Core2530
| ||
Introduction
ZigBee module, features the CC2530F256 onboard
| More |
Zigbee network experiment
Zigbee network needs minimum a coordinator and a router. Since the Core2530/XCore2530 module has a built-in Bootloader in default setting, you can download the firmware to the module directly via the serial port.
Notes: In the Zigbee network experiment, you may need to apply two pieces of Core2530/XCore2530 modules, and two pieces of ZB502/ZB600 baseboards.
Roles in Zigbee network
1. Coordinator
- Select a communication channel and a PAN ID to build a network;
- Allow other routers and end devices to join this network;
- Route the data in the network;
- Must be kept power supplying, and must not enter the SLEEP mode;
- Preserve data for the end devices entered SLEEP mode till them wake up and retrieve the data.
2. Router
- Must join a Zigbee network before performing data transmission;
- Allow other routers and end devices to join the network, after it joined one;
- Route the data in the network upon joining the network;
- Must be kept power supplying, and must not enter the SLEEP mode;
- Preserve data for the end devices entered the SLEEP mode till them wake up and retrieve the data.
3. End Device
- Must join a Zigbee network before performing data transmission;
- Not allow other devices to join the network;
- Transmit and receive data thought parent node, unable to route the data in the network;
- Support battery power supply and SLEEP mode.
Bootloader
1. Introduction
The built-in Bootloader enable users to download the program to the module directly via a serial port without using the CC Debugger. However, the CC Debugger is required in the course of programming the Bootloader into the module. For more detailed information, please refer to the Section How to program Bootloader.
There are two different Bootloaders available for this module: bootloader.hex and bootloader_wait.hex.
For easier understanding, we call the module with the bootloader.hex as module A, and the module with the bootloader_wait.hex as module B in this document.
The module A will execute the valid program immediately, if any, in the Flash memory, after powered up. Otherwise, its LED1 will keep blinking indicating that there is no program in the Flash memory and you can download a new one via the serial port in this case.
For module B, its LED1 and LED2 will blink alternately, if there is any valid program stored in the Flash memory, after powered up. Now, if you press the button KEY2, the module B will execute the program immediately; and if you press the button KEY1, the module B will enter the Bootloader mode under which you can download a new program to the module B. In case of no key-press action within 40 seconds after powered up, the module B will execute the program in the Flash memory automatically. When there is no valid program in the Flash memory, its LED1 will keep blinking, and you can download a new one via the serial port in this case.
The module A with bootloader.hex is suitable for independent application, since it can run the program directly without any external key-press trigger. However, the module B with the bootloader_wait.hex should work with the baseboard ZB502/ZB600 for relative experiments and studies. By default, the bootloader_wait.hex is programmed to the module.
2. CC debugger driver installation
- Unzip the package CC-Debugger_Drivers.7z to the installation directory;
- Double click the software Setup_SmartRF_Drivers-1.2.0.exe for installation;
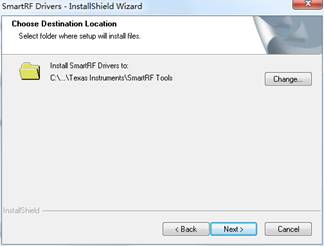
- Click the button Next, and select the installation path;
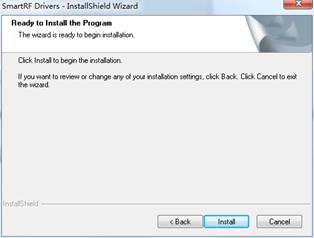
- Click the button Install, and wait till the installation finished.
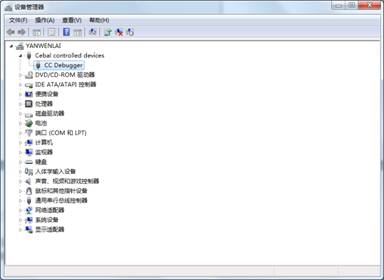
- When finished, connect the CC Debugger to your PC, and open the option Device Manager in Windows. You may find the option CC Debugger if its driver is installed successfully.
3. How to program Bootloader
- Install the module to the baseboard, and connect the baseboard and the CC Debugger to your PC with the USB cables;
- Power up the baseboard, and press the RESET key on the CC Debugger. If the communication is built up successfully, the indicator on the CC Debugger will light up and turn to green, indicating that it is ready to download new programs;
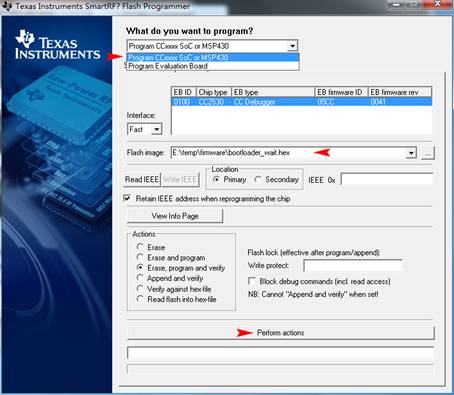
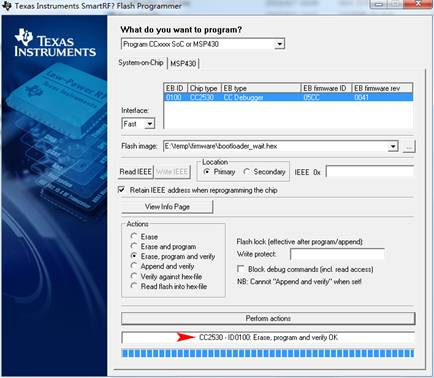
- Open the SmartRF Studio7, and select the button Flash Programmer on the upper right of the software interface to open another window.
- Select the option Program CCxxxx Soc or MSP430 in the pulled-down menu What do you want to program?, and choose the image file you want to program within the Flash image box. Here, it is bootloader_wait.hex. And then, click the button Perform actions to start programming.
- When finished, there will be a message "Erase, program and verify OK" appears on the bottom of the window, and the LED1 of the baseboard will keep blinking indicating that program downloading is successful.
Firmware downloading
In this section, we will illustrate how to build a Zigbee network by applying two groups of Core2530 + ZB600, one works as a coordinator and the other one works as a router. For easier understanding, we call the coordinator as Group A and the router as Group B.
- Connect the Group A and the Group B to your PC with the USB cables, respectively. And get their corresponding serial port numbers after powered up.
- If the firmware has been installed to the Group A or/and the Group B, the LED1 and the LED2 on the Core2530 module(s) will blink alternately after resetting. Pressing the button KEY1 as soon as possible to enter the Bootloader mode,when the board is powered on.Then you will see the LED1 keep blinking. When there is no firmware in the Core2530 module(s), the LED1 will keep blinking after powered up, which means the Core2530 module(s) has entered the Bootloader mode directly and there is no need to press the button KEY1 again.
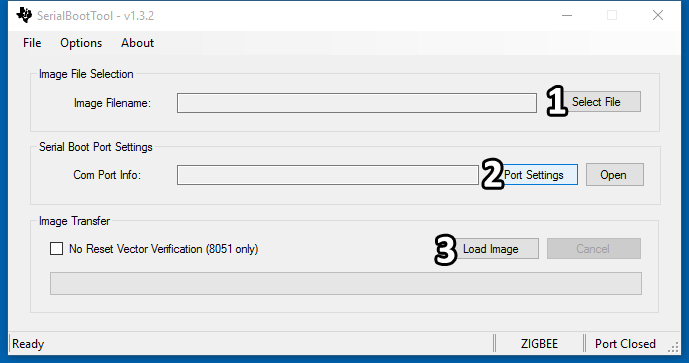
- Start the software Serial Boot Tool for firmware downloading.
- Select the firmware file Coordinator.bin of the Group A in the Select File box and select the corresponding serial port in the Port Settings box,set the Baud rate:115200, Then, click the button Load Image to start downloading.
- For the Group B, select the firmware file Router.bin. The file download method is the same as that of the Group A.
- Start two serial debug assistants, and enter the serial port number of the Group A to one of the assistants and the port number of the Group B to the other one. Then, set the Baud rate: 38400, Data bit: 8 and Stop bit: 1;
- Reset the Group A, you can see the LED1 and the LED2 on its Core2530 module blink alternately. Pressing the middle button of the joystick, you will see the message "Device starting ok" displayed in the window and the LED3 lights up, if the network is built up successfully.
- Reset the Group B, you can see the LED1 and the LED2 on its Core2530 module blink alternately. Pressing the middle button of the joystick, you will see the message ""Device starting ok" displayed in the window and the LED3 lights up, if the Group B, severing as a router, has joined the network successfully. Now, the Zigbee network is running. (If no external antenna is applied to the Group B, it is recommended to place the antenna interface of the Group B close to the antenna interface of the Group A, in order to ensure the wireless network signal is strong enough.)
Notes:
1. The middle button of the joystick on the ZB600 is corresponding to the button KEY2 on the ZB502.
2. The power amplifier (PA) of Xcore2530 has occupied the Pins P1_1 and P1_4. Hence, the LED2 will not blinking after the Xcore2530 module reset, and the LED3 will keep OFF even if the network is built up successfully.
Networking communicaiton
The operations presented below can be done directly by UART serial communication, baud: 38400.
Broadcast communication mode
Description: Under this mode, a device can broadcast messages to all the other devices in the Zigbee network. Load the Coordinator.bin image and the Router.bin image separately. Power up, first press the KEY2 (ZB502) or joystick CENTER (ZB600) on the coordinator then press the KEY2 (ZB502) or joystick CENTER (ZB600) on the router, by which let the router join the coordinator.
Format: Data to be sent
| EXAMPLE:
To broadcast the message "Hello Waveshare" throughout the network from a device, the relative operations are as follow: Enter the message to be broadcasted into the character string input box, and click the button Send:
All the other devices, including routers and coordinators, will receive this message in their character string receiving boxes.
|
Point to Point communication
Description: It is the communication between any two nodes in the same network.
Format: P2P Target address Data to be sent
Note: Point-to-point transmission mode, up to 40bytes of data can be transmitted at a time
| EXAMPLE:
To send the message "Hello World " from the module A to the module B, the relative operations are as follow: Read the short addresses of the module A and the module B by the command AT+GETADDR Enter the command AT+GETADDR into the character string input box:
Then, you may get the addresses of the module A and the module B:
On the module A, apply P2P command to send the message to the module B:
Except the module B, other nodes and routers in the network will not receive the message:
|
- 【Example】
Point to Multipoint communication
Description: A node sends data to the specified nodes in the same network.
Format: O2M Quantity of target address Target address 1 Target address 2 … Data to be sent
| EXAMPLE:
To send the message "Hello World" from the module A to the module B and the module C, the relative operations are as follow: Read the short addresses of the module A, the module B and the module C by the command AT+READ_ADDR Enter the command AT+GETADDR into the character string input box:
Then, you may get the addresses of the module A, the module B and the module C:
On the module A, apply O2M command to send the message to the module B and the module C:
Except the module B and the module C, other nodes and routers in the network will not receive the message:
|
Working with PC
Introduction
ZBSCOMM is the PC software for Core2530/XCore2530 developed by Waveshare. With ZBSCOMM, you can easily configure the module settings and read the current configurations of the module via your PC. Of course, you can control the module by AT command as well, if you do not want to use the PC for configuration.
AT commands
Table 1: Restart the module
| Command | AT+RESTART |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return value | RESTART OK |
| Remarks | When the message "RESTART OK" is returned, the module will restart |
Table 2: Restore the factory settings
| Command | AT+RESET |
| Return value | SETUART OK SETCHN OK SETPANID OK |
| Remarks | The settings listed below will be effective after the module restarts.
Factory settings: PANID : 0xFFFF (random) CHANNEL: 11/2405MHz UART: 0 (select COM port 0) Baud rate: 38400 Flow control: 0 (None) |
Table 3: Serial port information configuration
| Command | AT+SETUART Serial port number Baud rate Flow control (The command parameters are separated by spaces) |
| Function | Set the serial port number, Baud rate and flow control |
| Inputted parameters | Serial port number: it should be set to "0" to select COM Port 0 for configuration
Baud rate: 9600-115200 Flow control: it should be set to "0" to turn off flow control |
| Return value | Success: SETUART OK
Failure: SETUART ERR |
| Remarks | Factory settings: UART: 0 (select COM Port 0)
Baud rate: 38400 Flow control: 0 (None) |
| EXAMPLE:
To set the serial Baud rate, you only need to enter "AT+SETUART 0 38400 0" into the character string input box, and click the button Send. The new settings will be effective after the module restarts. The relative operations are as follow: Enter "AT+SETUART 0 38400 0" into the character string input box:
Then, you may receive "SETUART OK" in the character string receiving box:
|
Table 4: Channel setting
| Command | AT+SETCHN Channel |
| Function | Set the communication channel of the Zigbee network |
| Inputted parameters | Channel: range from 11 to 26 |
| Return value | Success: SETCHN OK
Failure: SETCHN ERR |
| Remarks | In a network, all the modules should be set to a same channel for networking. By default, the communication channel is allocated by the system automatically.
Factory setting: 11/2405MHz |
Table 5: Set the PAN ID
| Command | AT+SETPANID PAN ID |
| Function | Zigbee protocol use a 16-bit PANID to identify the network |
| Inputted parameters | PANID: range from 0x0000 to 0x3FFE |
| Return value | Success: SETPANID OK
Failure: SETPANID ERR |
| Remarks | If PANID=0xFFFF: the device will build up or join an optimum network.
If PANID≠0xFFFF: the device will build up or join a network with a given PANID. Normally, PANID comes up after determining the communication channel |
Table 6: Read all the configuration information
| Command | AT+GETCFG |
| Function | Read all the configuration information |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return value | UART: serial parameters (Baud rate, Flow control)
PANID: Local area network identifier ADDR: the short address of the device FADDR: the short address of the parent device CHANNEL: the communication channel of the module |
Table 7: Read the serial configuration information
| Command | AT+GETUART |
| Function | Read the serial configuration information |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return value | Serial port number: 0/1 (serial port 0/serial port 1)
Serial Baud rate: 9600-115200 Flow control: 0/1(None/flow control) |
Table 8: Read the current communication channel information
| Command | AT+GETCHN |
| Function | Read the current communication channel information of the module |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return value | CHANNEL: channel value |
Table 9: Read the current PAN ID of the module
| Command | AT+GETPANID |
| Function | Read the current PAN ID of the module |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return value | Success: PANID=0xxxx;
Failure: PANID=0xFFFE |
Table 10: Read the short address of the device
| Command | AT+GETADDR |
| Function | Read the short address of the device |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return | ADDR=0xXXXX; |
| Remarks | Short address length: 16 bits
This command is used in P2P or O2M communication |
Table 11: Read the short address of the parent node
| Command | AT+GETFADDR |
| Function | Read the short address of the parent node |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return value | FADDR=0xXXXX; |
| Remarks | Short address length: 16 bits |
Table 12: Read the IEEE address of the device
| Command | AT+GETIEEE |
| Function | Read the IEEE address of the device |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return | IEEE=xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx |
| Remarks | The IEEE of the device is a 64-bit address |
Table 13: Read the IEEE address of the parent node
| Command | AT+GETFIEEE |
| Function | Read the IEEE address of the parent node |
| Inputted parameters | None |
| Return value | MY_FIEEE=xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx |
| Remarks | The IEEE of the parent node is a 64-bit address |
Demonstrations for ZB500/ZB600
Notices
The following programs are used for the boards ZB500/ZB600. And the CC Debugger is a Must to download these programs, software:IAR.
LED_KEY
Program description
- When a key press event occurs, the corresponding value of the pressed key will be transmitted to the UART and displayed on the screen.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumpers of KEY JMP and UART0 with jumper caps
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- Press the key(s) on the board, the corresponding value(s) of the pressed key(s) is displayed on the screen.
Serial output:
HELLO Waveshare PRESS KEY1 PRESS KEY2 ...
Timer(T1)
Program description
- The Timer 1 is used for timing control the LED1 on and off.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumpers of LED1 JMP and UART0 with jumper caps
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The LED1 lights up and then lights off, continually and regularly.
Timer(T3)
Program description
- The Timer 3 is used for timing control the LED1 on and off.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumpers of LED1 JMP and UART0 with jumper caps
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The LED1 lights up and then lights off, continually and regularly.
DS18B20
Program description
- The interface 1-Wire is used for temperature detection with a sensor DS18B20+.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the DS18B20+ to the interface 1-WIRE (Notices: please make sure the DS18B20+ is installed correctly, or else it will be burned out when using)
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The temperature value detected by the DS18B20+ is displayed on the screen.
External interrupt
Program description
- The action of the LED1 is controlled by the external interrupt triggered from the key press event.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumpers of LED1 JMP and KEY1 JMP with jumper caps
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- Press the KEY1 and then the LED1 status changes.
UART0
Program description
- The UART0 is used for self-transmitting and self-receiving function.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumper of UART0 JMP
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The screen displays the test data of self-transmitting and self-receiving function.
Serial output:
HELLO waveshare HELLO waveshare HELLO waveshare ...
UART0 -printf
Program description
- The UART0 is used for external data communication.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumper UART0 JMP with jumper caps
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- Sends a character to the MCU via the serial assistant. And then MCU displays it out on the screen.
Serial output:
HELLO Waveshare StringsInput ...
SPI1_AT45DB
Program description
- Through the interface SPI, write data into the external chip AT45DBXX and then read the data out. The corresponding Read/Write statuses to the chip are displayed on the screen.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumper of UART0 JMP
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The operations to the AT45DBXX are displayed on the screen by serial assistant.
Serial output:
FLASH AT45DBXX Write Test OK FLASH AT45DBXX Read Test OK
ADC
Program description
- This program continually detects the analog value from the ADC7, and displays the detected data on the screen via UART0.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumper of UART0 JMP
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The analog values from the ADC7 are displayed on the screen by serial assistant.
Serial output:
AD_VALUE = 233 AD_VALUE = 234 AD_VALUE = 236 ...
AD_Thermometer
Program description
- This program is used to collect the temperature values from the sensor and print them out on the screen via UART0.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumper of UART0 JMP
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The temperature values from the sensor are displayed on the screen by serial assistant.
Serial output:
TempValue: 29.95 TempValue: 29.89 TempValue: 29.64 ...
Demonstrations for ZB600
Notices
The board ZB600 should be used in the following test
JOYSTICK
Program description
- Moving the JOYSTICK can trigger a key press event. The corresponding key press value will be printed out on the screen via UART0.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumper of UART0 JMP and KEY JMP
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- Moving the JOYSTICK, the corresponding key press value is printed out on the screen via the serial port.
Serial output:
HELLO Waveshare PRESS KEY_LEFT PRESS KEY_DOWN PRESS KEY_RIGHT PRESS KEY_UP PRESS KEY_CENTER
DHT11
Program description
- The pin P0_0 can serve as the ADC to get the temperature and humidity values from the sensor DHT11. And the related data will be printed out on the screen via the UART0.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect the jumper of UART0 JMP
- Connect to a DHT11 Temperature-Humidity Sensor
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The corresponding temperature value is printed out on the screen via the serial port.
Serial output:
HELLO Waveshare Temp = 38 Humidity = 26 ...
LCD_Touchpanel
Program description
- The 2.2inch LCD is driven via an IO interface. Both screen display and screen touch are supported.
Experiment operations
Steps
- Connect to a Touch LCD 2.2inch 320x240 Touch LCD (A)
- Power up and download the Demos
Result
- The 2.2inch LCD displays the screen. Screen touch and line drawing are enable.
Resources
Software
- Serial Bootloader Demo
- Serial Boot Tool
- Setup SmartRF Studio
- Flash programmer
- Setup ZigBee Sensor Monitor
- ZBSCOMM
- IAR
- CC Debugger Driver
- Serial Port Utility
Mother Board
FAQ
On 64-bit systems, you need to copy MSCOMM32.OCX to C:\Windows\SysWOW64 and then run the registration script.
Note: If you still get the same error as above, you also need to copy MSCOMM32.OCX to C:\Windows\System32 and run the registration script.
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)