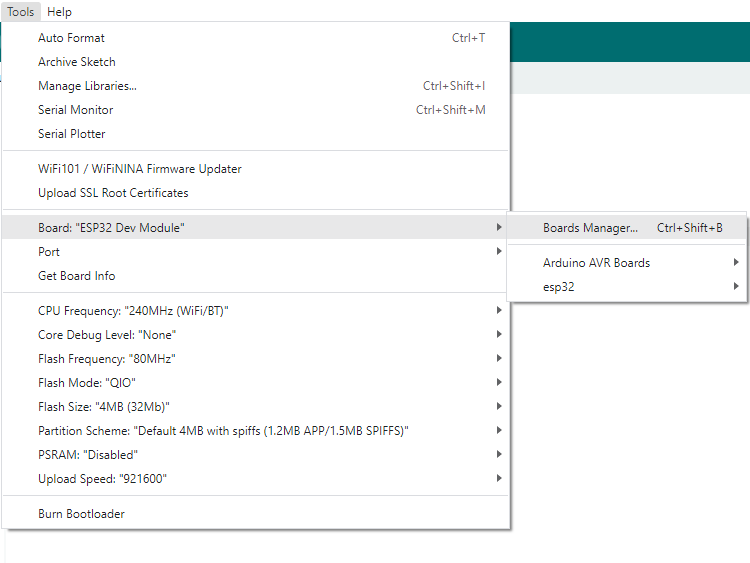
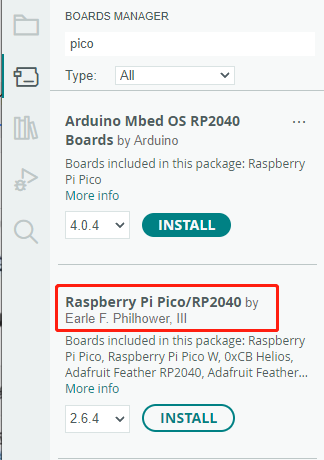
Click Tools > Development Board > Board Manager > Search pico, as my computer has already been installed, it shows that it is installed
Upload Demo at the First Time
-
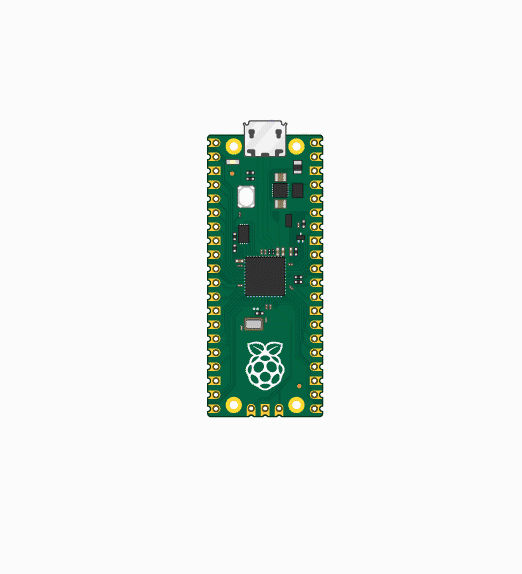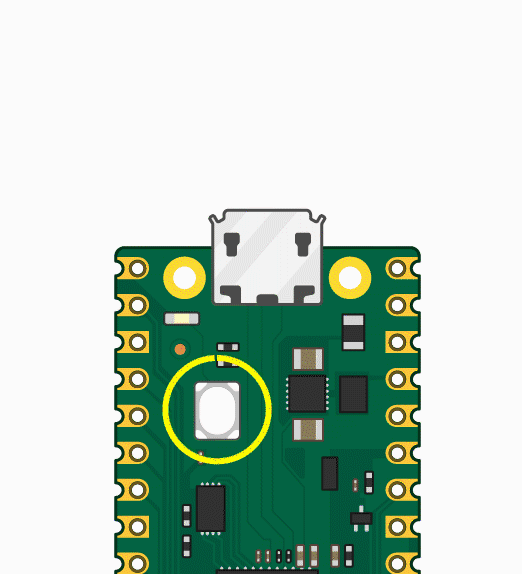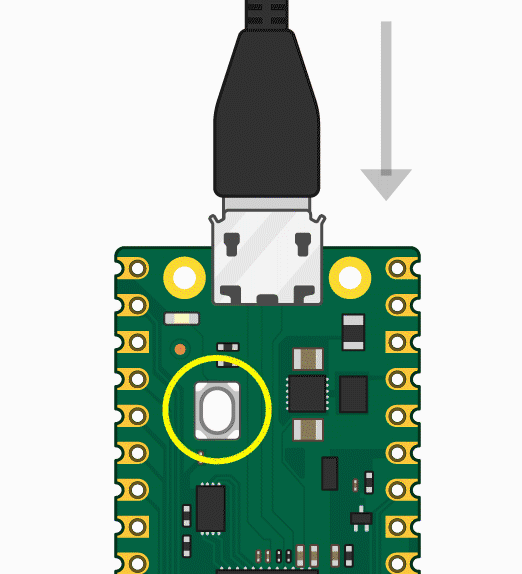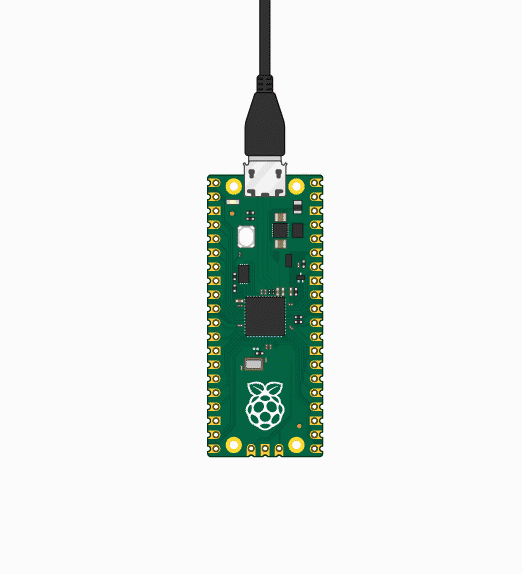
Press and hold the BOOTSET button on the Pico board, connect the pico to the USB port of the computer via the Micro USB cable, and release the button after the computer recognizes a removable hard disk (RPI-RP2).
- Download the program and open D1-LED.ino under the arduino\PWM\D1-LED path
-
Click Tools --> Port, remember the existing COM, do not click this COM (the COM displayed is different on different computers, remember the COM on your own computer)
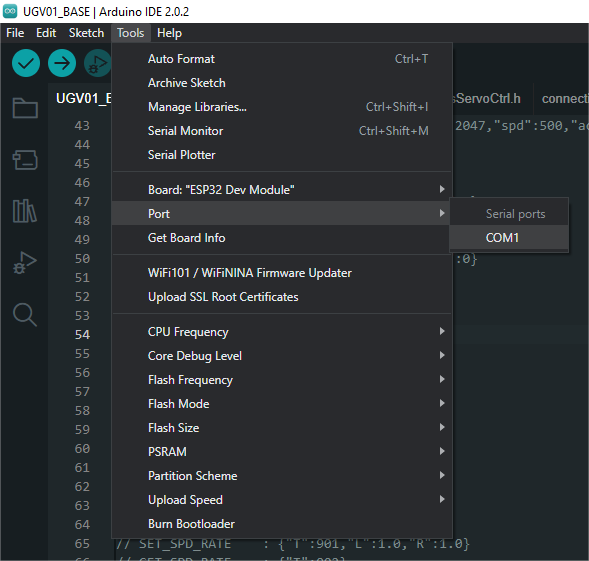
-
Connect the driver board to the computer using a USB cable. Then, go to Tools > Port. For the first connection, select uf2 Board. After uploading, when you connect again, an additional COM port will appear
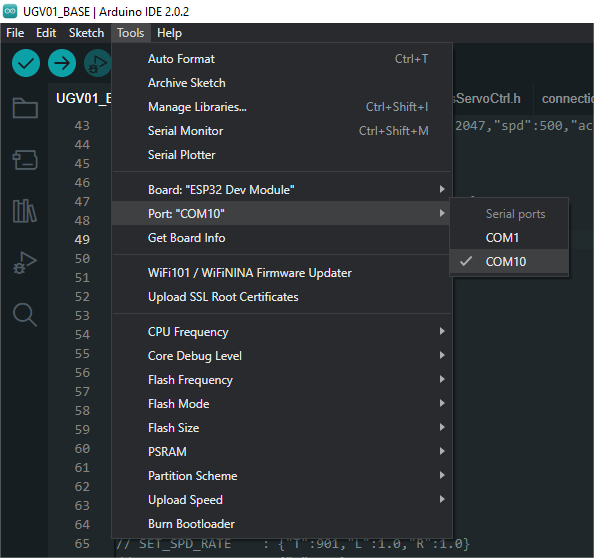
-
Click Tools > Development Board > Raspberry Pi Pico > Raspberry Pi Pico or Raspberry Pi Pico 2
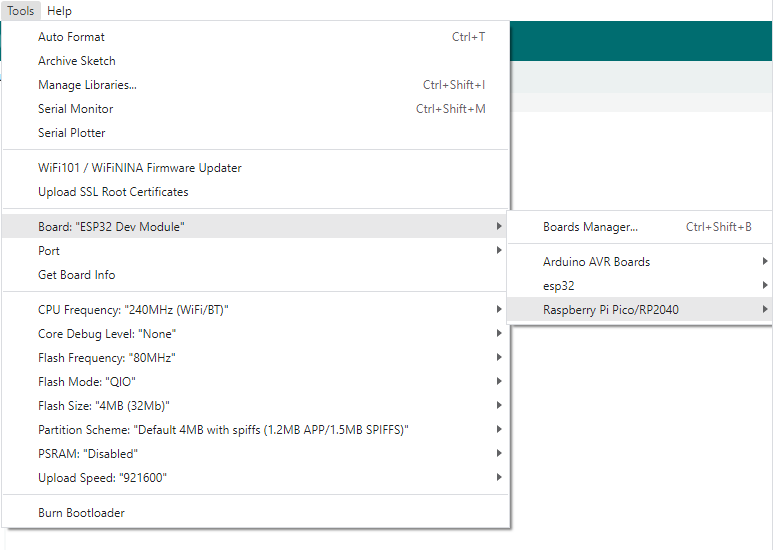
- After setting it up, click the right arrow to upload the program
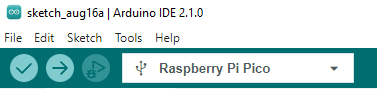
- If issues arise during this period, and if you need to reinstall or update the Arduino IDE version, it is necessary to uninstall the Arduino IDE completely. After uninstalling the software, you need to manually delete all contents within the C:\Users\[name]\AppData\Local\Arduino15 folder (you need to show hidden files to see this folder). Then, proceed with a fresh installation.
Open Source Demos
MircoPython video demo (github)
MicroPython firmware/Blink demos (C)
Raspberry Pi official C/C++ demo (github)
Raspberry Pi official micropython demo (github)
Arduino official C/C++ demo (github)
User Guide
Hardware Connection
When connecting the Pico, please be careful not to reverse the corresponding direction. You can judge the direction by observing the end with a USB silkscreen on the module and the USB port end of the Pico (you can also judge the direction by the pin number of the female connector on the module and the pin number of the Pico).

Demo Download
1. Download directly from Raspberry Pi
Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and execute:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full cd ~ sudo wget https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/Pico-Motor-Driver/Pico-Motor-Driver-code.7z 7z Pico_pico-Motor-Driver-code.7z -o./pico-Motor-Driver-code.7z cd ~/pico-Motor-Driver-code
2. Click Demo under Resources to download it
Working with Raspberry Pi
C
- The following tutorial is for operating on a Raspberry Pi, but due to the multi-platform and portable characteristics of cmake, it can also be successfully compiled on a PC, with some differences in operation that you will need to judge on your own
- For compilation, please make sure that it is in the c directory:
cd ~/pico-Motor-Driver-code/c/
Create and enter the build directory in the folder, and add the SDK: Here ../../pico-sdk is the directory of your SDK. There is a build in the demo, which can be accessed directly
cd build export PICO_SDK_PATH=../../pico-sdk (Note: Make sure to write the correct path to your own SDK)
Execute cmake, automatically generate the Makefile file:
cmake ..
Execute make to generate an executable file, the first compilation takes a long time
make -j9
After the compilation is completed, the uf2 file will be generated. Press and hold the button on the Pico board, connect pico to the USB port of the Raspberry Pi via Micro USB cable, then release the button. After connecting, the Raspberry Pi will automatically recognize a removable disk (RPI-RP2), and copy the main.uf2 file in the build folder to the recognized removable disk (RPI-RP2).
cp main.uf2 /media/pi/RPI-RP2/
Python
Working with Raspberry Pi
- 1. Flash the Micropython firmware and copy the pico_micropython_xxxxx.uf2 file into pico (more on this in the Windows tutorial below).
- 2. Open the Thonny IDE on the Raspberry Pi (click on the Raspberry Pi logo -> Programming -> Thonny Python IDE), you can view the version information by going to Help->About Thonny
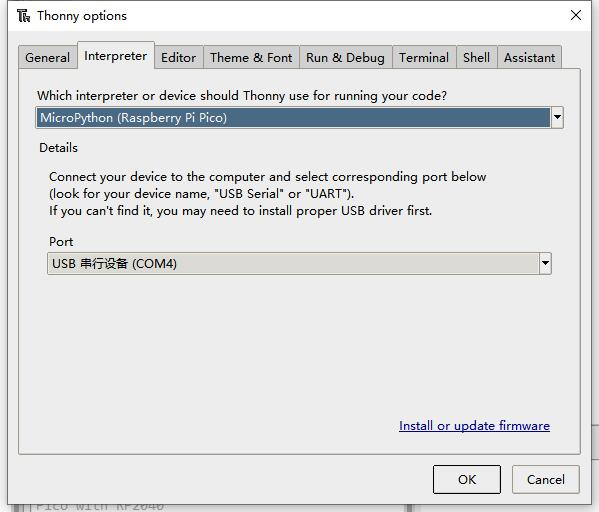
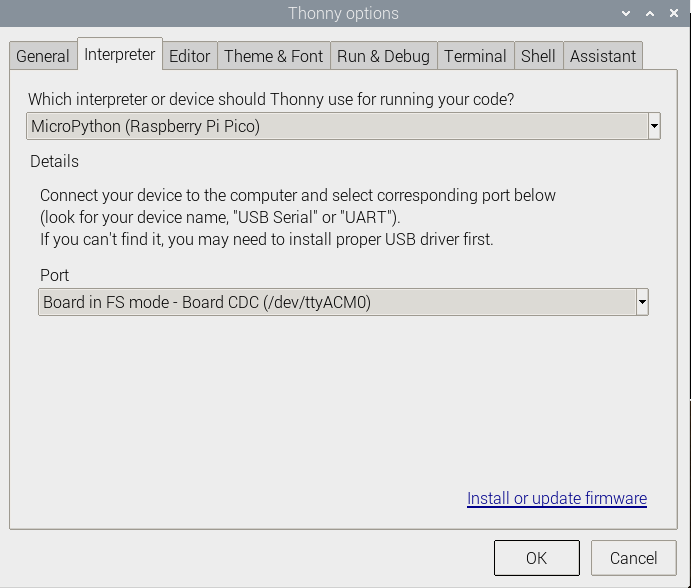
To ensure your version is supported by the Pico package, you can also click on Tools -> Options... -> Interpreter and select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico and ttyACM0 port)
As shown below:
If your current Thonny version does not have the pico support package, input the following command to update the Thonny IDE
sudo apt upgrade thonny
3. Click File->Open...->python/pico-Motor-Driver-code/PCA9685.py to run the script
Experimental Phenomenon: Motors A and B will rotate at full speed in the positive direction for 2S, and then rotate at half speed in the reverse direction for 4S
Working with Windows
python
Working with Windows
- 1. Press and hold the BOOTSET button on the Pico board, connect the pico to the USB port of the computer via the Micro USB cable, and release the button after the computer recognizes a removable hard disk (RPI-RP2).
- 2. Download pico_micropython_xxxxx.uf2 file,and copy it to the recognized removable disk (RPI-RP2)
- 3.Open Thonny IDE (Note: Make sure to use the latest version of Thonny, otherwise there is no support package for Pico, the latest version under Windows is v3.3.3)
- 4. Click Tools > Settings - > Interpreter and select Pico and the corresponding port as shown in the figure
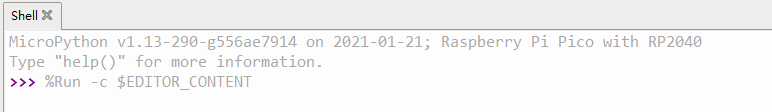
- 5. File ->Open->servo.py, click Run, as shown in the figure that the program has been run:
The experimental phenomenon is exactly the same as the C demo and will not be repeated here
FAQ
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)