SIM7600X 4G DONGLE
| ||
Introduction
SIM7600X 4G DONGLE is an industrial-grade 4G dongle, which features up to 150Mbps downlink rate and 50Mbps uplink rate, supports operating systems including Windows/Linux/Android. By simply connecting it to a laptop, PC, Raspberry Pi, IoT, industrial computer, or other IoT host device, it is easy to use a 4G network connection on the go.
Selection Guide
| Type | GNSS | Avaialbel Area |
|---|---|---|
| SIM7600CE 4G DONGLE | No | Mainly for China |
| SIM7600G-H 4G DONGLE | Support(GNSS antenna should be purchased separately) | Global |
Features
- Supports 2G/3G/4G network connection.
- Driver provided, for operating systems including Windows/Linux/Android.
- Supports TCP/UDP/FTP/FTPS HTTP/HTTPS protocols.
- Supports network protocols such as TCP/IP/IPV4/IPV6/Multi-PDP/FTP/FTPS/HTTP/HTTPS/DNS.
- Onboard USB port, for directly connecting with ARM/X86 hosts or other industrial computers.
- Onboard UART port with hardware flow control, for connecting with host boards like Arduino/STM32.
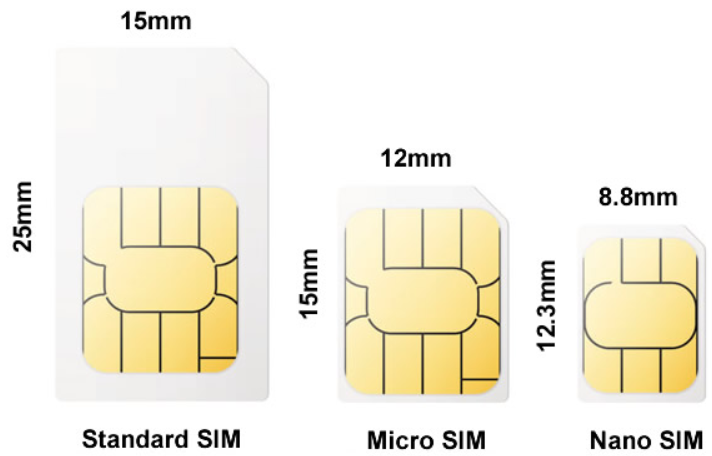
- Nano SIM card slot; supports 1.8V / 3V nano-SIM card.
- 3 x LED indicators, easy to monitor the working status.
- Portable customized enclosure, mini size, nice looking.
- Baudrate support: 300bps ~ 4Mbps (115200bps by default).
- Baudrate auto-negotiation: 9600bps ~ 115200bps.
Hardware Connection
- Prepare:
- SIM7600X 4G DONGLE
- A 4G Nano SIM card (The card should be workable and 4G accessible)
- Assemble the 4G antenna.
- Open the SIM card buckle, and pull the SIM card slot according to the arrow below;
- Plug the 4G SIM card and LOCK the SIM card slot according to the arrow, then close the buckle.
- Connect the USB port of the DONGLE to your PC. Raspberry Pi or other devices
- If you want to use GPS, please make sure that the DONGLE you bought is the SIM7600G-H version. You should set the receiver on the outside for GPS testing.
4G Connecting
Networking in Windows PC
1. Hardware Connection
2. Driver Installation
- Download Driver: SIM7600X driver.
- Connect the DONGLE to Windows PC (Hereafter we use Windows 10 PC as an example).
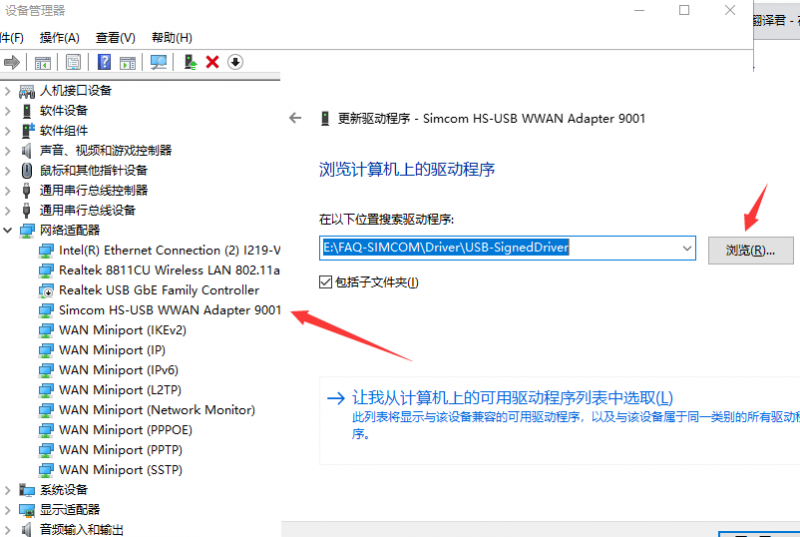
- Unzip the driver file --> Double-click the exe driver file with the left mouse button --> Select the installation path --> NEXT --> Wait for the installation to complete --> Restart the computer --> Complete the driver installation.
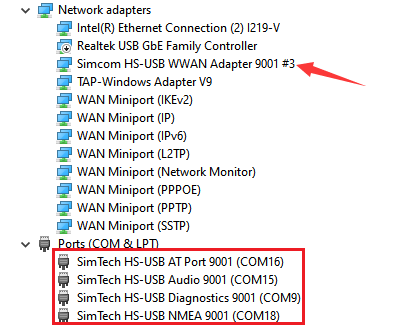
- After installation, all the devices should be recognized normally as below:
3. Dailing up
NDIS Dail-up
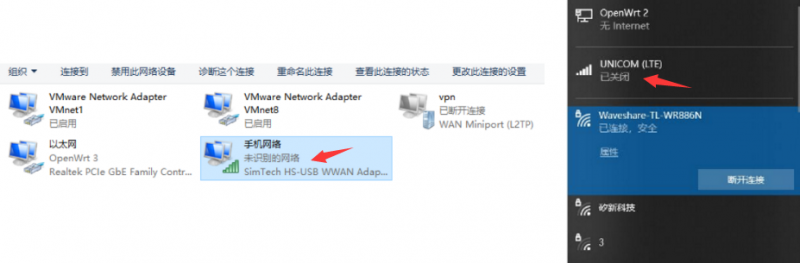
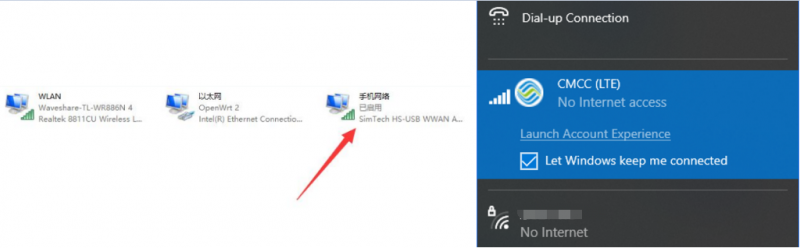
- Currently access to Windows 10 operating system use, connected to the 4G DONGLE module (equipped with mobile / telecom / Unicom 4G card), after installation of the driver, most of the current computers will automatically connect.
- If Windows can not access the Internet, you need to manually start NDIS dial-up.
- Download SIM7600 SSCOM.
- Open SIM7600 AT port and send the command:
AT$QCRMCALL=1,1+Enter

At this point, NDIS dial-up takes effect and the computer is ready to connect to the network.
RNDIS Dail-up
- Installed the SIM card and antenna, USB connected to the computer, and provide the power supply.
- Refer to the above to install the USB driver.
- Open the serial assistant, find the serial port number corresponding to AT serial port, and send:
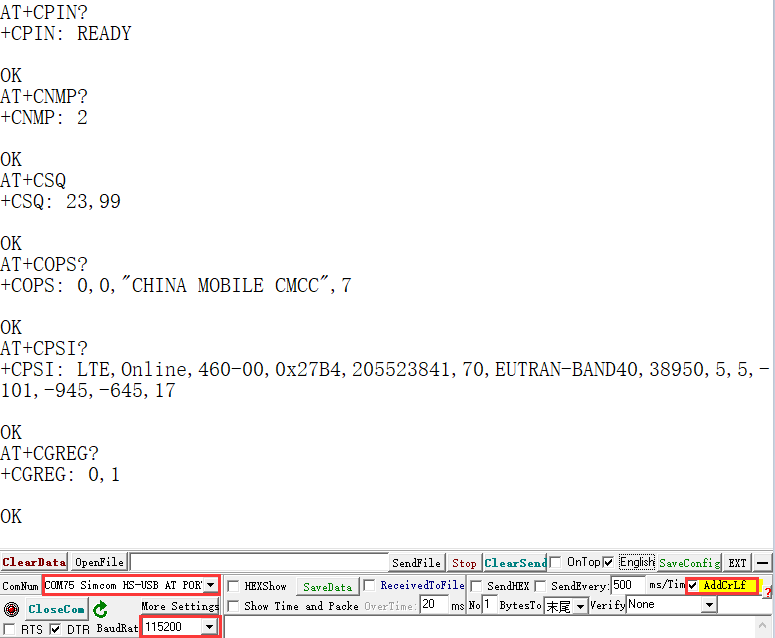
AT+CPSI? //query if it is registered on the network
- If you have successfully registered to the network, send another AT command to enable USB dial-up access:
at+Cusbpidswitch=9011,1,1
- Sending is successful, return OK, and Dongle will reboot automatically.
- Observe the device manager and find some unrecognized devices, such as RNDIS (with an exclamation mark):
- Right-click RNDIS, search for the device software prompt window, and select "Browse My Computer". Select "Network Adapters" from the list of devices.
- Select Microsoft Corporation from the list of manufacturers in the network adapter window, and then select "Remote NDIS Compatible Device" from the list on the right.
Click Next and wait for the installation to finish, the RNDIS Kitl device will be installed successfully. At this point, the dial-up function setup is complete and you can see that the PC can access the Internet through Dongle.
at+Cusbpidswitch=9001,1,1
PPP Dail-up
- Connect the 4G DONGLE to Windows 10 PC, and install drivers as the guide above. Then most of the PC will auto-connect to the 4G network.
If your PC cannot auto-connect, you can try with PPPoE method:
In theory, the uplink speed of a 4G network is up to 150Mbps and the downlink speed is up to 50Mpbs.
However, the actual speed is influenced by the Network coverage rate, time, network situation and the base station, etc.
Therefore, the actual speed of the 4G network will be slower than the expected data. In this case, you can change the area test it again, or try it at other times.
Common AT Command
- SIM7600X module supports AT command control, some basic AT commands are shown in the table below:
(For the complete AT command set, please refer to: For more AT commands, please refer to: SIM7600X series AT command set)
| Command | Description | Return |
|---|---|---|
| AT | AT Test Command | OK |
| ATE | ATE1 set echo ATE0 close echo |
OK |
| AT+CGMI | Query module manufacturer | OK |
| AT+CGMM | Query module model | OK |
| AT+CGSN | Query product serial number | OK |
| AT+CSUB | Query module version and chip | OK |
| AT+CGMR | Query the firmware version serial number | OK |
| AT+IPREX | Set the module hardware serial port baud rate | +IPREX: OK |
| AT+CRESET | reset module | OK |
| AT+CSQ | Network signal quality query, return signal value | +CSQ: 17,99 OK |
| AT+CPIN? | Query the status of the SIM card and return READY, indicating that the SIM card can be recognized normally | +CPIN: READY |
| AT+COPS? | Query the current operator, the operator information will be returned after normal networking | +COPS: OK |
| AT+CREG? | Query network registration status | +CREG: OK |
| AT+CPSI? | Query UE system information | |
| AT+CNMP? | Network mode selection command: 2:Automatic 13:GSM only 38:LTE only 48 : Any modes but LTE ... .... |
OK |
Setup 4G Connection for Raspberry Pi (Raspbian)
1. Hardware connection
2. Setting
The driver of SIM7600X has been pre-installed in Raspberry Pi OS (Raspbian), you need to install it again. You can be following the following guide to set up a 4G network connection. There are three ways:
- Raspberry Pi networked via RNDIS ——(Simplest)
- SIM868 PPP Dail-up Networking ——(Simple)
- Setup wwan0 interface for 4G network (Related code) ——(Complicated)
Set up Network for Jetson Nano
1. Hardware connection
2. Setting
Please connect all the hardware and start Jetson Nano.
- Check and make sure that the module work normally by the demo codes above.
- Open minicom by command
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2
- Type the following command to check.
AT+CNMP=38 AT+CSQ AT+CREG? AT+COPS? AT+CPSI?
- Download driver
cd wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/4/46/Simcom_wwan.zip tar zxvf Simcom_wwan.zip cd Simcom_wwan sudo make
- Use root permission to install the driver.
sudo su insmod simcom_wwan.ko lsmod dmesg
- Check if the wwan0 interface is recognized.
ifconfig -a
- Enable the wwan0 interface.
ifconfig wwan0 up
- Dailing by minicom.
minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB2 AT$QCRMCALL=1,1
- Allocate IP.
apt-get install udhcpc udhcpc -i wwan0
- Now you can use a 4G network.
- If you get a DNS error, please fix it with this command.
route add -net 0.0.0.0 wwan0
USB Voice Call
Due to the need to reduce size, the SIM7600G-H 4G Module does not come with built-in audio input-output interfaces in its design. However, the SIM7600 chip can input and output audio data in binary form through the Audio port in the USB port when using the voice call function. This example uses the audio output interface of the Raspberry Pi and the input function of a USB sound card to achieve real-time voice calls through data transmission via the USB port.
Hardware Preparation:
- Raspberry Pi development board
- SIM7600G-H 4G Module
- USB Type-C cable
- A SIM card capable of regular call services
- An external sound card device with a microphone (a USB sound card is used in this example)
Hardware Connections:
- Insert the SIM card into the SIM7600G-H 4G Module's card slot before powering it up.
- Connect the SIM7600G-H 4G Module to the Raspberry Pi development board using the USB data cable.
- Wait for the module to power on and connect to the communication network (as described in the previous section, 'NET LED Working Status').
- Connect the sound card device to the Raspberry Pi.
Software Preparation:
Enter the running command to confirm the status of the SIM7600G-H driver.
ls /dev/ttyUSB*
If it's the latest Raspberry Pi system, the system should come with the driver for this module. It should display five ports from ttyUSB0 to ttyUSB4, indicating that there's no need for additional installation.
Install python function library:
#pyaudio is the python module, installing pyaudio under Raspberry Pi, First you need to install portaudio.dev sudo apt-get install portaudio.dev #And then use sudo apt-get install python-pyaudio #Or sudo apt-get install python3-pyaudio #python3
Download demo and unzip.
Check the sound card driver status according to the selected sound card device (the USB sound card used in this example is a driverless sound card).
Querying the selected audio device number can be done with the pyaudio module:
sudo python Audio_check.py
The program will list all available devices along with their corresponding numbers. Once you find the device based on its name, make a note of its corresponding number.
Test Process
As there are differences between the Raspberry Pi system and the audio device, it is recommended to modify the parameters before running the demo:
stream_in=p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(2),channels=1,rate=8000,input=True,input_device_index=1,stream_callback=pcm_out) #This code initializes the audio input object, "input_device_index=1" indicates this object corresponds to the audio input device number, which may vary somewhat from device to device.
If there's an issue with the audio input, first check if the device is functioning properly. If the device is working correctly, the problem might be due to selecting the wrong device number. You can try the loopback test program below:
sudo python Audio_test_R
This program will play audio data received from the audio input device on the audio output device. If there is no sound, you can try referring to the previously obtained list of audio devices. Modify the 'input_device_index' and 'output_device_index' parameters in the PyAudio initialization object statement.
stream1=p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(2), channels=1, rate=8000, input=True,input_device_index=1,stream_callback=pcm_in,frames_per_buffer=800) #Parameter input_device_index stream2=p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(2), channels=1, rate=8000, output=True,output_device_index=0,stream_callback=pcm_out,frames_per_buffer=800) #Parameter output_device_index
GNSS
GPS Positioning
1. Hardware connection
- Note: SIM7600CE-CNSE 4G DONGLE doesn't feature GPS function. If you want to use GPS, please purchase SIM7600G-H 4G DONGLE and GPS antenna separately.
- Remove the case, assemble the GPS antenna and replace it, and close.

- When testing, you should set the receiver of the GPS antenna outside, and please test it on a sunny day. Power on and wait for several minutes to get the position;
2. AT Commands for GPS
- Commands and test results:
AT+CGPS=1 //Open GPS AT+CGPSINFO //Print GPS information to the serial port AT+CGPS=0 //Close GPS
3. Obtain GPS data by software
Send SMS
- Assemble SIM card and LTE antenna. Connect DONGLE to the PC and power on it.
- Check if the indicators work normally, PWR keeps lighting and NET is blinking.
- Set local SMS center: AT+CSCA="+8613800755500"+ ENTER,It will response OK.
Note: the number of SMS centers is different among different areas, please confirm your local SMS center and modify it. - AT+CMGF=1: Set the SMS mode as TEXT.
- AT+CMGS=" phone number"<ENTEER>, Set the target phone number, and it will respond: ">", input the content and send, for example: "Send message test!", Add 1A in hex at the end of the content to confirm the SMS content and send it without ENTER (You can also send 1B in hex to cancel the sending), Module response +CMGS: 15 if SNS is sent successfully.

Receive Message
- Send a message from the phone to the SIM7600 DONGLE: "This is a receive test for SIM7600X!"
- The serial port will print data when receiving, for example: "SM" 20 means that there are 20 messages in SM and the last message received is the 20th message.
- Read message: AT+CMGR=20 Read the 20th message (AT+CMGL="ALL" to read all messages)
- Delete message: AT+CMGD=20
- Convert the message to the string by convertor.
...
Resource
Driver
Demo Codes
Software
Datasheets
SIM7600CE Resources link
SIM7600G-H Resources link
Certification
FAQ
In this case, it may be that you have not successfully connected to the network, you can follow the steps below to troubleshoot:
1. First check the hardware connection:
- Check if the MAIN antenna is well connected;
- Whether the connected SIM card can call and surf the Internet normally on mobile phones and other devices:
- It is recommended to replace the SIM cards of different operators. Under the comparison test, the network frequency bands and base station layouts supported by different operators are different. Changing the SIM card can also eliminate problems such as card arrears
2. After confirming that there is no problem with the hardware, the software can use these instructions:
- Check whether the sim card is in good contact: AT+CPIN?
- Check whether RF is turned on (flight mode is turned off): AT+CFUN?
- Check if the network mode setting is correct: AT+CNMP?
- Check the signal quality of the current environment: AT+CSQ
- Check the operator's access situation: AT+COPS?
- Check the connection status: AT+CPSI?
- Check the operator's access situation: AT+CGDCONT?
- Check the connection status: AT+SIMCOMATI
- Check whether it is successfully registered to the network: AT+CGREG?
{{{5}}}
{{{5}}}
Restart SIM7600E-H after sending the following commands:
AT+CGPSNMEAPORTCFG=3 AT+CGPSNMEA=197119 AT+CGPSINFOCFG=10,31
AT+CLBS=? //View the range of parameters that can be set AT+CNETSTART//Open the network; if it fails to open the network, you can use the command AT+CNETSTOP to close and then open AT+CLBS=1 //Get the current latitude and longitude AT+CLBS=2 //Get the detailed address
{{{5}}}
This problem is generally caused by poor contact between the SIM card and the SIM card socket of the module.
ATE1
{{{5}}}
Since the Raspberry Pi serial port is used for terminal debugging by default, if you need to use the serial port, you need to modify the Raspberry Pi settings. Execute the following command to enter the Raspberry Pi configuration:
sudo raspi-config
Select Interfacing Options ->Serial ->NO ->YES to disable serial debugging

Open the /boot/config.txt file, and find the following configuration statement to enable the serial port, if not, add it at the end of the file:
enable_uart=1Restart to take effect
{{{5}}}
It may be that the APN has not been obtained. Generally, the APN can be obtained automatically. In some areas (IoT card), it needs to be obtained manually. For example, it can be set by the following instructions:
AT+CGDCONT=1,"IP","Your_APN" //The APN of different operators is different, here the APN is changed to the corresponding operator, for example: China Mobile APN: CMNET; China Unicom APN: 3GNET; China Telecom APN: CTNET

It can be set by the following commands:
AT+CGDCONT=1,"IPV6","APN" //Switch to IPV6, the APN of different operators is different, pay attention to distinguish the settings AT+CGDCONT=1,"IP","APN" //Switch back to IPV4
- No APN is set, configure APN as described above.
- After being banned, high-traffic (real-name IoT) cards are bound by chance cards and can only be used on one device (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Ministry of Public Security, must be issued to operators); The operator checks the status of the card and unlocks it.
The VOLTE function can be turned on with the following command:
at+voltesetting=1 at+cnv=/nv/item_files/modem/mmode/ue_usage_setting,1,01,1
The VOLTE function can be turned off with the following command:
at+voltesetting=0 at+cnv=/nv/item_files/modem/mmode/ue_usage_setting,0,01,1
AT+CSCA="+8613800755500"
Command to add + Enter, return OK. Note: China Mobile's SMS service center number is +861380xxxx500, where xxxx is the long-distance telephone area code where you are located. The SMS center may be different from place to place. For details, you can query Baidu or call the customer service of China Mobile Unicom. This SMS center is Shenzhen (0755).
- Confirm that SIM7600X is registered to the network, and confirm that the SIM card can send and receive text messages normally on mobile phones and other devices;
- Set the correct SMS center number;
- Initialize SMS settings with the following commands:
AT+CSCS="IRA" AT+CSMP=17,167,0,0
The AUX antenna can increase the downlink rate: The AUX antenna is also a diversity antenna, which plays the role of receiving signals, improves the signal reception capability, and works with the MAIN antenna to increase the downlink rate.
- Under normal circumstances, SIM7600X has been automatically dialed after receiving the Windows system, and there is no need to repeat dialing. Repeated dialing will return NO CARRIER
- If you still can't dial-up Internet access, please use the following command to change to Windows default dial-up Internet access mode
AT+CUSBPIDSWITCH=9001,1,1
- The display is turned off, and the mobile network is not enabled, you can ignore it and go online directly;
- You can also install the driver SIM7600X dial-up Driver to update the network card.
- The network card display is enabled after installing the driver.
- Generally, the default configuration of SIM7600 is to automatically select the network standard, and it is likely to choose 2G Internet access; if you need to force the use of 4G mode, you need to enter the following AT command configuration:
AT+CNMP=38 //Fixed 4G LTE, if there is no local 4G coverage, you may not be able to register to the network
- If 4G has been fixed, the speed is still not ideal, it may be a frequency band problem;
AT+CNBP? //Back up the current frequency band (the returned frequency band information can be copied to notepad, etc.)
AT+CNBP=0x0002000000400183,0x000001E000000000,0x0000000000000021 //After returning OK, measure the speed
AT+CNBP=0x0002000004400180,0x000001E000000000,0x000000000000003F //If the speed does not improve, try this
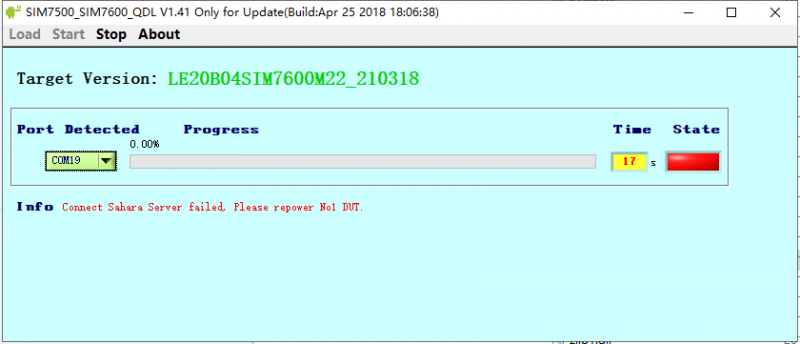
1. Pay attention to checking the device manager, the new device will be prompted during the upgrade process, and there will be no device driver during the first upgrade;
2. Pay attention to the USB cable. The speed of the USB cable is higher during the upgrade process. You need to choose a better-quality USB cable to avoid poor contact.
3. You need to run the upgrade tool with administrator privileges (SIM7500_SIM7600_QDL V1.41 only for Update)
4. Uninstall and reinstall the upgrade tool (SIM7500_SIM7600_QDL V1.41 only for Update)
5. For more operation details, please refer to this video: https://www.waveshare.net/wiki/SIM7600-Firmware-upgrade-Video
If the short message is stored in the SIM card, usually 50 is the upper limit. You can use the command: AT+CPMS? Make a query
- Gain: 9dbi ± 0.7dbi
- It is recommended to use the more convenient RNDIS dial
- Can burn the latest Raspberry Pi Raspbian system, reconfigure NDIS dial-up
- Or use the image that has been configured with the driver NDIS dial-up and start the Raspbian system image (the driver has been installed)
- Currently there is the driver source code of Android4-Android11, that is, the system version is Android4-Android11 only supported;
- Get the source code and SDK of the Android system of the target device (requires official image support), then add SIMCOM's Android system driver source code to the Android source code, and recompile (the compilation time varies from 1-10 hours, it is recommended to use a high-configuration PC operate);
- If the USB can be recognized, it means that the Android driver has been installed successfully. Set the module to 9011 mode or 9018 mode, and you can dial up to access the Internet;
- The steps to install the Android driver are cumbersome, and the operator is required to have certain Android system development experience and R&D capabilities.
The IP obtained by different dialing methods is different and has different characteristics. Please refer to the following table for details:
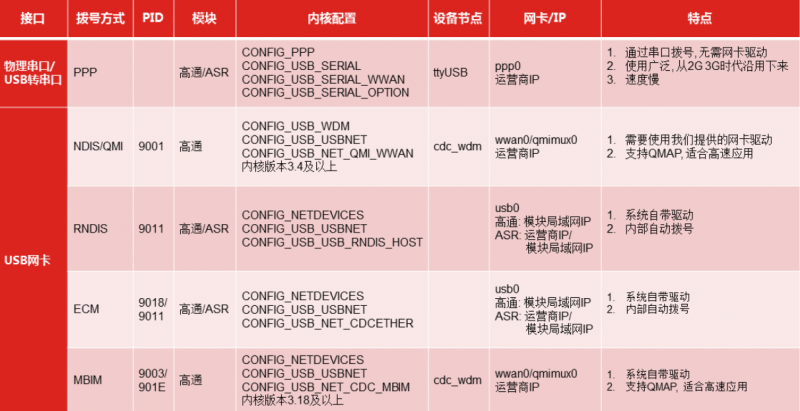
Below is a detailed description of the various dials:
- NDIS driver for Internet access (9001 mode)
This method must depend on the Linux system and is suitable for application scenarios that need to be developed using Linux network socket programming. After loading the driver into the kernel, connect the SIM7600 to the motherboard with a USB cable. After the SIM7600 is turned on, the wwan0 network can be recognized. port, you can access the Internet through this network port. The bottom layer of this method depends on the USB virtual serial port of SIM7600. This dial-up method can obtain the IP provided by the public operator, and the network speed is faster.
- RNDIS (9011 mode)
RNDIS refers to Remote NDIS. The implementation of RNDIS based on USB is TCP/IP over USB, which is to run TCP/IP on the USB device, making the USB device look like a network card. This method only needs simple configuration, the motherboard will recognize the USB0 network card, and quickly obtain the USB0 network card and module or the operator's IP network access; RNDIS network speed is relatively fast, which is one of the most commonly used dial-up methods.
- ECM (9018 mode)
These two are the "NDIS" standard under Linux. ECM is the abbreviation of the Ethernet Networking Control Model. ECM meets the requirements of the CDC on USB. The data call established through standard CDC-ECM is routed through the router, and the obtained IP address is a private IP such as 192.168; if the kernel supports this way, no additional driver is required. All data interacting with the module through the USB bus is constrained by relevant protocols and standards, and the module reaches the module through the USB hardware to complete the interaction with the Linux motherboard.
- PPP dial-up
This method must depend on the Linux system and is suitable for application scenarios that need to be developed using Linux network socket programming. After configuring and running the relevant scripts, connect the SIM7600 with a USB cable. After the SIM7600 is powered on, dial up the pppd script to identify it. To the ppp0 network port, you can access the Internet through this network port and obtain the operator's IP. The bottom layer of this method depends on the USB virtual serial port of SIM7600.
- AT command uses encapsulated TCP, MQTT, HTTP(S)
This method is suitable for microprocessors with limited resources, such as MCU, or for application scenarios with a relatively small amount of data, such as uploading sensor data to servers, cloud platforms, etc. through http(s), MQTT. If the network application is not complicated and the amount of data is relatively small (such as transmitting sensor data to the server and receiving control commands from the server), the function can be quickly used by using AT commands.
Question:When executing the chmod 777 sim7600_4G_hat_init command, an error is reported: "chmod: cannot access 'sim7600_4G_hat_init': No such file or directory"
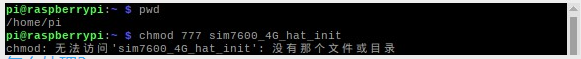
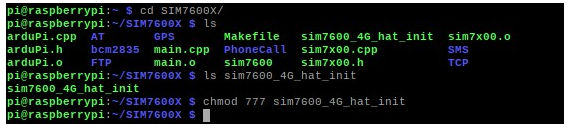
The general operation is: download the sample program, after decompression, rename the c folder under the Raspberry folder to SIM7600X, then copy the entire SIM7600X folder to the Raspberry Pi /home/pi directory, and enter the command line to /home/pi /SIM7600X directory, and then execute the chmod 777 sim7600_4G_hat_init command.
Restart SIM7600E-H after sending the following commands:
AT+CGPSNMEAPORTCFG=3 AT+CGPSNMEA=197119 AT+CGPSINFOCFG=10,31 AT+CGPSAUTO=1
- Currently there is the driver source code of Android4-Android11, that is, the system version is Android4-Android11 only supported;
- Get the source code and SDK of the Android system of the target device (requires official image support), then add SIMCOM's Android system driver source code to the Android source code, and recompile (the compilation time varies from 1-10 hours, it is recommended to use a high-configuration PC operate);
- If the USB can be recognized, it means that the Android driver has been installed successfully. Set the module to 9011 mode or 9018 mode, and you can dial up to access the Internet;
- The steps to install the Android driver are cumbersome, and the operator is required to have certain Android system development experience and R&D capabilities.
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)