Pico-RGB-Matrix-P3-64x32
| ||
Introduction
This product is an RGB LED full-color multi-function digital clock, using the Raspberry Pi Pico master control, onboard a variety of peripheral resources, providing C++/Python demos and learning tutorials, open source software and hardware, suitable for makers or electronics enthusiasts to get started learning, or DIY secondary development into other desktop or wall-mounted display applications.
Features
- Standard Raspberry Pi Pico header, supports Raspberry Pi Pico series.
- Using P3 fine-pitch RGB LED matrix panel, with 2048 individual RGB LEDs, 64 × 32 pixels, 3mm pitch, allows displaying text, colorful images, or animation.
- Onboard high precision RTC chip DS3231, with backup battery holder (battery included), maintains accurate timekeeping when main power is off.
- Real-Time Clock Counts Seconds, Minutes, Hours, Date of the Month, Month, Day of the Week, and Year with Leap-Year Compensation Valid Up to 2100.
- Optional format: 24-hour OR 12-hour with an AM/PM indicator.
- 2 x programable alarm clock.
- Digital temperature sensor output: ±3°C accuracy
- Embedded photosensor for auto brightness adjustment due to the ambient light, power saving, and eye care.
- Embedded buzzer for alarm or hourly ring, etc.
- IR receiver, combined with the IR remote controller, supports IR wireless control.
- 5 x buttons for configuration, reset, and code programming.
- High-quality acrylic back panel and dimmer panel, better looking, more comfortable displaying.
- Comes with online development resources and manual (Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ and MicroPython examples).
Usage Scenarios
Hardware Introduction
Introduction to Onboard Resources
Directions for Raspberry Pi
Please refer to github information: Demo, wiring reference
If the overall brightness of the indicator is dim, click setting to set the brightness.
User Guides for Pico
Pico connection pins
| Board | Pico | Pin description |
|---|---|---|
| Pins used by RGB LED Matrix (HUB75 interface) | ||
| R1 | GP02 | R higher bit data |
| G1 | GP03 | G higher bit data |
| B1 | GP04 | B higher bit data |
| R2 | GP05 | R lower bit data |
| G2 | GP08 | G lower bit data |
| B2 | GP09 | B lower bit data |
| A | GP10 | A line selection |
| B | GP16 | B line selection |
| C | GP18 | C line selection |
| D | GP20 | D line selection |
| E | GP22 | E line selection |
| CLK | GP11 | clock input |
| STB/LAT | GP12 | latch pin |
| OE | GP13 | output enable |
| Board | Pico | Pin description |
|---|---|---|
| Pins used by other resources of the board | ||
| K0 | GP15 | KEY0 button, the MENU menu of the digital clock, can also be customized |
| K1 | GP19 | KEY1 button, + / Down button of digital clock, can also be customized |
| K2 | GP21 | KEY2 button,-/ UP button of digital clock, can also be customized |
| RUN | RUN | RESET button, can be used for Pico reset |
| BOOTSET | BOOTSET | BOOT button, can be used for Pico burning program (long press BOOT, then press RESET to enter the firmware download mode) |
| SDA | GP06 | I2C data pin, used to control DS3231 RTC clock chip |
| SCL | GP07 | I2C clock pin, used to control DS3231 RTC clock chip |
| BUZZ | GP27 | Buzzer control pin |
| AIN | GP26 | Photoresistor control pin |
| IRM | GP28 | Infrared receiving control pin |
See detailed hardware design of the circuit diagram.
| Carrier Board | Pico | Pin Description |
|---|---|---|
| Pins used by other resources on the baseboard | ||
| K0 | GP15 | KEY0, MENU for the digital clock, can be customized |
| K1 | GP19 | KEY1, + / Down button for digital clock, also customizable |
| K2 | GP21 | KEY2, + / Down button for digital clock, also customizable |
| RUN | RUN | RESET key, can be used to reset Pico |
| BOOTSET | BOOTSET | BOOT key, which can be used as Pico programming, (Long press BOOT, then press RESET to enter firmware download mode) |
| SDA | GP06 | I2C data pin, used to control the DS3231 RTC chip |
| SCL | GP07 | I2C clock pin, used to control the DS3231 RTC chip |
| BUZZ | GP27 | Buzzer control pin |
| AIN | GP26 | Photoresistor Control Pin |
| IRM | GP28 | IR receiver control pin |
Click here to see schematic diagram.
Hardware Connection
Materials needed
- Pico-RGB-Matrix-P3-64 x 32 (this product).
- Raspberry Pi Pico (must be purchased separately, if not, it is recommended to buy a version with soldered headers, which is convenient for direct insertion and use).
- Micro USB cable (must be purchased separately).
Hardware connection steps
- Align the pin header which is marked in red and then connect the RGB LED Matrix panel to the driver board.
- Cut the adapter cable (about 10cm) by plier
- Connect the cable which is cut in the last step to the RGB LED Matrix and the driver board
- Assemble the Acrylic backplane and fix it with magnetic screws
- Optional: If you feel that the RGB LED Matrix is too bright, you can stick the black Acrylic font panel on the Matrix.
Example display
Multi-Features Digital Clock
This example is developed based on the C++ SDK. In order to quickly demonstrate the effects and functions of the example, you can skip the steps of "#C++ SDK Development Tutorial" and "Program Debugging and Development" and directly "#Download and burn programs". After the burning is completed, the effect of the instance running is shown in the following figure:
【Function Description】
- Time display screen:
- Display date, day of the week, hour, minute, lunar calendar and temperature
- Function setting menu
- Date setting
- time setting
- BEEP setting (buzzer setting)
- Auto brightness
- Language setting (under development)
Fruit machine
This example is developed based on CircuitPython[1] , and the program is downloaded[2] . The effects and functions of the example are as follows:
【Function Description】
- The display can display a variety of fruits or other small BMP icons
- Automatically scroll icons at regular intervals, and randomly display the results of the scrolling
- ↑ CircuitPython is a fork of MicroPython, For specific usage, please refer to the RGB-Matrix related CircuitPython tutorial
- ↑ Pico must first install CircuitPython,and then copy the corresponding CircuitPythond code to the recognized U disk to complete the download.
Infrared transceiver test
This example is developed based on CircuitPython,and the example effects and functions are as follows:
【Function Description】
- The infrared serial code generated by the corresponding button of the infrared remote control can be recognized
C++ SDK Development Tutorial
Development environment setup
For a complete tutorial on how to get started with the C/C++ SDK, You can directly refer to the Offical manual of Raspberry Pi.
Raspberry Pi development environment setup
If you plan to develop for Pico on the Raspberry Pi, you can quickly set up the C/C++ toolchain by running our "setup script" from the command line.
Instructions: Before running the installation script, you should make sure that the operating system on your Raspberry Pi is up to date.
Windows development environment setup
For Windows development environment construction, please refer to:
Download and burn programs
C++ SDK program programming
The following is an example of programming a simple "blinking LED" program:
- Download blink.uf2 ("Blink LED" flash file)
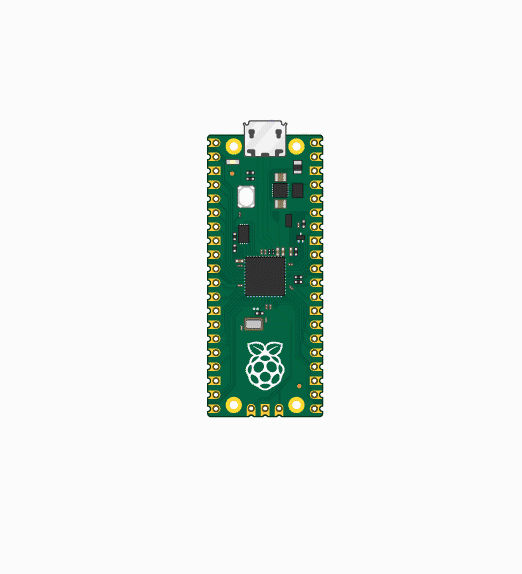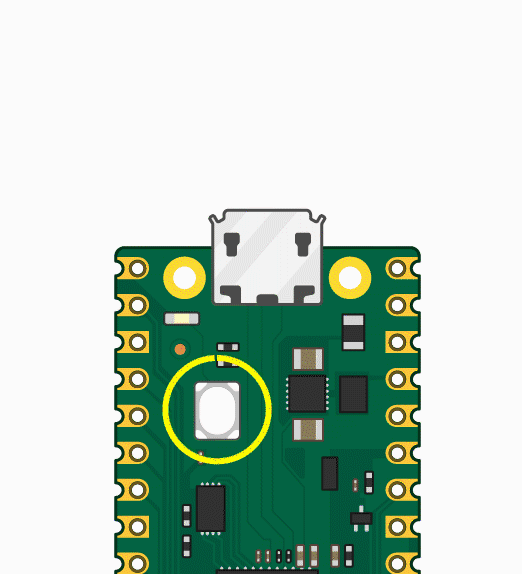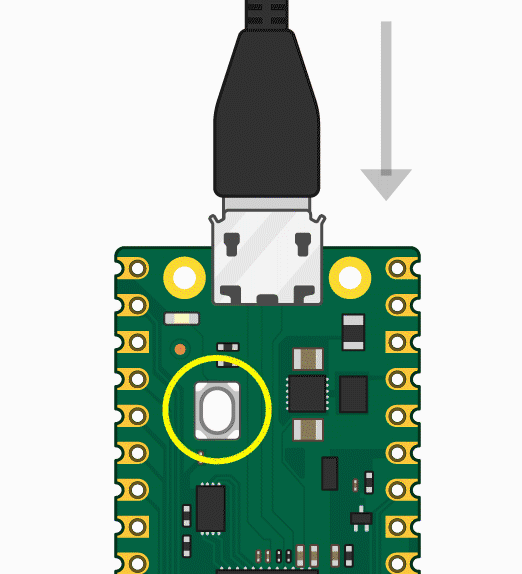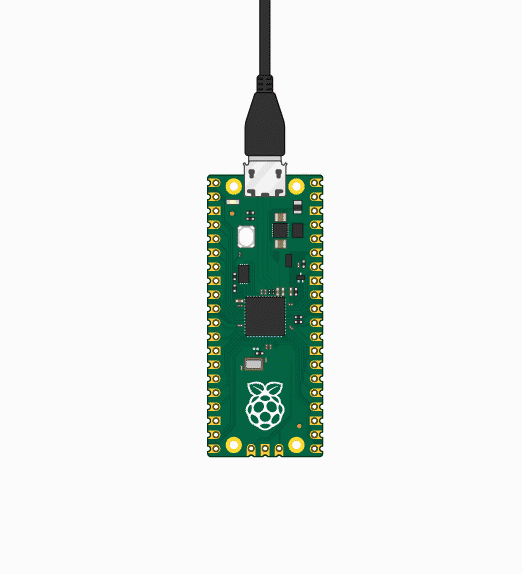
- Press and hold the BOOTSEL button, then plug the Pico into the USB port of your Raspberry Pi or other computer.
- It will be mounted as a mass storage device named "RPI-RP2". Drag and drop the blink.uf2 binary onto the "RPI-RP2" drive letter. The Pico will restart and the onboard LEDs should start blinking.
- Check out the Github source code for "Blink LED"
CircuitPython Development Tutorial
If you are not familiar with CircuitPython, you can first study the official recommended guide "Introduction to CircuitPython for Raspberry Pi Pico".
This guide covers the basics of getting started with CircuitPython and using the editor.
Development environment setup
In order to facilitate the programming, development and debugging of CircuitPython, it is recommended to use the "Mu Editor" development software. You can use Mu Editor for Pico's CircuitPython development on Windows.
The following describes the development and use of Mu Editor under Windows.
Windows development environment (Mu Editor) build and use
- Download Mu Editor and follow the steps to install
- After the installation is complete, it is the first time to configure the language and select the mode. Since we are using CircuitPython, pay attention to the mode selection CircuitPython option.
- After the configuration is complete, it will show that the device cannot be found, that is because Pico has not downloaded the CircuitPython firmware library.
- Download the CircuitPython firmware library and burn it into Pico
- Download the CircuitPython UF2 file.
- Press and hold the BOOTSEL button, then plug the Pico into the USB port of your Raspberry Pi or other computer. Release the BOOTSEL button after connecting the Pico.
- It will be mounted as a mass storage device named "RPI-RP2".
- Drag and drop the CircuitPython UF2 file onto the "RPI-RP2" volume. Your Pico will reboot, a new disk drive named CIRCUITPY will appear, and you're done.
- The new disk drive will have a default code.py file, you open it with Mu Editor, the content is: "print("Hello World!")", the specific opening steps are shown in the last figure.
- Open the serial port, click the blank area and press Ctrl+C, then press Ctrl+D or click the blank area of the code interface and press Ctrl+S to run the program. You can observe the running effect in the CircuitPython REPL window.
User Guides of ESP32-S2-Pico
Environment Setting Up
The demo is based on Arduino, please refer to Arduino Environment.
Examples
Note: A Pico baseplate is required for use here. Click to download the program, after the download is complete, go to Pico-RGB-Matrix-P3-64x32-Demo\ESP32-S2-Pico\Arduino,
- Copy RGBMatrix-master to the libraries in the Arduino installation directory;
- Go back to RGB-Matrix-P3-64x32-Demo\\ESP32-S2-Pico\Arduino, open the .ino file in EzTimeTetrisClockESP32S2 and follow the steps below to download
Display Effect
【Function】
- Time display interface:
- Display date, week, hour, minute, lunar calendar, and temperature
- Function setting menu
- Date setting
- Time setting
- BEEP setting (beep setting)
- Auto Brightness
- Language settings
Resources
Document
Development Softwares
- Zimo221.7z
- Image2Lcd.7z
- Font Library Tutorial
- Image Extraction Tutorial
- Thonny Python IDE (Windows V3.3.3)
Pico Getting Started
Firmware Download
- MicroPython Firmware Download
- C_Blink Firmware Download
Introduction
MicroPython Series
Install Thonny IDE
In order to facilitate the development of Pico/Pico2 boards using MicroPython on a computer, it is recommended to download the Thonny IDE
- Download Thonny IDE and follow the steps to install, the installation packages are all Windows versions, please refer to Thonny's official website for other versions
- After installation, the language and motherboard environment need to be configured for the first use. Since we are using Pico/Pico2, pay attention to selecting the Raspberry Pi option for the motherboard environment
- Configure MicroPython environment and choose Pico/Pico2 port
- Connect Pico/Pico2 to your computer first, and in the lower right corner of Thonny left-click on the configuration environment option --> select Configture interpreter
- In the pop-up window, select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico), and choose the corresponding port
Flash Firmware
- Click OK to return to the Thonny main interface, download the corresponding firmware library and burn it to the device, and then click the Stop button to display the current environment in the Shell window
- Note: Flashing the Pico2 firmware provided by Micropython may cause the device to be unrecognized, please use the firmware below or in the package
- How to download the firmware library for Pico/Pico2 in windows: After holding down the BOOT button and connecting to the computer, release the BOOT button, a removable disk will appear on the computer, copy the firmware library into it
- How to download the firmware library for RP2040/RP2350 in windows: After connecting to the computer, press the BOOT key and the RESET key at the same time, release the RESET key first and then release the BOOT key, a removable disk will appear on the computer, copy the firmware library into it (you can also use the Pico/Pico2 method)
MicroPython Series
【MicroPython】 machine.Pin class function details
【MicroPython】machine.PWM class function details
【MicroPython】machine.ADC class function details
【MicroPython】machine.UART class function details
【MicroPython】machine.I2C class function details
【MicroPython】machine.SPI class function details
【MicroPython】rp2.StateMachine class function details
C/C++ Series
For C/C++, it is recommended to use Pico VS Code for development. This is a Microsoft Visual Studio Code extension designed to make it easier for you to create, develop, and debug projects for the Raspberry Pi Pico series development boards. No matter if you are a beginner or an experienced professional, this tool can assist you in developing Pico with confidence and ease. Here's how to install and use the extension.
- Official website tutorial: https://www.raspberrypi.com/news/pico-vscode-extension/
- This tutorial is suitable for Raspberry Pi Pico, Pico2 and the RP2040 and RP2350 series development boards developed by Waveshare
- The development environment defaults to Windows11. For other environments, please refer to the official tutorial for installation
Install VSCode
-
First, click to download pico-vscode package, unzip and open the package, double-click to install VSCode
Note: If vscode is installed, check if the version is v1.87.0 or later
Install Extension
-
Click Extensions and select Install from VSIX
-
Select the package with the vsix suffix and click Install
-
Then vscode will automatically install raspberry-pi-pico and its dependency extensions, you can click Refresh to check the installation progress
-
The text in the right lower corner shows that the installation is complete. Close VSCode
Configure Extension
-
Open directory C:\Users\username and copy the entire .pico-sdk to that directory
-
The copy is completed
-
Open vscode and configure the paths for the Raspberry Pi Pico extensions
The configuration is as follows:Cmake Path: ${HOME}/.pico-sdk/cmake/v3.28.6/bin/cmake.exe Git Path: ${HOME}/.pico-sdk/git/cmd/git.exe Ninja Path: ${HOME}/.pico-sdk/ninja/v1.12.1/ninja.exe Python3 Path: ${HOME}/.pico-sdk/python/3.12.1/python.exe
New Project
-
The configuration is complete, create a new project, enter the project name, select the path, and click Create to create the project
To test the official example, you can click on the Example next to the project name to select
-
The project is created successfully
Compile Project
-
Select the SDK version
-
Select Yes for advanced configuration
-
Choose the cross-compilation chain, 13.2.Rel1 is applicable for ARM cores, RISCV.13.3 is applicable for RISCV cores. You can select either based on your requirements
-
Select Default for CMake version (the path configured earlier)
-
Select Default for Ninjaversion
-
Select the development board
-
Click Complie to compile
-
The uf2 format file is successfully compiled
Import Project
-
Select the project directory and import the project

- The Cmake file of the imported project cannot have Chinese (including comments), otherwise the import may fail
-
To import your own project, you need to add a line of code to the Cmake file to switch between pico and pico2 normally, otherwise even if pico2 is selected, the compiled firmware will still be suitable for pico
set(PICO_BOARD pico CACHE STRING "Board type")
Update Extension
-
The extension version in the offline package is 0.15.2, and you can also choose to update to the latest version after the installation is complete
Arduino IDE Series
Install Arduino IDE
-
First, go to Arduino official website to download the installation package of the Arduino IDE.

-
Here, you can select Just Download.

-
Once the download is complete, click Install.

Notice: During the installation process, it will prompt you to install the driver, just click Install
Arduino IDE Interface
-
After the first installation, when you open the Arduino IDE, it will be in English. You can switch to other languages in File --> Preferences, or continue using the English interface.

-
In the Language field, select the language you want to switch to, and click OK.

Install Arduino-Pico Core in the Arduino IDE
-
Open the Arduino IDE, click on the file in the top left corner, and select Preferences
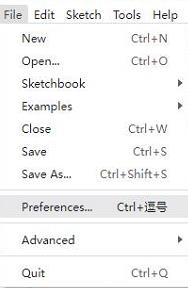
-
Add the following link to the attached board manager URL, and then click OK
https://github.com/earlephilhower/arduino-pico/releases/download/4.0.2/package_rp2040_index.json
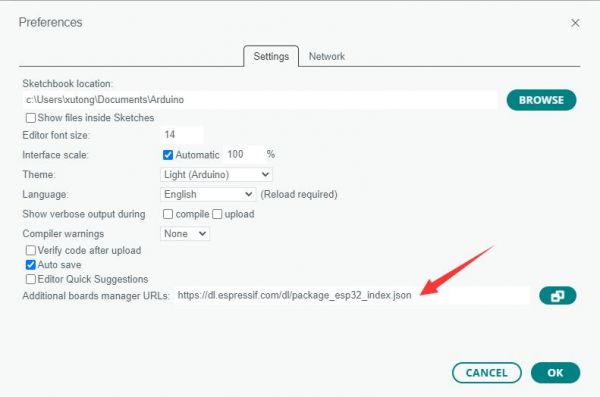
Note: If you already have an ESP32 board URL, you can use a comma to separate the URLs as follows:https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json,https://github.com/earlephilhower/arduino-pico/releases/download/4.0.2/package_rp2040_index.json
-
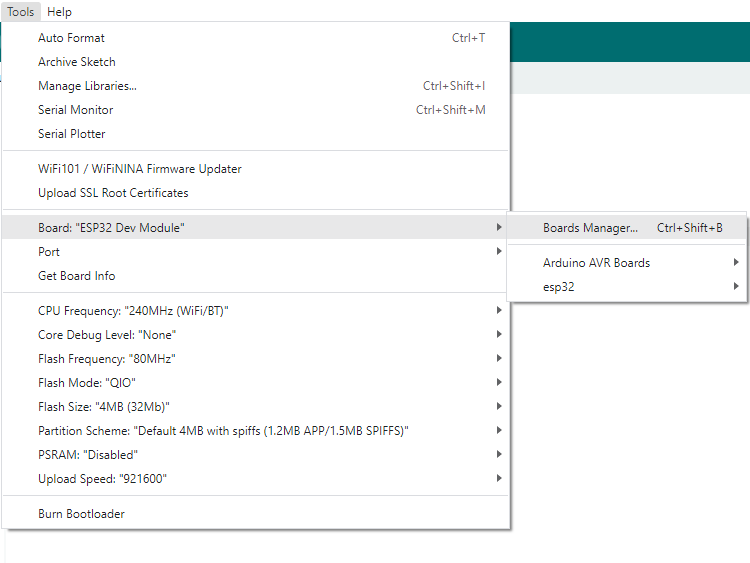
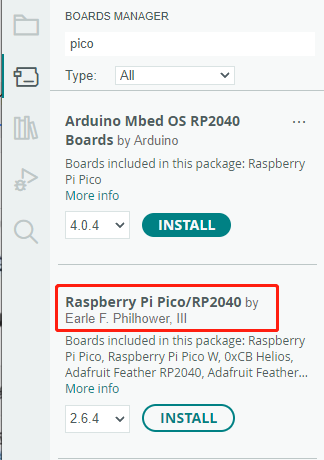
Click Tools > Development Board > Board Manager > Search pico, as my computer has already been installed, it shows that it is installed
Upload Demo at the First Time
-
Press and hold the BOOTSET button on the Pico board, connect the pico to the USB port of the computer via the Micro USB cable, and release the button after the computer recognizes a removable hard disk (RPI-RP2).
- Download the program and open D1-LED.ino under the arduino\PWM\D1-LED path
-
Click Tools --> Port, remember the existing COM, do not click this COM (the COM displayed is different on different computers, remember the COM on your own computer)
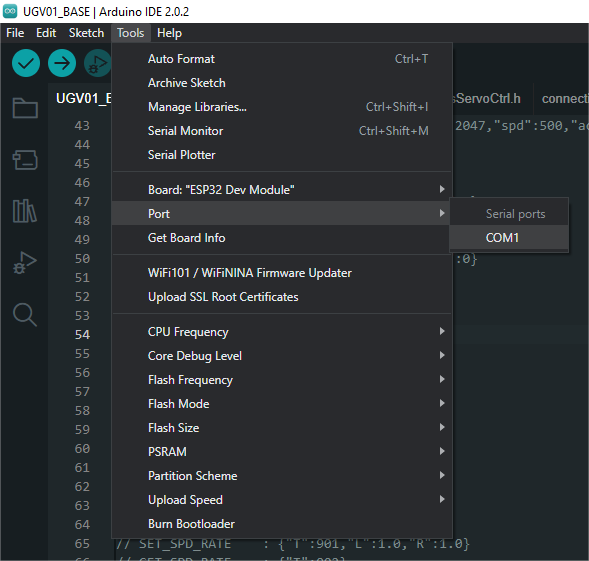
-
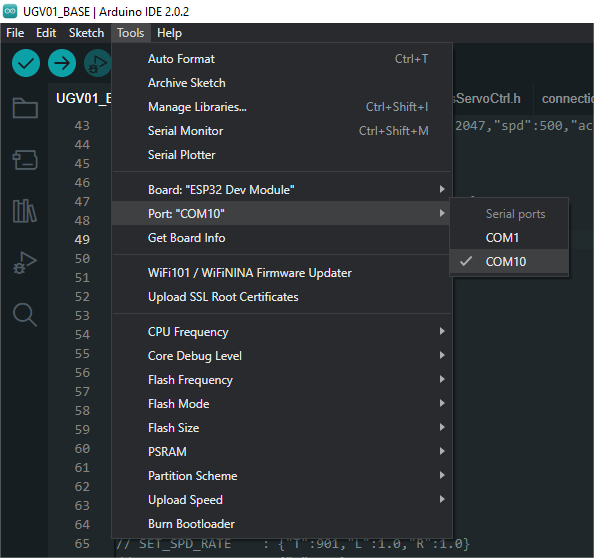
Connect the driver board to the computer using a USB cable. Then, go to Tools > Port. For the first connection, select uf2 Board. After uploading, when you connect again, an additional COM port will appear
-
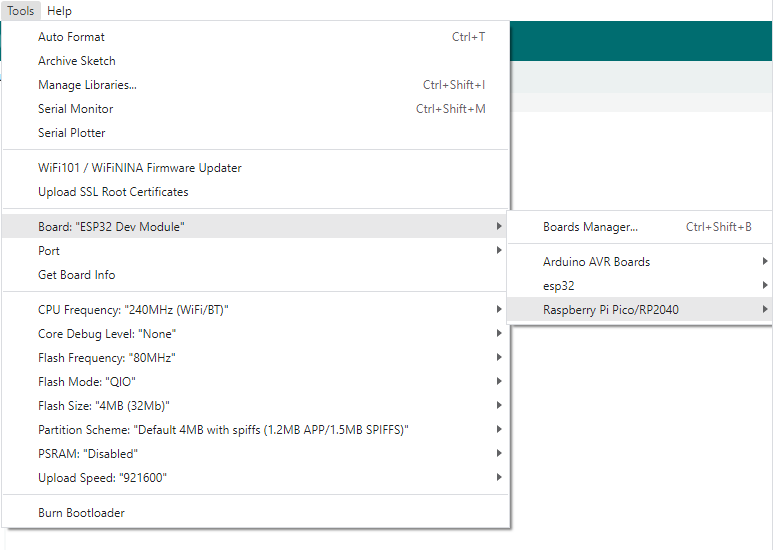
Click Tools > Development Board > Raspberry Pi Pico > Raspberry Pi Pico or Raspberry Pi Pico 2
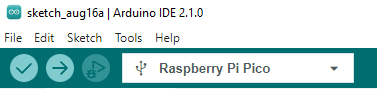
- After setting it up, click the right arrow to upload the program
- If issues arise during this period, and if you need to reinstall or update the Arduino IDE version, it is necessary to uninstall the Arduino IDE completely. After uninstalling the software, you need to manually delete all contents within the C:\Users\[name]\AppData\Local\Arduino15 folder (you need to show hidden files to see this folder). Then, proceed with a fresh installation.
Open Source Demos
MircoPython video demo (github)
MicroPython firmware/Blink demos (C)
Raspberry Pi official C/C++ demo (github)
Raspberry Pi official micropython demo (github)
Arduino official C/C++ demo (github)
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)



























