Raspberry-Pi-Pico-Kit-B
| ||
Raspberry Pico
Raspberry Pi Pico is a low-cost, high-performance microcontroller board with flexible digital interfaces. It incorporates Raspberry Pi's own RP2040 microcontroller chip, with a dual-core Arm Cortex M0+ processor running up to 133 MHz, embedded 264KB of SRAM, and 2MB of onboard Flash memory, as well as 26x multi-function GPIO pins.
For software development, either Raspberry Pi's C/C++ SDK or the MicroPython is available. There are also complete development resources and tutorials to help you get started easily, and integrate it into end products quickly.
Details of the Start Kit
- Raspberry Pi Pico with pre-soldered header x1
- Pico-LCD-1.14 x 1
- Pico-10DOF-IMU x 1
- Breadboard x1
- 1*3PIN yellow pin header x 1
- Pico-Dual-Expander x 1
- USB-A to micro-B cable x 1
- Jumper wires x 1
Features
- RP2040 microcontroller chip designed by Raspberry Pi in the United Kingdom.
- Dual-core Arm Cortex M0+ processor, a flexible clock running up to 133 MHz.
- 264KB of SRAM, and 2MB of onboard Flash memory.
- Castellated module allows soldering direct to carrier boards.
- USB 1.1 with device and host support.
- Low-power sleep and dormant modes.
- Drag-and-drop programming using mass storage over USB.
- 26 × multi-function GPIO pins.
- 2 × SPI, 2 × I2C, 2 × UART, 3 × 12-bit ADC, 16 × controllable PWM channels.
- Accurate clock and timer on-chip.
- Temperature sensor.
- Accelerated floating-point libraries on-chip.
- 8 × Programmable I/O (PIO) state machines for custom peripheral support.
Pinout
Dimensions
User Guides for MicroPython
Flash Firmware
- Download Testing Firmware to your computer and extract it.
- There are two uf2 files, the pico_micropython_20210121.uf2 file is MicroPython firmware.
- Press the button on the Pico board, connect the Pico to the USB port of the computer via the Micro USB cable, and then release the button.
- After connecting, the computer will automatically recognize a removable disk (RPI-RP2).
- After connecting, the computer will automatically recognize a removable disk (RPI-RP2).
- Copy and drag the firmware file downloaded earlier to the RPi-RP2 mobile disk.
- After the copy is completed, Pico will automatically restart, and after the automatic restart, pico will be recognized as a virtual serial port.

【Note】 1. Is the mobile disk not automatically recognized after connecting to Pico?
▶ Check that the BOOTSEL button is not pressed or released in the middle.
▶ The Micro USB cable used must be a data cable, and the USB cable that can only be used for power supply cannot be used.
2. You can also operate on the Raspberry Pi, the operation steps are the same, also connect the pico to the Raspberry Pi, and then drag the firmware to the mobile disk.
Software Environment Debugging
Windows
To facilitate the development of Pico boards using MicroPython on the computer, it is recommended to download Thonny IDE.
- Download Thonny IDE and follow the steps to install
- After the installation is completed, the first time you need to configure the language and motherboard environment because we are using Pico, so pay attention to selecting the Raspberry Pi option.
Raspberry
If you want to control Pico on Raspberry Pi, please refer to this configuration step.
Current Raspberry Pi systems come with Thonny IDE.
But if Thonny is not updated to the latest version, there is no Pico support package, and you need to update Thonny to the latest v3.3.3 version.
- Enable a terminal and enter the following command to update thonny.
sudo apt upgrade thonny
- Open Thonny IDE (click Raspberry logo -> Programming -> Thonny Python IDE).
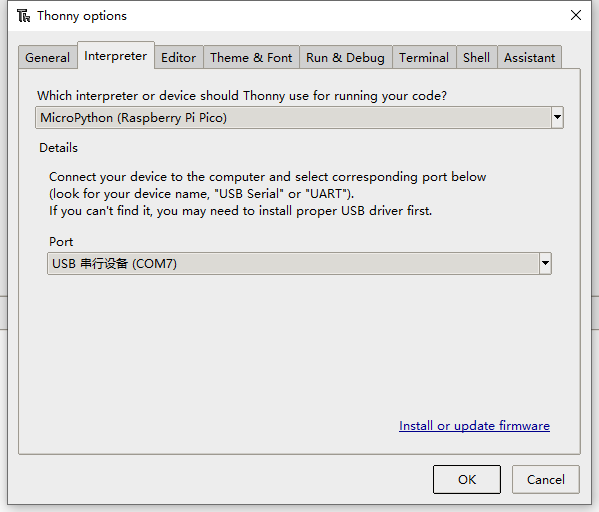
- Select Tools -> Options... -> Interpreter.
- Select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico and ttyACM0 port.
LED Control Demo
- Connect the Pico to the computer (without pressing any keys), if you have not flashed MicroPython before, please follow the #Flash Firmware operation.
- Select Tools -> Options... -> Interpreter.
- Select Raspberry Pi Pico in the interpreter options (be careful to download the latest version of Thonny, otherwise there is no option).
- port selection.
- On the computer, the port is selected as, after connecting to Pico, the COM port recognized by the computer.
- On the Raspberry Pi, the port is identified as /dev/ttyACM0.
- Then confirm.
- After confirmation, you can see that there will be multiple Pico information in the command line interface, and now you can enter the MicroPython program here to control the Pico.
- Looking at the pin diagram of Pico, we know that the control pin of Pico's on-board LED is GPIO25, here we try to control the on-board LED.
- Run the following code in sequence in Thonny:
>>> from machine import Pin >>> led = Pin(25, Pin.OUT) >>> led.value(1) >>> led.value(0)

After running the code in sequence, you can see that the Pico onboard LED lights are turned on and then off.
【Note】
If you want to know more about the functions of Pico Micropython, you can refer to Pico Python SDK Manual.
Hardware Connection
Please take care of the direction when you connect Pico, an USB port is printed to indicate. You can also check the pin of Pico and the LCD board when connecting.
You can connect the display according to the table.
| LCD | Pico | Description |
| VCC | VSYS | Power Input |
| GND | GND | GND |
| MPU.INT | GP2 | INT pin of ICM20948 |
| LPS.INT | GP3 | INT pin of LPS22HB |
| SDA | GP6 | SDA pin of I2C |
| SCL | GP7 | SCL pin of I2C |
| FSYNC | GP22 | FSYNC pin of ICM20948 |
Connect the expansion board
Environment Building
Please refer to Here.
Download the examples
Open a Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following commands:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full cd ~ sudo wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/c/c5/Pico-Kit-B-code.7z 7z x Pico-Kit-B-code.7z -o./Pico-Kit-B-code cd ~/Pico-Kit-B-code cd c/build/
How to use
C Example
Go to the directory of the C example and build it.
cd ~/Pico-Kit-B-code/c/
Create the build folder and enter it. add the SDK:
../../pico-sdk #should be the path of the SDK according to the actual situation.
We have created the build folder in the example, you can just enter it.
cd build export PICO_SDK_PATH=../../pico-sdk (Note: Please check if you set the correct path of SDK, it may be different for different users)
Run cmake to generate the Makefile
cmake ..
Run make to build the example, it will take minutes.
make -j9
uf2 is generated after building.
Press and hold the button of the Pico board, and then connect the Pico to your Raspberry Pi or PC by USB cable, then release the button. Then copy the main.uf2 file which is saved in the build folder to the Pico (It should be recognized as a portable drive, which is named RPI-RP2).
Python example
Work with windows PC
- 1. Press and hold the BOOTSET button of Pico, and connect the Pico to your PC by USB cable. Release the button if the Pico is recognized as a portable drive.
- 2. Copy the rp2-pico-20210205-unstable-v1.14-8-g1f800cac3.uf2 from the Python directory to the Pico.
- 3. Open Thonny IDE (Note: Please use the newest version).
- 4. Click Tools -> Options -> Interpreter and choose the Port of Pico (you can check it in the Device Manager).
- 5. Click File -> Open..., choose Raspberry-Pi-Pico-Kit-B.py, and run it.
Working with Raspberry Pi
- 1. The steps to download the firmware is the same as Windows PC. Copy the rp2-pico-20210205-unstable-v1.14-8-g1f800cac3.uf2 to Pico.
- 2. Open the Thonny IDE in Raspberry Pi(Menu -> Programming -> Thonny Python IDE, you can check the version information in Help -> About Thonny to make sure that it is the version that supports Pico.
- 3. Click Tools -> Options... -> Interpreter to choose the MicroPython(Raspberry Pi Pico and the ttyACM0 port.
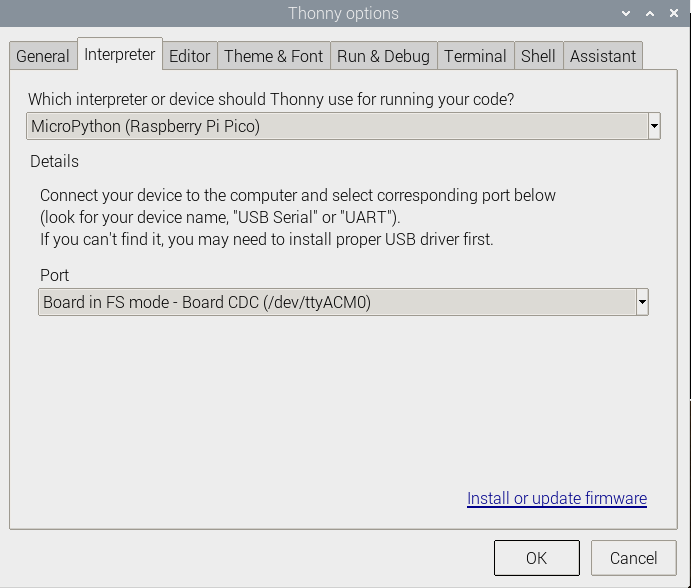
Please update the Thonny IDE if the pre-installed one doesn't support Pico.
sudo apt upgrade thonny
- 3. Click File -> Open...-> Pico-Kit-B-code/python/Raspberry-Pi-Pico-Kit-B.py and run the codes.
Expected result
- 1. The LCD keeps blank if you didn't run the demo codes;
- 2. After running the codes, the LCD turns on and displays the data which is collected by the Pico-10DOF-IMU.
Resources
Supporting Resources
Documents
Demo
Application
Official Resources
Raspberry Pi Official Documents
- Get Started with MicroPython on Raspberry Pi Pico
- Raspberry Pi related books download
- Raspberry Pi Pico Schematic
- Pico Pinout definition
- Getting started with Pico
- Pico C SDK User Manual
- Pico Python SDK User Manual
- Pico Datasheet
- RP2040 Datasheet
- RP2040 Hardware Design Manual
Raspberry Pi Open Source Demos
Other Documents
Pico W
Firmware
Pico
User Manual
Demo Codes
Related Product
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)