Pi4B
| ||
Introduction
Raspberry Pi 4 Model B, the completely upgraded, re-engineered model of the Pi family. It has more powerful processor, faster networking, supports dual 4K output, and provides different choice of RAM.
Features
- BCM2711B0 (ARM Cortex-A72)
- 64-bit 1.5GHz quad-core
- Choice of RAM
- PI4B-1GB: 1GB
- PI4B-2GB: 2GB
- PI4B-4GB: 4GB
- Gigabit Ethernet
- 802.11ac 2.4GHz/5GHz dual-band NIC
- Bluetooth 5.0, BLE
- USB 3.0 x 2, USB 2.0 x 2
- micro HDMI x 2 (supports 4Kp60)
- PoE header (supports PoE HAT)
- MicroSD slot
- 3.5 mm audio jack
- 40PIN GPIO header
- CSI camera interface
- DSI display interface
- USB Type C power supply (5V/3A or above)
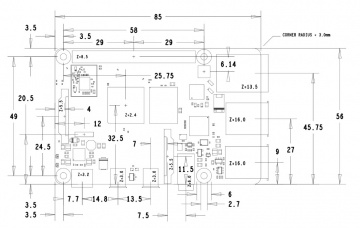
Product Size
How to use
1. Prepare: SD card, card reader.
2. Download the system (click me to download) Raspberry Pi 4 needs to download the latest released system (or the following version as shown in the figure) before it can be used.

3. Format the SD card: Use a card reader to insert the SD card into the computer, and use the SDFormatter.exe software to format the SD card. Click here to download SDFormatter.exe, click to format SD card.
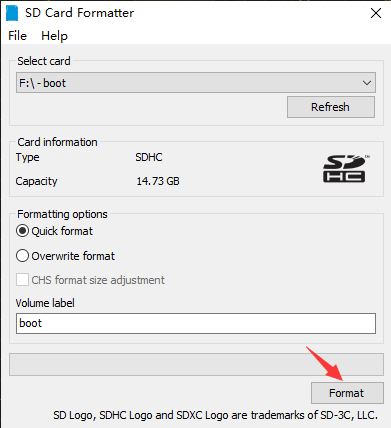
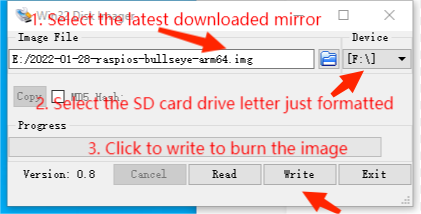
4. Burn the image: use Win32DiskImager.exe to burn the image. Select the image to be burned, click "Write" to burn, (click here to download Win32DiskImager.exe). After the burning is completed, you will be prompted whether you want to format, here you need to click Cancel
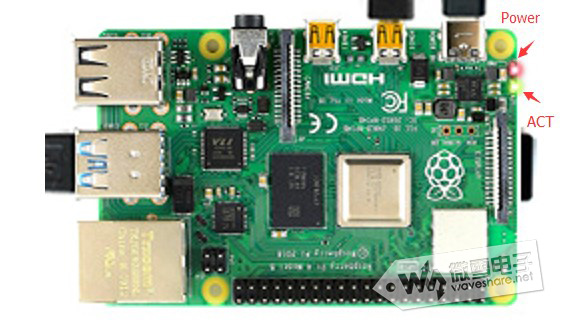
5. Start RPI4B: Insert the SD card after programming into the Raspberry Pi, and connect the adapter with the Type-C interface of 5V 3A to start the Raspberry Pi. Normally, you can see that the Power light is always on red, and the ACT green light is flashing.
6. Connect peripherals such as on-screen mouse and keyboard to start your Raspberry Pi journey.

Resource
- Raspberry Pi Hardware Resouces (official)
- Help Center
- Panasonic_SDFormatter
- Win32DiskImager
- putty
- wiringPi & bcm2835 C LIB
- Image
General Tutorial Series
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: Access your Pi
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: Getting Started with lighting up an LED
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: External Button
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: I2C
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: I2C Programming
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: 1-Wire DS18B20 Sensor
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: Infrared Remote Control
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: RTC
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: PCF8591 AD/DA
- Raspberry Pi Tutorial Series: SPI
FAQ
1. Enter xrandr on the Raspberry Pi terminal to check the HDMI-ID where the main screen is located (mostly HDMI-1);
2. Enter xinput in the Raspberry Pi terminal to check the touch ID where the main screen is located (there are 2 touch IDs, if you don't know which one is the main screen, you can try both);
3. Run the command: xinput map-to-output <touch ID> <HDMI-ID>
(After matching the ID value, run the command to specify the touch to the main screen, such as: xinput map-to-output 7 HDMI-1 )
4. Since the command needs to be re-entered every time the boot is turned on, this command can be added to the boot auto-start:
sudo nano /etc/xdg/lxsession/LXDE-pi/autostart
Add: xinput map-to-output 7 HDMI-1 (remember to change to your own corresponding ID), then restart.
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
|