Template: Alphabot 2 Pi
Raspberry Pi Example Program (AlphaBot-Pi)
Python demo also is provided.
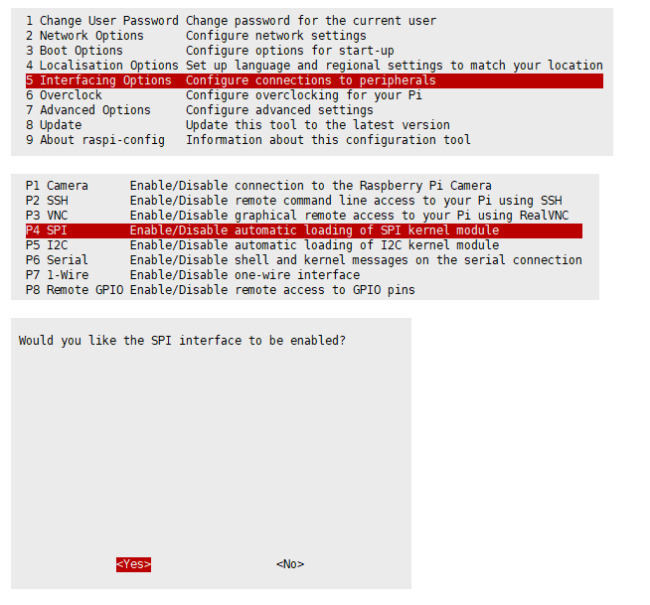
Enable SPI interface
- Open the terminal, and use the command to enter the configuration page.
sudo raspi-config Choose Interfacing Options -> SPI -> Yes to enable the SPI interface
sudo reboot
Make sure that the SPI is not occupied by other devices, you can check in the middle of the /boot/config .txt.
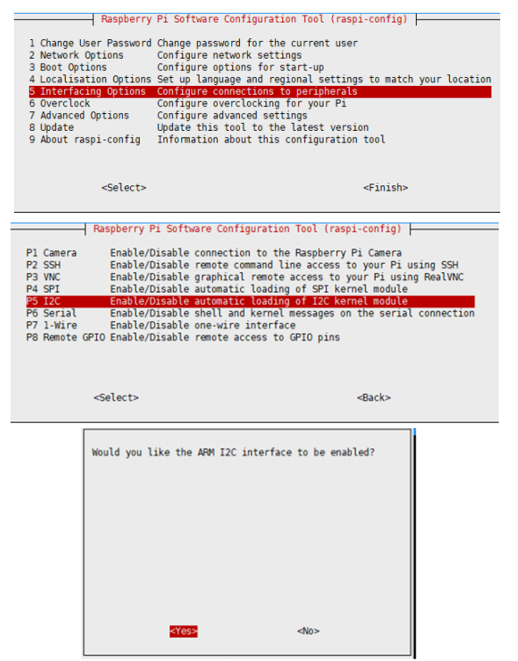
Enable I2C Interface
Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo raspi-config Choose Interfacing Options -> I2C -> Yes.
Reboot Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
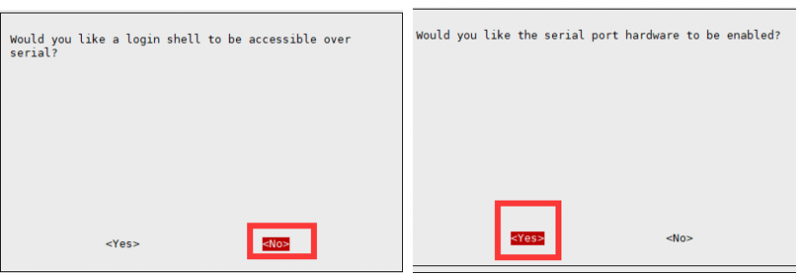
Enable UART
Execute the following command to enter the Raspberry Pi configuration:
sudo raspi-config
Choose Interfacing Options -> Serial -> No -> Yes:
You need to disable the login shell and enable the srial port hardware:
Reboot Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
Open the /boot/config.txt file and find the following configuration statement to enable the serial port, if not, add it at the end of the file:
enable_uart=1
Reboot to take effect.
Install Libraries
- python2
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install ttf-wqy-zenhei sudo apt-get install python-pip sudo pip install RPi.GPIO sudo pip install spidev sudo apt-get install python-smbus sudo apt-get install python-serial sudo pip install rpi_ws281x
- python3
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install ttf-wqy-zenhei sudo apt-get install python3-pip sudo pip3 install RPi.GPIO sudo pip3 install spidev sudo apt-get install python3-smbus sudo apt-get install python3-serial sudo pip3 install rpi_ws281x
Download Examples
Open a terminal and run the following commands:
wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/3/39/AlphaBot2-Demo.zip unzip AlphaBot2-Demo.zip
Motor Test
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python AlphaBot2.py
- Expected result: After the program runs, the motor rotates and the trolley moves forward.
- If the direction is wrong, you need to modify the motor wiring accordingly or modify the pins in the program. The second method is recommended. If the rotation direction of the left wheel is not correct, then ain1 and ain2 will be used. If the rotation direction of the right wheel is not correct, then switch bin1 and bin2.
def __init__(self,ain1=12,ain2=13,ena=6,bin1=20,bin2=21,enb=26):
Joystick Direction
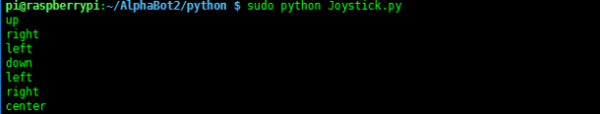
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python Joystick.py
- Expected result: Joystick Joystick in 5 directions, including up, down, left, right, and OK. When the button is pressed, the control port will display the key position of the current button, the motor will rotate according to the direction of the button, and the buzzer will sound.
- If the rotation direction of the wheel is different from the direction of the button, you need to modify the pin.
IR Remote Control Car
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python IRremote.py
- Expected result: Press the number keys of the infrared remote control to control the car. 2, 8, 4, 6, and 5 respectively represent forward, backward, turn left, turn right, and stop. Press - or + to adjust the speed. (Note: Different infrared remote controllers may have different key codes, if they are different, you need to modify the corresponding program.)
Infrared Obstacle Avoidance
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python Infrared_Obstacle_Avoidance.py
- When there is no obstacle before the car, the front green LED will turn off. When the car encounters an obstacle, the green LED light in front will light up. If the LED is not on or is always on, you can adjust the two potentiometers on the bottom of the trolley so that the LED is just off.
- Expected result: If the sensor on the left side of the car does not reach an obstacle, the car will go straight and turn left when an obstacle is detected.
Ultrasonic Ranging (the Raspberry Pi 3B package does not include the ultrasonic module)
- Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python Ultrasonic_Ranging.py
- Expected results: the terminal will display the current measuring distance.
Ultrasonic Obstacle Avoidance (Raspberry Pi 3B package does not include ultrasonic module)
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python Ultrasonic_Obstacle_Avoidance.py
- Expected result: If the sensor on the left side of the car does not reach an obstacle, the car will go straight and turn right when an obstacle is detected.
RGB Light
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python ws2812.py
- Expected result: there are four RGB LEDs on the bottom of the car: Red, Green, Blue, and Yellow.
If the displayed color is wrong, you can add the following statement to the /boot/config.txt file, and then restart to take effect. Since the RGB LEDs are controlled by DMA and the audio output of the Raspberry Pi is a DMA channel, the following statement will disable the headphone port.
hdmi_force_hotplug=1 hdmi_force_edid_audio=1
Tracking Sensor Test
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python TRSensors.py
- Expected result: The terminal prints five sets of data, corresponding to five sensors respectively. When the car is placed on the white bottom plate, the value is about eight or nine hundred. The number is about one hundred to three hundred.
IR Tracking Program
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python Line_Follow.py
- Expected result: When the program is running, it will rotate left and right for automatic calibration. After the calibration is completed, move the Alphabot2 left and right, and the terminal will display the current position of the black line and the values of the five sensors. Straighten the car, and press the button in the middle of the five-way joystick, the car will move along the black line, and the RGB LED at the bottom of the car will display different colors.
Servo
Run in the terminal of the Raspberry Pi:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/python/ sudo python PCA9685.py
- Expected result: the servo will move left and right, and the rotation range is about 180 degrees.
MJPG-streamer Software Real-time Monitoring
"MJPG-streamer", is an open-source project which is used to capture images from the camera, and transmit the video data to a webpage via the network.
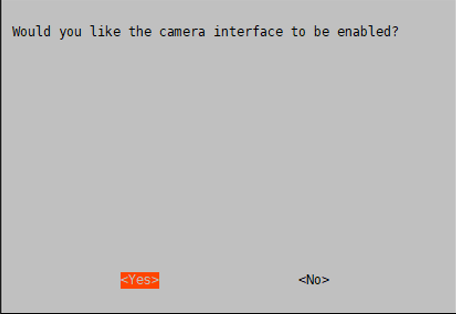
- To use the camera, you need to first enable the camera
sudo raspi-config *Choose Enable Camera -> Yes
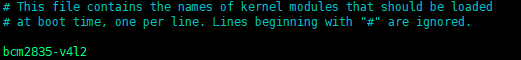
- If it is a camera using the CSI interface, the system cannot find the device node of /dev/video0. A line for bcm2835-v4l2 needs to be added to the /etc/modules file:
sudo nano /etc/modules
- Append the line to the file
bcm2835-v4l2
- Reboot and check the device:
sudo reboot ls /dev/video*
video0 device will be listed as expected.
Note: After performing the first steps, please confirm that the operation and instructions are correct.
- Run the following commands:
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/ sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install cmake libjpeg9-dev git clone https://github.com/jacksonliam/mjpg-streamer cd mjpg-streamer/mjpg-streamer-experimental/ sudo make clean all sudo ./start.sh
Open a Chorme, and go to Ip_address:8080, click stream to check the camera.
For more information about the mjpg-streamer:https://github.com/jacksonliam/mjpg-streamer

Remotely Control Alphabot By Bottle
"Bottle" is a simple and efficient WSGI-compliant micro python web framework. You can quickly implement web control with Bottle.
Run the following commands in the terminal:
Python2:
sudo apt-get install python-bottle
Python3:
sudo apt-get install python3-bottle
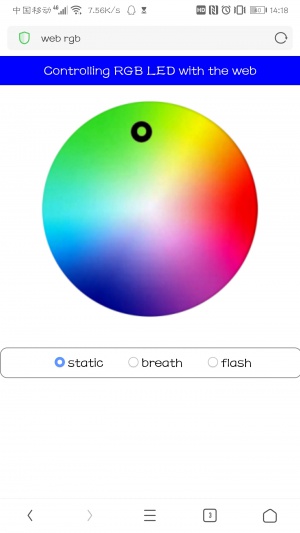
- Web Control RGB LED via Bottle
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/Web-RGB sudo python main.py
Enter the IP address of the Raspberry Pi in the address bar of the mobile phone browser (computer browsers are not supported), the port number is 8002, and the following page will be displayed. By clicking on different positions of the picture, the RGB LED will display different colors. "static", "breath", and "flash" correspond to three display modes respectively.
- Realize web video control the car through Bottle.
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/Web-Control sudo python main.py
Open Chrome, and go to Ip_address:8000, click stream to check the camera.
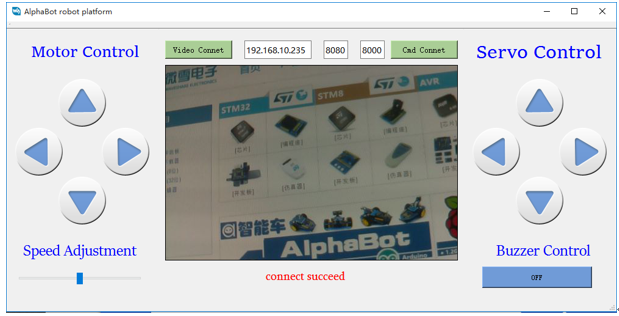
You can control it by telephone or PC.
Control it by telephone:
- To set it to autostart, you can modify /etc/rc. local file and add the following lines
sudo nano /etc/rc.local #Without the nano editor, enter the following command to download sudo apt-get install nano
Add:
cd AlphaBot_Demo/AlphaBot_Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot/Web-Control sudo python main.py &
Finally, edit main.py. This step is very important. If it is not set, the program will not be able to run after booting. This step is to wait for the host to connect to the network and the added delay.
sudo nano /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/Web-Control/main.py #Find the 23rd line, delete the # sign in front of time.sleep(12), if your system boots slowly, you can increase the parameters in parentheses
As we know, the IP address of Raspberry Pi is dynamic and changes all the time. You can configure static IP by modifying the /etc/dhcpcd.conf file.
interface wlan0 static ip_address = 192.168.1.114/24 static routers = 192.168.1.1
192.168.1.1 is the IP address of the router and 192.168.1.114 is the static IP set, /24 should be added in the end
Note:
You need to set the jumpers IN1, IN2, ENA, ENB, IN3, and IN4 which are in the A area to P12, P13, P6, P26, P20, and P21 for controlling Alphabot by Pi. The jumpers S1, and S2 of the C areas should be connected to P27 and P22. After rebooting, you can go to ip_address:8000 to enter the control webpage.
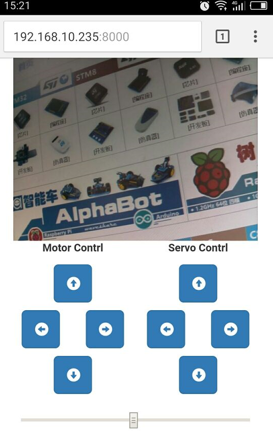
Remote Control Alphabot2 With The Software
- Control the car through the mobile phone or PC software video.
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/App-Control sudo python main.py
- Open another terminal and run mjpg-streamer
cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/mjpg-streamer/mjpg-streamer-experimental sudo ./start.sh
Open the AlphaBot.exe program on the computer, enter the IP address, the port number of mjpg-stream, and the port number of the car Soket server.
Click Video Connet to connect the video, the button turns green and the connection is successful, click Cmd Connect to the car server. If the button turns green, the connection is successful. The button on the left controls the movement of the car, and the button on the right controls the rotation of the camera servo.
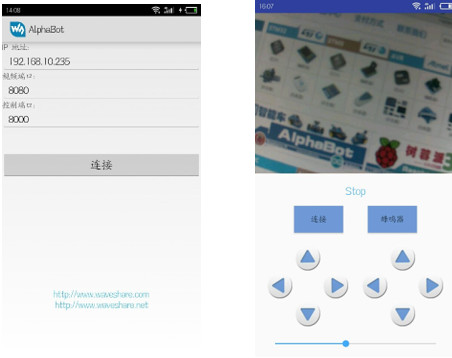
Scan the QR code below with your mobile phone to download the corresponding APP.

If it fails, please click here to download [APP https://files.waveshare.com/upload/5/53/Alphabot_app.zip]
Enter the actual address of the Raspberry Pi, click the link to see the image captured by the camera, click the connection, after the button changes from green to blue, it indicates the control port connection program, the corresponding button of the motor can control the movement of the car, the rotation of the servo, and pull the slider to Change the trolley speed.
Open the /etc/rc.local file with a text editor and add the following command to set the boot to start.
sudo nano /etc/rc.local #There is no nano editor, enter the following command to download sudo apt-get install nano
Add the following command between fi and exit 0, then save the file and exit.
cd /home/pi/mjpg-streamer/mjpg-streamer-experimental sudo ./start.sh & cd /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/App-Control sudo python main.py &
Finally, edit main.py. This step is very important. If it is not set, the program will not be able to run after booting. This step is to wait for the host to connect to the network and the added delay.
sudo nano /home/pi/AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/APP-Control/main.py #Find the 15th line, delete the # sign in front of time.sleep(8). If your system boots slowly, you can increase the parameters in the parentheses
Every time the Raspberry Pi starts, it needs to connect to the router. Of course, we can also enable the AP function of the Raspberry Pi wireless network adapter and use the Raspberry Pi as a router. For details, please refer to the Raspberry Pi tutorial, which will not be described in detail here.
Remote Control Car Via Raspberry Pi Bluetooth
- Upgrade and install Bluetooth-related software packages, and install Bluetooth dependency library.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade -y sudo apt-get dist-upgrade -y sudo apt-get install pi-bluetooth bluez bluez-firmware blueman
- Add a Pi user to the Bluetooth group.
sudo usermod -G bluetooth -a pi
- Reboot the Raspberry Pi.
sudo reboot
- Start/increase SPP, and turn on Bluetooth device.
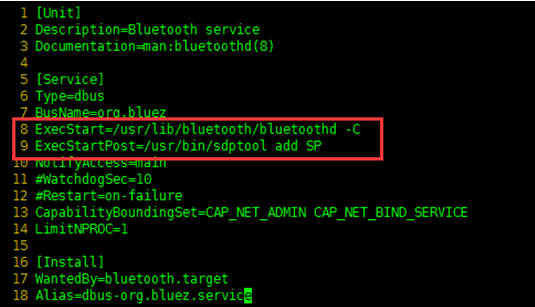
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.bluez.service
Modify these two statements in the file.
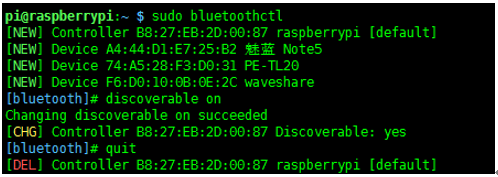
After rebooting the Raspberry Pi, you can enter the command "hciconfig" (similar to "ifconfig" command) to check the Bluetooth service.
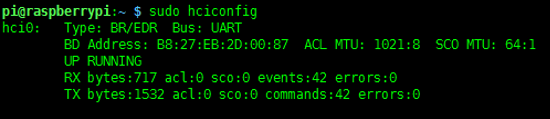
If you can see "hci0" device, the Bluetooth is enabled to work. If not, the Bluetooth device is not identified.
Note: If there is dtoverlay=pi3-miniuart-bt in the /boot/config.txt file, this statement needs to be commented out, otherwise the Bluetooth device will not work properly.
- Connect to the Bluetooth device
Enter the following command to enter the Bluetooth control interface. (input "help" to enter the interface to check the command list.)
sudo bluetoothctl agent on
After entering the interface: (input "help" to enter the interface to check the command list.)
agent on default-agent
After "scan on", you can see the physical address of the scanned Bluetooth devices, that is, Addresses like XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.

Use the following command for pairing (please replace XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX with the address of your own device, Android phone can see the Bluetooth address in Settings->About Phone->Status Information.)
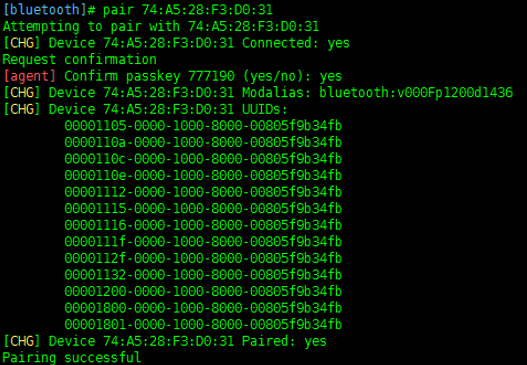
Add the device to the trusted list after pairing.
trust XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
connect XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
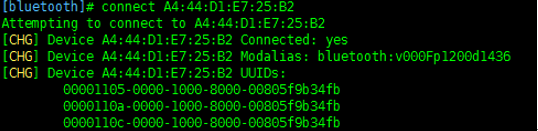
Finally, click "quit" to exit. After the Bluetooth device is turned on, the Raspberry Pi will automatically connect.
Note: If the link under the command line is unsuccessful, you can connect under the graphical interface.
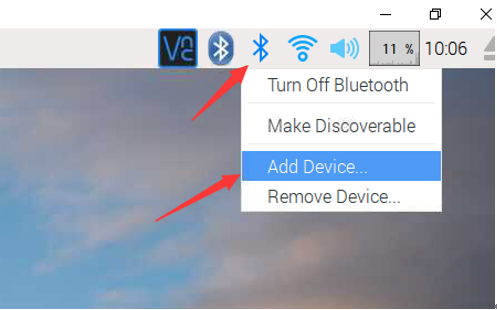
Click the Bluetooth icon to add a Bluetooth device.
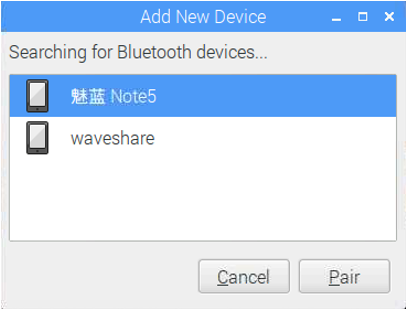
Select the corresponding mobile phone Bluetooth device, note that the mobile phone Bluetooth must be turned on to be discoverable.
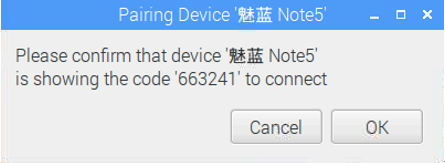
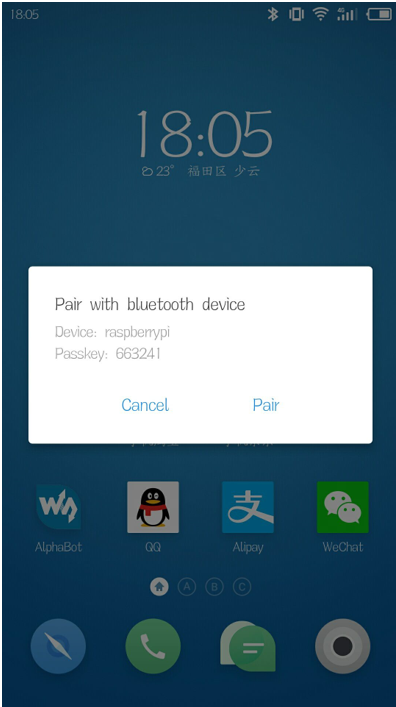
On the Raspberry Pi side, select ok for pairing, and on the mobile phone side, select "Pair" for pairing.
It prompts that the configuration is successful, but there is no service.

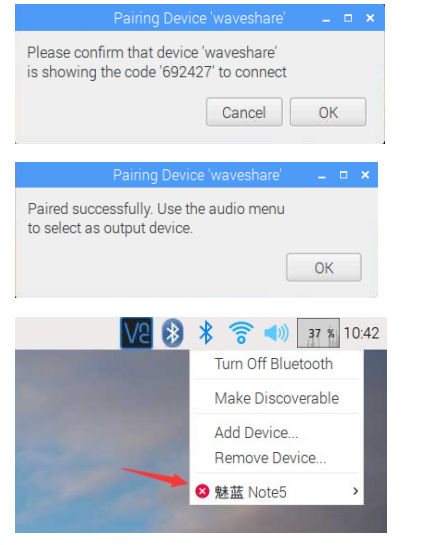
Connected successfully. Run the following command to start the program:
cd AlphaBot2-Demo/RaspberryPi/AlphaBot2/Bluetooth-Control sudo rfcomm watch hci0 1 python bluetooth.py
Scan the QR code below with your mobile phone to download the corresponding APP. (This software is Dual-mode Bluetooth module control software. If this software has been installed in the above Arduino operation, it is not necessary to install it again.)

If it fails, you can click here to download.
Start the APP, and click "Scan" (Note: the mobile phone needs to turn on the Bluetooth function), the corresponding Bluetooth devices will be displayed in the list normally. Select the "raspberrypi" device. Go to the next page and select "Remote Mode" to enter the remote mode.

If the Raspberry Pi Bluetooth is not found, you can run the following command to enable Bluetooth discovery.