UPS HAT (E)
| ||
Overview
Introduction
The UPS HAT (E) is an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) expansion board specially designed for the Raspberry Pi series. Onboard battery meter chip, fast-charging chip, and high-power buck chip which can provide high-power input and output as well as monitor the operating state of the module via the I2C interface.
SAFETY CAUTIONS
- Li-ion and Li-po batteries are quite unstable. They may cause fire, personal injury, or property damage, if they're not properly recharged or used.
- Do not reversely connect the polarities when recharging or discharging the battery. Do not use inferior charger/charging panel to recharge the battery.
- Do not mix use old batteries with new ones, avoid using batteries of different brands.
- When buying Lithium battery, make sure the battery specification is compatible with the expansion board. Choose batteries from formal manufacturer, and ensure the batteries will work stably and safely by aging test.
- Lithium batteries have limited cycle life, they will also deteriorate as time goes by. Should be replaced with new ones when the batteries reaching their max cycle life, or working over two years, whichever comes first.
- Should be placed carefully and properly, keep it away from inflammables and explosives articles, away from children, avoid any safety accident caused by careless storage.
Feature
- Adopts pogo pins connector design, compatible with Raspberry Pi 5/4B/3B+.
- Onboard Type-C port with bi-directional fast charging, supports multiple charging input / output protocols such as PD3.0, up to 40W charging power.
- Onboard battery fuel gauge IC for reading battery voltage, current, power, remaining capacity and other parameters.
- Supports I2C bus communication for monitoring the operating status of Type-C port and batteries in real time.
- Supports 4× 21700 Li batteries (NOT included), larger capacity and longer battery life.
- Onboard high-power buck chip for stable 5V 6A power output.
- Onboard MCU management, supports detecting power connection and booting the Raspberry Pi.
- Supports displaying battery level on the system, easy to check the operating state of the HAT.
- Comes with online development resources and manuals.
Specification
- OUTPUT VOLTAGE: 5V
- CONTROL BUS: I2C
- RECHARGING BATTERY: bidirectional input/output protocol, support up to 40W
- OUTPUT POWER: 5V 6A
- BATTERY SPECIFICATION: 21700 RECHARGEABLE BATTERIES 3.6V
- CURRENT CAPACITY: 5000mAh (Standard)
- DIMENSIONS: 56mm × 88mm
- MOUNTING HOLE SIZE: 3.0mm
Onboard Interface
Hardware Description

The USB Type C interface is the bidirectional recharging interface and supports recharging and output with a maximum power of 40W. USB Type A interface is the 5V output interface, the LED is the fast-recharging indicator and turns on when it is in the fast recharging state. 0FF/ON is the power switch silkscreen.
Note 1: Do not charge when the battery is connected reversely. Reversing the battery connection may damage the battery protection chip.
Note 2: When assembling the battery, please follow the V1-V2-V3-V4 order to install. Otherwise, the reverse connection may turn on the warning indicator. The disassembled battery needs to be connected to the charger to charge in order to activate the output.
Note 3: After replacing the battery, it needs to complete several full charge/discharge cycles, so that the chip automatically calculates the battery parameters, and the capacitance is more accurate.
Note 4: The actual output current of the module can be up to 10A, due to heat dissipation reasons, it is recommended that the use of no more than 6A, and the use of larger currents should be added to the active cooling.
Note 5: Due to the battery type and temperature effects, the battery capacity may be inaccurate, to determine whether the voltage is charged or not should be based on voltage values.
Raspberry Pi Demo
Enable I2C Interface
- Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and input the following commands to enter the configuration interface:
sudo raspi-config Select Interfacing Options -> I2C -> yes to enable i2C kernel driver
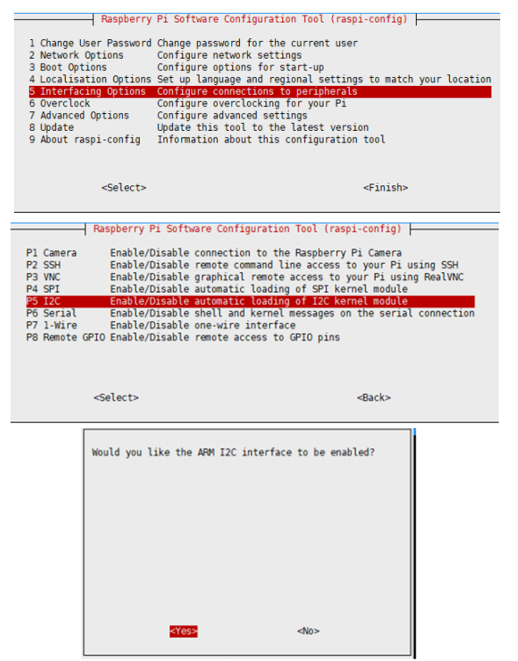
And then reboot the Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
INA219 Baterry Level Detection
To demonstrate this demo on the Raspberry Pi, you only need to insert the module into the Raspberry Pi headers or connect it to the I2C interface of the Raspberry Pi via a cable with VCC connected to 3.3V.
Enter the following command to run the demo:
sudo apt-get install p7zip wget https://files.waveshare.com/wiki/UPS-HAT-(E)/UPS_HAT_E.7z 7zr x UPS_HAT_E.7z -r -o./ cd UPS_HAT_E python3 ups.py
The demo will output values such as battery voltage, current, power and the remaining battery capacity percentage after it runs.

The negative VBUS current value indicates type-c output current and the positive one indicates input current. If the battery current is negative, it indicates the battery output current (which can be the Raspberry Pi load current), and if the battery current is positive, it indicates the battery charging current.
When the system load is high and the battery voltage is low, it is undesirable to see that the battery current may be insufficient, leading to continuous system restarts. In practical applications, you can prevent this by shutting down the system automatically when the battery voltage is too low.
In the example demo, battery voltage checking has been added. If the battery voltage is too low and there is no external charging power, the demo will shut down the system within 60 seconds.
The demo will display the following statement to indicate that the battery voltage is too low, and it is necessary to charge it promptly, otherwise, the demo will shut down automatically:
Voltage Low, please charge in time, otherwise, it will shut down in 58 s
Battery Level Display
Open the terminal and execute:
cd ~/UPS_HAT_E DISPLAY=':0.0' python3 batteryTray.py
Run the demo to display the upper right corner of the battery logo. If it does not display and the demo does not report errors, you should check the I2C interface and the installation of libraries.

After reboot the battery logo appears in the upper right corner indicating that the setup is successful, mouse over the battery icon position will show the battery level, voltage and charge.
When the battery level drops below 5%, a low battery warning will appear. After 60 seconds, it will power off automatically.

If it has no effects, you can test as below:
cd ~/UPS_HAT_E ./main.sh #Do not add "sudo" sudo reboot
Raspberry Pi 5 Set 5A Current
The Raspberry Pi 5 will detect the PD protocol at Type-C interface, and it will limit the current to 3A if the protocol is not detected and display the following prompts:

Run the following commands to open "eeprom" to edit:
sudo rpi-eeprom-config --edit
Add the following settings to remove the 3A current limit, and provide 5A current.
PSU_MAX_CURRENT=5000
Boot When Power Applied
When a low voltage is detected, you can use a demo to control the Raspberry Pi to save data before shutting down, thereby avoiding data loss due to sudden power loss.
However, after the Raspberry Pi shuts down while still powered, it will not automatically restart when power is applied again. But you can enable this function through I2C setting.
To detect I2C addresses, open the terminal and execute the following command.
i2cdetect -y 1

0x2D is the I2C address of IMU chip. Run the following commands, you can check the register values, and the corresponding values of registers with the addresses 0x00, 0x01 respectively are 0x0a and 0x0b.

After changing the value of the 0x01 register to 0x55, the MCU will disconnect the Raspberry Pi power supply after 30s, and detect the charging port after 60s. If it is charged, it will automatically reboot the Raspberry Pi.
Run the following commands to set the 0x01 register as 0x55.
i2cset -y 1 0x2d 0x01 0x55
Note 1: The Raspberry Pi needs to be turned off immediately after setting 0x01 to 0x55, otherwise, the data may get lost after it powers off in 30s.
Note 2: The start when power applied function has been added to the sample demo.
Resource
Document
Demo Code
FAQ
- To resume output after changing the battery, you need to charge the battery first or press the BOOT button to activate the battery protection circuit. Then, switch the power to ON to enable output.
{{{5}}}
- The output power of the type-c interface is 40W, and for the pogo pin, it can reach up to 5V 10A. However, it is recommended to control the current less than 6A for controlling the temperature.
{{{5}}}
- Capacity may be inaccurate depending on battery type and temperature. The replaced batteries need to complete several full charge/discharge cycles so that the chip will be accurate after calculating the battery parameters.
- Batteries used should be as consistent as possible, mixing old and new batteries with large differences in battery voltage may reduce capacity.
{{{5}}}
21700 Lithium batteries with an outline diameter of 21mm and a height of 70.0mm. The standard voltage is 3.7V and the voltage is 4.2V after fully charged.
{{{5}}}
- The onboard LED indicates the fast-charging state and is on when identifies the fast-charging protocol. Please note that this LED will not be on when it is normally charged by 5V.
{{{5}}}
Negative indicates output current and positive is input current. Positive battery current indicates charging and negative battery current indicates discharging.
{{{5}}}
- The fast-charging power supply should be plugged into the USB Type-C interface rather than USB Type-C interface of the Raspberry Pi.
- The module should be used with a fast charging power supply, normal charging will result in insufficient input power and lower and lower battery voltage.
{{{5}}}
- I2C is not enabled, please enable the I2C of the Raspberry Pi.
- The poor contact of the pogo pins, and you can detect whether the device is recognized with the following commands:
Install i2c-tools. To check the I2C address easily, you can input the following commands in the console:
sudo apt-get install i2c-tools
After installation, you can check the I2C address with the following commands:
sudo i2cdetect -y 1
If UPS HAT is inserted by default, you can get the following result after running the commands:

If it is not recognized:
It is recommended to lock the screws and solder the pin headers for better contact.
{{{5}}}
The Pi 5 will detect the power of the USB power supply. If the USB power supply is not applicable, the current would be limited. You can add the following command to the /boot/firmware/config.txt file to solve:
usb_max_current_enable=1
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)

