4inch e-Paper HAT+ (E) Manual
| ||
| ||
Introduction
Parameters
| Size | 4inch |
| Driver Board Dimensions | 101.0 × 68.0mm |
| Outline Dimensions | 99.00 × 66.00 × 0.85mm |
| Display Dimensions | 84.6 × 56.40mm |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V / 5V (The IO level voltage should be the same as the supply voltage) |
| Communication Interface | SPI |
| Dot Pitch | 0.141 × 0.141mm |
| Resolution | 600 × 400 |
| Display Color | E6 full color |
| Grey Scale | 2 |
| Refresh Time | 19s |
| Refresh Power | < 70 mW(typ.) |
| Standby Current | < 0.01uA (almost 0) |
| Operation Temperature | 0 ~ 50 ℃ |
| Storage Temperature | -25 ~ 60 ℃ |
- Refresh time: The refresh time is the experimental results, the actual refresh time will have errors, and the actual effect shall prevail. There will be a flickering effect during the global refresh process, this is a normal phenomenon.
- Power consumption: The power consumption data is the experimental results. The actual power consumption will have a certain error due to the existence of the driver board and the actual use situation. The actual effect shall prevail.
- In a low-temperature environment, refreshing the display may cause color cast. To make it operate normally, you need to put it in a 25℃ environment for 6 hours before refreshing the display.
Communication Method
Working Principle
Programming Principles
- For computers, pictures are composed of pixels, and the space occupied by each pixel determines the possible state (color) of the pixel. The simplest black-and-white picture only occupies one bit per pixel. (1Bit), either 0 or 1 is either black or white. As the color increases, the space occupied by each pixel becomes larger and larger, eight bits, sixteen bits, twenty-four bits...
- This module uses a non-standard 24-bit image. If you need to make your own images, you can refer to #Picture Processing.
- We define the pixels in a monochrome picture, 0 is black and 1 is white.
- White:□: Bit 1
- Black:■: Bit 0
- White:□: Bit 1
- The dot in the figure is called a pixel. As we know, 1 and 0 are used to define the color, therefore we can use one bit to define the color of one pixel, and 1 byte = 8pixels
- For example, If we set the first 8 pixels to black and the last 8 pixels to white, we show it by codes, they will be 16-bit as below:
For the computer, the data is saved in MSB format:

So we can use two bytes for 16 pixels.
- Now suppose we have six colors, so we need at least three bits of data to represent all colors, but for the operation, we add a 0 in front of it, that is, use four bits of data to represent the color of a pixel, such a byte (1Byte) Two pixels can be represented. In fact, the controller of this module adopts this method.
| Color | BIN | HEX | The color (reference) |
| Black | 0b0000 | 0x0 | |
| White | 0b0001 | 0x1 | |
| Green | 0b0010 | 0x2 | |
| Blue | 0b0011 | 0x3 | |
| Red | 0b0100 | 0x4 | |
| Yellow | 0b0101 | 0x5 |
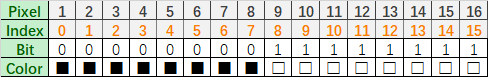
For example, if you want to display four colors: green, yellow, red and blue, it should be like as below:
| Pixel | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||||
| Bit | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| Data | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Color | ||||||||||||||||
For a computer, its data storage method is high-order first, low-order last, and a byte has only eight bits, so it is stored in a byte like this:
| Pixel | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||||
| Bit | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Data | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Color | ||||||||||||||||
| Byte | 0x25 | 0x36 | ||||||||||||||
Precautions
- For E-paper displays that support partial refresh, please note that you cannot refresh them with the partial refresh mode all the time. After refreshing partially several times, you need to fully refresh EPD once. Otherwise, the display effect will be abnormal, which cannot be repaired!
- When using the e-Paper display, it is recommended that the refresh interval be at least 180s, and refresh at least once every 24 hours. If the e-Paper is not used for a long time, you should use the program to clear the screen before storing it. (Refer to the datasheet for specific storage environment requirements.)
- After the screen enters sleep mode, the sent image data will be ignored, and it can be refreshed normally only after initializing again.
- If you find that the created image data is displayed incorrectly on the screen, it is recommended to check whether the image size setting is correct, change the width and height settings of the image and try again.
- The working voltage of the e-Paper display is 3.3V. If you buy the raw panel and you need to add a level convert circuit for compatibility with 5V voltage.
- The FPC cable of the screen is relatively fragile, pay attention to bending the cable along the horizontal direction of the screen when using it, and do not bend the cable along the vertical direction of the screen.
- The screen of e-Paper is relatively fragile, please try to avoid dropping, bumping, and pressing hard.
- We recommend that customers use the sample program provided by us to test with the corresponding development board.
Picture Processing
Picture production and conversion of multi-color E-ink.
Picture Production
Preparation
Required software: Adobe PhotoShop CC, Painting
Introduction
- Floyd-Steinberg dithering algorithm is very suitable for showing rich layering where the number of colors is small. It makes it possible to get more color combinations for better shadow rendering of the original image. It is especially suitable for various usage scenarios of e-ink screens.
- The following will introduce how to convert ordinary pictures into Floyd-Steinberg scatter plots.
- If you are interested in the actual algorithm, you can read about our algorithm porting on ESP32 and ESP8266. Here, no further elaboration will be given.
Operating Steps
Preparation: Download color sheet to PC, and unzip to get the file as shown below, we are going to use "N-color.act" or "4-color.act".

1. The new Photoshop project sets the width and height according to the actual resolution of the e-Paper display, the color mode uses RGB. The resolution of this module is 800*480. Change the width to 800 pixels and the height to 480 pixels.
2. Prepare the corresponding picture, copy it into the project, and adjust the parameters such as size and contrast (similar to the steps for processing pictures in general Photoshop).
3. Select File -> Export -> Save for Web (Legacy).
4. Select the color table as shown below. Load the color table provided in Preparation.

5. For seven-color pictures, load N-color. act, then click Save and save as a gif file. Then convert it into BMP format and use it on this module.
For four-color images, load 4-color. act, then click Save and save as a gif file. Then convert it into BMP format and use it on this module.
For six-color images, load 6-color. act, then click Save and save as a gif file. Then convert it into BMP format and use it on this module.
6. Open the gif file with Paint and save it as a 24-bit BMP image.

7. By now, the color picture available for this module has been made, and it can be put into the TF card of the Raspberry Pi or e-Paper Shield module for use, or refer to the next section to convert to an array for use by other embedded devices.
Image Data Conversion
Download the Program
- Four color image conversion application: Coverterto4color
- Six color image conversion application: ConverterTo6color
- Seven color image conversion application: Converterto7color
- Source code: Convertertocolor
Note: This application is provided for your convenience and open source. Our company does not provide technical support for it.
Bug Fixing
If your computer is running on the Win10/Win11 system and doesn't have Microsoft Visual Studio or any other Microsoft development tools installed, you may encounter error prompts: "ucrtbased.dll" and "vcruntime 140d.dll".
This indicates that your computer lacks these two components. Here's the solution:
- Install VS (Microsoft Visual Studio) or other Microsoft development tools (such as Visual C++ Redistributable).
- Use the file we provide:

Place these two files into the directory C:\Windows\System32, then restart your computer.
How to Convert
- Put the prepared picture and the corresponding "exe" application in the same folder, and you can put multiple pictures at the same time.
- Drag and drop the picture in the "exe" file, and the program will convert the picture into a ".c" file with a fixed name.
- Double-click the "cmd" file, and the program will convert all the pictures in the folder that meet the size to generate ".c" files with the corresponding names.
- Click on the image to see the demonstration.
- Four-color single-image demonstration:
- Four-color multi-picture demonstration:
- Seven-color single-picture demonstration:
- Seven-color multi-picture demonstration:
Working With Raspberry Pi
Hardware Connection
When connecting the Raspberry Pi, you can directly insert the board into the 40PIN pin header of the Raspberry Pi, and pay attention to the correct pins.
If you choose to connect with an 9PIN cable, please refer to the pin correspondence table below:
| e-Paper | Raspberry Pi | |
| BCM2835 | Board | |
| VCC | 3.3V | 3.3V |
| GND | GND | GND |
| DIN | MOSI | 19 |
| CLK | SCLK | 23 |
| CS | CE0 | 24 |
| DC | 25 | 22 |
| RST | 17 | 11 |
| BUSY | 24 | 18 |
| PWR | 18 | 12 |
Enable SPI Interface
- Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and enter the following command in the config interface:
sudo raspi-config Choose Interfacing Options -> SPI -> Yes Enable SPI interface

Then reboot your Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
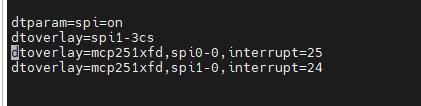
- Check /boot/config.txt, and you can see 'dtparam=spi=on' was written in.
- To make sure SPI is not occupied, it is recommended to close other drivers' coverage. You can use ls /dev/spi* to check whether SPI is occupied. If the terminal outputs /dev/spidev0.1 and /dev/spidev0.1, SPI is not occupied.
C
- Install lg library
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following commands: wget https://github.com/joan2937/lg/archive/master.zip unzip master.zip cd lg-master make sudo make install #For more details, you can refer to the source code: https://github.com/gpiozero/lg
- Install gpiod library (Optional)
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following commands: sudo apt-get update sudo apt install gpiod libgpiod-dev
- Install BCM2835:
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command wget http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/bcm2835-1.71.tar.gz tar zxvf bcm2835-1.71.tar.gz cd bcm2835-1.71/ sudo ./configure && sudo make && sudo make check && sudo make install # For more information, please refer to the official website: http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/
- Install WiringPi (Optional)
#Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command: sudo apt-get install wiringpi #For Raspberry Pi systems after May 2019 (earlier than before, you may not need to execute), you may need to upgrade: wget https://project-downloads.drogon.net/wiringpi-latest.deb sudo dpkg -i wiringpi-latest.deb gpio -v #Run gpio -v and version 2.52 will appear. If it does not appear, the installation is wrong. #Bullseye branch system use the following command: git clone https://github.com/WiringPi/WiringPi cd WiringPi ./build gpio -v # Run gpio -v and version 2.60 will appear. If it does not appear, it means that there is an installation error.
- Download the demo via GitHub (You can skip this step if you have downloaded it.)
git clone https://github.com/waveshare/e-Paper.git cd e-Paper/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Download the demo (You can skip this step if you have downloaded it.)
wget https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/4inch-e-Paper-HAT%2B-(E)/4inch_e-Paper_E.zip unzip 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -d 4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Alternate method of decompression:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full 7z x 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -O./4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Compile the demo (Note: -j4 is to compile with 4 threads, the numbers can be modified by yourself.
# Now at 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano cd c sudo make clean sudo make -j4
- Run the demo
sudo ./epd
Python
- Install the function library.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python3-pip sudo apt-get install python3-pil sudo apt-get install python3-numpy sudo pip3 install spidev
- Install function library (python2).
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python-pip sudo apt-get install python-pil sudo apt-get install python-numpy sudo pip install spidev
- Install gpiozero library (it is installed in the system by default, if not, you can install it by following the commands below)
sudo apt-get update # python3 sudo apt install python3-gpiozero # python2 sudo apt install python-gpiozero
- Download the demo via GitHub (You can skip this step if you have downloaded it.)
git clone https://github.com/waveshare/e-Paper.git cd e-Paper/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Download the demo (You can skip this step if you have downloaded it.)
wget https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/4inch-e-Paper-HAT%2B-(E)/4inch_e-Paper_E.zip unzip 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -d 4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Alternate method of decompression:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full 7z x 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -O./4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Run the demo.
#At 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/ cd python/examples/ python3 epd_4in0e_test.py
Working With Arduino
Hardware Connection
Use an 9PIN cable to connect, please refer to the pin correspondence table below:
| e-Paper | Arduino UNO | Mega2560 |
| VCC | 5V | 5V |
| GND | GND | GND |
| DIN | D11 | D51 |
| CLK | D13 | D52 |
| CS | D10 | D10 |
| DC | D9 | D9 |
| RST | D8 | D8 |
| BUSY | D7 | D7 |
| PWR | D6 | D6 |
Install IDE
Run The Demo
- Download the demo in Resource, unzip it to the "E-Paper_code" directory, and you can see the following content:
- Open the test demo: 4inch_e-Paper_E\Arduino_R4\Arduino_R4.ino.
- Select the corresponding Board and Port in the Tools in the Arduino IDE.
- Finally, click upload, the upload is successful as follows (Arduino 1.8.13).
Working With Jetson Nano
Hardware Connection
The 40PIN pin of Jetson Nano is compatible with the 40PIN pin of Raspberry Pi and provides a Jetson.GPIO library with the same API as the RPI.GPIO library of Raspberry Pi, so the serial number connected here is the same as that of Raspberry Pi. The module can be directly inserted into the 40Pin headers of the Jetson Nano when using the 40PIN interface.
If you choose to connect with an 9PIN cable, please refer to the pin correspondence table below:
| e-Paper | Jetson Nano Developer Kit | |
| BCM2835 | Board | |
| VCC | 3.3V | 3.3V |
| GND | GND | GND |
| DIN | 10 (SPI0_MOSI) | 19 |
| CLK | 11 (SPI0_SCK) | 23 |
| CS | 8 (SPI0_CS0) | 24 |
| DC | 25 | 22 |
| RST | 17 | 11 |
| BUSY | 24 | 18 |
| PWR | 18 | 12 |
C
- Download the demo via GitHub (you can skip this step if you have downloaded it.)
git clone https://github.com/waveshare/e-Paper.git cd e-Paper/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Download the test demo: (you can skip this step if you have downloaded it.)
wget https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/4inch-e-Paper-HAT%2B-(E)/4inch_e-Paper_E.zip unzip 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -d 4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Alternate method of decompression:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full 7z x 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -O./4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Compile the demo (Note: JETSON is the specified device, and RPI is not specified by default. -j4 is to compile by 4 threads, and the number can be changed by yourself.
# Now at 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano cd c sudo make clean sudo make JETSON -j4
- Run the demo:
sudo ./epd
Python
- Install function library:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python3-numpy sudo apt-get install python3-pip sudo pip3 install Jetson.GPIO
- Download the demo via GitHub (you can skip this step if you have downloaded it.)
git clone https://github.com/waveshare/e-Paper.git cd e-Paper/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Download the demo (you can skip this step if you have downloaded it.)
wget https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/4inch-e-Paper-HAT%2B-(E)/4inch_e-Paper_E.zip unzip 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -d 4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Alternate method of decompression:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full 7z x 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -O./4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Run the demo:
# At 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/ cd python/examples/ python3 epd_4in0e_test.py
Working With Sunrise X3 Pi
Hardware Connection
When connecting the Sunrise X3 Pi, you can directly insert the board into the 40PIN pin header of the Sunrise X3 Pi, and pay attention to the correct pins.
If you choose to connect with an 9PIN cable, please refer to the pin correspondence table below:
| e-Paper | Sunrise X3 Pi | |
| BCM | Board | |
| VCC | 3.3V | 3.3V |
| GND | GND | GND |
| DIN | MOSI | 19 |
| CLK | SCLK | 23 |
| CS | CE0 | 24 |
| DC | 25 | 22 |
| RST | 17 | 11 |
| BUSY | 24 | 18 |
| PWR | 18 | 12 |
Enable SPI
- SPI is enabled by default. If you have disabled it, you can enable it by following the steps below.
- Enter the command: sudo srpi-config
Python
- The corresponding library has been installed in the function. If you uninstall it accidentally, please use the following command to install it.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python-pip sudo apt-get install python-pil sudo apt-get install python-numpy sudo pip install Hobot.GPIO sudo pip install spidev
- Download the demo via GitHub (skip this step if you have downloaded it).
git clone https://github.com/waveshare/e-Paper.git cd e-Paper/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Download the demo (skip this step if you have downloaded it).
wget https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/4inch-e-Paper-HAT%2B-(E)/4inch_e-Paper_E.zip unzip 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -d 4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Alternate method of decompression:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full 7z x 4inch_e-Paper_E.zip -O./4inch_e-Paper_E cd 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/
- Run the demo
# Make sure in 4inch_e-Paper_E/RaspberryPi_JetsonNano/ cd python/examples/ python3 epd_4in0e_test.py
Working With STM32
Hardware Connection
| e-Paper | STM32 |
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| DIN | PA7 |
| CLK | PA5 |
| CS | PA4 |
| DC | PA2 |
| RST | PA1 |
| BUSY | PA3 |
| PWR | PA6 |
Run The Program
- Click to download the demo, and then unzip it into the E-Paper_code directory to see the following content.
- Use Keil to open epd-demo.uvprojx in the 4inch_e-Paper_E\STM32-F103ZET6\MDK-ARM directory
- Open Keil's compilation toolbar (usually already open).
- Click to compile.
- Make sure the appropriate programmer is connected, then click LOAD to download the demo to the microcontroller.
Resource
Document
Demo
Development Resources
- E-Paper Floyd-Steinberg
- E-Paper API Analysis
- Zimo221.7z
- e-Paper Font Library Tutorial
- Image2Lcd.7z
- Image2Lcd Image Modulo
- pwnagotchi Usage
Related Resources
FAQ
Questions about Software
- Enter the command: ls /dev/spi*.
- The result may appear as shown in the figure.
- This is because the SPI interface is occupied in the /boot/config.txt file.
{{{5}}}
- Our demo uses STM32f103ZET6. If the customer modifies other models in MDK, such as STM32F103RBT6, the RAM space becomes smaller, and the stack size and heap size in the startup file need to be modified on the original basis.
{{{5}}}
- When transmitting B/W data, use Data Start Transmission 1; When transmitting RED data, use Data Start Transmission 2.
{{{5}}}
- The border display color can be set through the Border Waveform Control register or the VCOM AND DATA INTERVAL SETTING register.
{{{5}}}
- In this case, the customer needs to reduce the position of the partial refresh and clear the screen after 5 rounds of partial refreshing (increasing the voltage of VCOM can improve the color, but it will increase the afterimage).
{{{5}}}
- The process of re-awakening the e-Paper screen is actually the process of re-powering. Therefore, when the EPD wakes up, the screen must be cleared first, so as to avoid the afterimage phenomenon to the greatest extent.
{{{5}}}
- It may be caused by the unsuccessful SPI driver.
- 1. First check whether the wiring is correct.
- 2. Check whether the SPI is enabled and whether the parameters are configured correctly (SPI baud rate, SPI mode and other parameters).
- 1. First check whether the wiring is correct.
{{{5}}}
- The full refresh initialization function needs to be added when the e-Paper screen is switched from partial refresh to full refresh.
{{{5}}}
- It may be a demo based on the BCM2835 library that has run the C language before. At this time, you need to restart the Raspberry Pi and then run the Python demo.
{{{5}}}
- Install the imaging library using the command "sudo apt-get install python-imaging".
{{{5}}}
Questions about Hardware
- Yes, now there is a level conversion chip onboard, supporting a 5V drive.
{{{5}}}
- The rated input voltage of the e-Paper screen is 2.3~3.6V. If it is a 5V system, level conversion is required. In addition, the voltage should not be lower than 2.5V, so as not to affect the display effect of the e-Paper screen.
- Device selection can use the model in the schematic diagram we provide or choose according to the datasheet.
{{{5}}}
- Yes, pay attention to the correct timing.
{{{5}}}
- Check if SPI communication is normal.
- Confirm whether the BUSY pin is normally initialized to input mode.
- It may be that there is no normal reset, try to shorten the duration of the low level during reset (because the power-off switch is added to the drive circuit, the reset low level is too long, which will cause the drive board to power off and cause the reset to fail).
- If the busy function sends the 0x71 command, you can try to comment it out.
{{{5}}}
- 1.64inch, 2.36inch, 3inch, 0.5mm pitch, 26Pin.
- 1.02inch, 0.5mm pitch, 30Pin.
- 4.37inch, 7.3inch, 0.5mm pitch, 50Pin.
- The rest (non-parallel ports) are 0.5mm pitch, 24Pin.
{{{5}}}
- Cable socket 0.5-XXpin rear-flip 2.0H (FPC connector).
{{{5}}}
Questions about Screen
- 【Working conditions】Temperature range: 0~40°C (seven-color screen: 15~35°C); Humidity range: 35%~65%RH.
- 【Storage conditions】Temperature range: below 30°C; Humidity range: below 55%RH; Maximum storage time: 6 months.
- 【Transportation conditions】Temperature range: -25~50°C; Maximum transportation time: 10 days.
- 【After unpacking】Temperature range: 20°C±5°C; Humidity range: 50±5%RH; Maximum storage time: Assemble within 72 hours.
{{{5}}}
- Refresh mode
- Full refresh: The e-Paper screen will flicker several times during the refresh process (the number of flickers depends on the refresh time), and the flicker is to remove the afterimage to achieve the best display effect.
- Partial refresh: The e-Paper screen has no flickering effect during the refresh process. Users who use the partial refreshing function note that after refreshing several times, a full refresh operation should be performed to remove the residual image, otherwise the residual image problem will become more and more serious, or even damage the screen (currently only some black and white e-Paper screens support partial refreshing, please refer to product page description).
- Full refresh: The e-Paper screen will flicker several times during the refresh process (the number of flickers depends on the refresh time), and the flicker is to remove the afterimage to achieve the best display effect.
- Refresh rate
- During use, it is recommended that customers set the refresh interval of the e-Paper screen to at least 180 seconds (except for products that support the partial refresh function).
- During the standby process (that is, after the refresh operation), it is recommended that the customer set the e-Paper screen to sleep mode, or power off (the power supply part of the e-Paper screen can be disconnected with an analog switch) to reduce power consumption and prolong the life of the e-Paper screen. (If some e-Paper screens are powered on for a long time, the screen will be damaged beyond repair.)
- During the use of the three-color e-Paper screen, it is recommended that customers update the display screen at least once every 24 hours (if the screen remains the same screen for a long time, there will be a screen burn that is difficult to repair).
- During use, it is recommended that customers set the refresh interval of the e-Paper screen to at least 180 seconds (except for products that support the partial refresh function).
- Usage Environment
- The e-Paper displays are recommended for indoor use and not for outdoor use.
- If the usage scenario is outdoors, we do not guarantee the display effect. If the e-Paper screen is damaged due to outdoor use, we do not provide warranty service.
- Here are some protective measures for outdoor use, but we do not guarantee that the e-Paper screen will function normally even after taking these precautions:
- Avoid exposing the e-Paper screen to direct sunlight and ensure UV protection. Prolonged exposure to strong light can dry out the charged particles, rendering them inactive and unable to refresh, which is irreversible.
- Completely cover the white glue part of the e-Paper screen's connection ribbon with 3M tape. Complete coverage and no coverage show different effects under UV light.
- Place the e-Paper screen in relatively shaded areas, such as under trees or the shadow of eaves.
- When designing e-Paper screen products, customers should ensure that the usage environment meets the requirements of the e-Paper screen.
{{{5}}}
- Ideally, with normal use, it can be refreshed 1,000,000 times (1 million times).
{{{5}}}
- Power on the development board for a long time, after each refresh operation, it is recommended to set the screen to sleep mode or directly power off, otherwise, the screen may burn out when the screen is in a high voltage state for a long time.
{{{5}}}
- Yes, but you need to re-initialize the electronic paper with software.
{{{5}}}
- Maybe the SPI rate is too high, resulting in data loss, try to reduce the SPI rate.
- Insufficient or unstable power supply leads to data loss.
- The data cable is so long to cause data loss, the extension cable should not exceed 20cm.
{{{5}}}
- The display gray scale of electrophoretic electronic paper is determined by the spatial position of the particles in the Microcapsule or Microcup. The electrophoresis phenomenon occurs between black particles and white particles under the action of voltage. This voltage sequence that promotes the electrophoretic movement of the particles is the driving waveform of the electronic paper. The driving waveform is the core part of the electronic paper display, and the optimization of the driving waveform will directly affect the display effect of the display. The driving waveform file is used to describe the parameters formed by the voltage sequence that promotes the electrophoretic movement of the particles, and it needs to be called regularly when the electronic paper is refreshed.
- For different batches of e-Paper diaphragms, electrophoretic matrices require different voltage values when driving the display due to materials, manufacturing processes, etc. The waveform of the e-Paper screen is reflected in the relationship between grayscale, voltage and temperature. Generally speaking, after each batch of electrophoresis matrix is generated, there will be a corresponding waveform file in the form of a .wbf file. The film manufacturer will provide the waveform file and electrophoresis matrix to the manufacturer of the e-Paper screen, and then the manufacturer of the e-Paper screen integrates the protection board, substrate and driver and then provides it to customers; if the waveform file does not correspond to the screen, it is likely that the display cannot be displayed or the display effect is unsatisfactory. Generally, the waveform file has OTP built into the driver IC of the e-Paper screen when leaving the factory, and some programs we provide also called external waveform files to drive the e-Paper screen.
{{{5}}}
- LUT is the abbreviation of LOOK UP TABLE, and OTP is the abbreviation of ONE TIME PROGRAM. The original intention of LUT is to load waveform files, and the waveform files are divided into OTP and REGISTER. Among them, OTP is the built-in waveform storage method, and REGISTER is the external waveform storage method.
{{{5}}}
- There are mainly two types of e-Paper screens.
- One is to refresh the background image first.
- The other is to alternately refresh old data and new data.
- One is to refresh the background image first.
{{{5}}}
- Simultaneous partial refreshing in different locations needs to be operated in the program design, that is, first refreshing the data of different locations into the electronic paper IC, and finally doing the Update/TurnOnDisplay uniformly.
{{{5}}}
- Yes, when the e-Paper is batched, there will be some color difference, which is a normal phenomenon. Store the e-Paper faces up to reduce the reddish/yellowishness to a certain extent.
{{{5}}}
- With film.
{{{5}}}
- At present, all screens have built-in temperature sensors, and you can also use IIC pins external LM75 temperature sensor.
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)