RPi Zero Relay
| ||
Overview
Introduction
C and Python demos are available.
Features
- Equipped with CAN functionality, using CAN controller MCP2515 with SPI interface, with the transceiver SN65HVD230
- Equipped with RS485 function, using UART control, half-duplex communication, transceiver is SP3485
- Onboard TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor), effectively suppress surge voltage and transient spike voltage in the circuit for RS485 transceiving, lightningproof & anti-electrostatic
Specifications
- Supply voltage: 7V~36V
- CAN control chip: MCP2515
- CAN Transceiver: SN65HVD230
- 485 Transceiver: SP3485
- Product size: 123mmx87.92mm
- Fixed hole diameter: 3.5mm
Pinouts
- CAN bus
| PIN | Raspberry Pi (BCM) | Description |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| SCK | SCK | SPI clock input |
| MOSI | MOSI | SPI data input |
| MISO | MISO | SPI data output |
| CS | CE0 | Data/command selection |
| INT | 25 | Interrupt output |
- RS485 bus
| PIN | Raspberry Pi (BCM) | Description |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| RXD | RXD | UART receive |
| TXD | TXD | UART transimit |
- Relay interfaces
| PIN | Raspberry Pi (BCM) | Description |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| IN_CH1 | GPIO5 | Relay Channel 1 |
| IN_CH2 | GPIO6 | Relay Channel 2 |
| IN_CH3 | GPIO13 | Relay Channel 3 |
| IN_CH4 | GPIO16 | Relay Channel 4 |
| IN_CH5 | GPIO19 | Relay Channel 5 |
| IN_CH6 | GPIO20 | Relay Channel 6 |
Onboard resources
| No. | Name | Description | |
| 1 | MCP2515 | CAN controller | |
| 2 | SI8642ED-B-IS | Digital isolator | |
| 3 | SN65HVD230 | CAN transceiver | |
| 4 | SP3485EN | RS485 transceiver | |
| 5 | LM2596 regulator chip | Provides stable 5V voltage | |
| 6 | Optocoupler isolation | Avoids interference with the control chip by the external high-voltage circuit of the relay | |
| 7 | |Contact rating per channel: ≤ 10A 250V AC or ≤ 10A 30V DC | ||
| 8 | Power isolation | Provides a stable isolation voltage, and no additional power supply is required for the isolation terminal | |
| 9 | Resettable fuse | Resettable fuse | |
| 10 | TVS diode | Transient voltage protection | |
| 11 | Relay and power LED indicator | The LED lights up to indicate that the corresponding relay is engaged | |
| 12 | 40PIN GPIO header | Applicable to Raspberry Pi Zero series motherboards with pre-soldered pinheaders | |
| 13 | Relay screw terminal | Convenient for connection with user devices | |
| 14 | Power supply screw terminal | Supports 7~36V DC power supply | |
| 15 | RS485 bus interface | Connects RS485 devices | |
| 16 | CAN bus interface | Connects CAN devices | |
| 17 | RS485 120Ω terminal resistor switch | RS485 120Ω terminal resistor switch | |
| 18 | CAN 120Ω terminal resistor switch | CAN 120Ω terminal resistor switch | |
| 19 | Relay control pins | Can disconnect or connect relay control | |
| 20 | External power supply jack | Round hole 7~36V DC power supply | |
| 21 | Thickened tracks | Supports access to high-current devices |
Install libraries
wiringPi
git clone https://github.com/WiringPi/WiringPi cd WiringPi ./build gpio -v # Run gpio -v and corresponding version information will appear. If it does not appear, there is an installation error.
python
In the latest version of the system, some python libraries cannot be installed normally, you need to use a virtual environment, and then install the library and run the program
Non-virtual environment configuration
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python3-serial sudo apt-get install python3-can sudo apt-get install python3-gpiozero
Virtual environment configuration, execution, exit
# Install the libraries required for the virtual environment sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install git python3-pip -y sudo apt install python3-venv # Create a new virtual environment (myenv is the name of the virtual environment, which can be modified) python3 -m venv myenv # Activate the virtual environment source myenv/bin/activate # Install the library pip3 install pyserial pip3 install python-can pip3 install gpiozero # Download demo (see the corresponding location in the wiki) # Run demo (see the corresponding location in the wiki) # Exit the virtual environment deactivate
Download demo
Run on the Raspberry Pi terminal:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full wget https://www.waveshare.net/w/upload/2/2f/RPi_Zero_Relay_Code.7z 7z x RPi_Zero_Relay_Code.7z -r -o./RPi_Zero_Relay_Code sudo chmod 777 -R RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/
Relay usage
The program phenomenon is to close the relay sequentially and then disconnect the relay sequentially
C
cd RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/Relay/wiringPi/ make clean make sudo ./relay
python
cd RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/Relay/python/ python3 relay.py
CAN usage
This demo program uses two RPi-Zero-Relay modules
Providing Python and C language demos
Preliminary Work
Connect the modules, then modify the boot script config.txt
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Add the following to the last line:
dtparam=spi=on dtoverlay=mcp2515-can0,oscillator=16000000,interrupt=25,spimaxfrequency=3000000
After saving the exit, restart the Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
After the restart, run the command to check whether the initialization is successful:
dmesg | grep -i '\(can\|spi\)'

If the module is not connected, the prompt may be as follows:

Please check whether the module is connected; whether SPI and MCP2515 kernel driver are enabled; whether it is restarted.
Make sure both RPi-Zero-Relay modules are handled in the same way, connect the H of one module to the L of the other module
If you are using other CAN devices, make sure to connect H-H, L-L
C
- Block reception, open the terminal on the Raspberry Pi and run:
cd RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/CAN/wiringPi/receive/ make clean make sudo ./can_receive
The receiving program is blocked.

- Send, the Raspberry Pi opens the terminal and runs:
cd RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/CAN/wiringPi/send/ make clean make sudo ./can_send
Enter the corresponding value:

At this time, a packet with the corresponding ID is received:

python
The Raspberry Pi opens the terminal and runs:
# Enter the corresponding directory cd RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/CAN/python/ # The receiver runs the program first: sudo python can_reveive.py # After the receiver runs the program, the sender runs the program: sudo python can_send.py
How to use with other CAN devices
1. Make sure the hardware wiring is correct, i.e. H-H, L-L connection
2. Make sure that the baud rate settings on both sides are consistent, the demo baud rate is set to 100K by default
3. Ensure that the CAN IDs on both sides are consistent, otherwise reception will not be possible
4. If there is frame loss when sending data for a long time, you can try to reduce the baud rate to solve it
RS485 usage
This demo program uses two RPi-Zero-Relay modules
Providing Python and wiringPi language demos
Preliminary Work
Enable UART interface
Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and enter the following command to enter the configuration interface
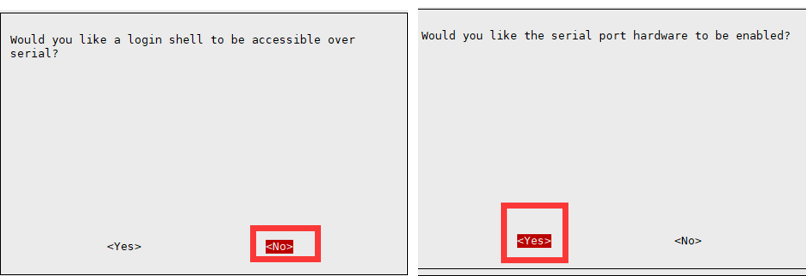
sudo raspi-config Select Interfacing Options -> Serial, disable shell access, and enable the hardware serial port
Open the /boot/config.txt file, find the following configuration statement to enable the serial port, if not, you can add it to the end of the file.
enable_uart=1
Then restart Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
Make sure both Raspberry Pis are processed in the same way, then connect the A of one module to the B of the other module
If you are using other 485 devices, make sure to connect A-A, B-B
C
- Block reception, open the terminal on the Raspberry Pi and run:
cd RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/485/WiringPi/receive make clean make sudo ./485_receive
The receiving program is blocked.

- Send, the Raspberry Pi opens the terminal and runs:
cd RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/485/WiringPi/send make clean make sudo ./485_send
Enter the corresponding value:

At this time, the receiver receives the program

python demo
# Enter the corresponding directory cd RPi_Zero_Relay_Code/485/python/ # The receiver runs the program first sudo python receive.py # After the receiver runs the program, the sender runs the program sudo python send.py
Troubleshooting
If the 485 communication is not normal, debug step by step:
- Confirm if serial login to the Raspberry Pi shell is blocked;
- Determine whether A,B of 485 correspond to A,B of controlled 485 equipment one by one;
- You can start by using a USB to 485 device to communicate with the RPi Zero Relay, ensuring that the Raspberry Pi's setup is correct;
Resources
Document
Demo
Datasheets
FAQ
There is a problem with the corresponding library, such as incomplete installation, etc.; Uninstall the corresponding library file and reinstall it
For example:
# Uninstall pyserial pip3 uninstall pyserial # Install pyserial pip3 install pyserial
This warning does not affect the execution of the program, but the corresponding function in the library does not find the corresponding dependency, and our demo does not actually use this part;
If you want to dismiss these warnings, just install the corresponding library
For example:
# Install lgpio pip3 install lgpio # Install RPi.GPIO pip3 install RPi.GPIO
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)