CM4-DUAL-ETH-WIFI6-BASE
| ||
| ||
Overview
Introduction
CM4-DUAL-ETH-WIFI6-BASE, the IO board of the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4, is a carrier board that can be used with the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 and supports 7~12V DC power supply, and the board has three USB ports 2.0, WIFI6, dual Ethernet ports, suitable for soft routing and other scenarios that require multiple Ethernet ports.
Note
1. Do not unplug any device except USB and HDMI when the power is on.
2. Check the fan voltage before connecting. It supports 5V and 12V. The default connection is 12V. Before switching, please modify the resistance of FAN_VCC.
3. The Type C interface is only used as a USB SLAVE interface to burn images, and cannot be used as a power supply.
4. When CM4 is in normal use, it needs to provide at least a 12V 1.5A power supply. Otherwise, problems such as automatic shutdown and frequency reduction may occur.
5. See instructions for use about Opwenwrt.
6. This expansion board does not support the POE function.
Dimensions
CM4-DUAL-ETH-WIFI6-BASE

Compute_Module 4

Onboard Resources
| Label | Name | Description | |
| 1 | CM4 connector | for all versions of Compute Module 4 | |
| 2 | 40PIN GPIO header | easy to connect various HAT modules | |
| 3 | RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet port | RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet port, support 10/100/1000M network access ETHERNET 0: CM4 original network port ETHERNET 1: USB expansion network port | |
| 4 | RJ45 100M Ethernet port | RJ45 100M Ethernet port, support 10/100 network access ETHERNET 0: CM4 original network port ETHERNET 1: USB expansion network port | |
| 5 | USB 2.0 ports | 3-way USB 2.0 ports, supporting various USB devices | |
| 6 | M.2 connector | M.2 E KEY slot, support 2230 and 2240 | |
| 7 | HDMI port | Dual HDMI port, support dual 4K 30fps output | |
| 8 | RTC battery connector | can be connected to CR1220 button battery | |
| 9 | CAM port | Dual MIPI CSI camera port | |
| 10 | DC power header | 7~36V DC wide voltage power supply | |
| 11 | Double LEDs holder | Red light: Raspberry Pi power indicator Green light: Raspberry Pi working status indicator | |
| 12 | Micro SD card slot | It is used to insert the Micro SD card with the system to start Compute Module 4 Lite | |
| 13 | FAN header | Easy access to the cooling fan, support speed adjustment and measurement | |
| 14 | DISP1 port | MIPI DSI display port, DISP1 port | |
| 15 | USB SLAVE port | Compute Module 4 eMMC version can program the system image by this port | |
| 16 | 100M Ethernet port chip | RTL8152 100M network port chip |
| Label | Name | Description | |
| 17 | USB HUB | USB 2.0 HUB chip | |
| 18 | System function switching | BT_DIS: Disable Bluetooth, only for CM4 version with antenna WiFi_DIS: Disable WiFi, only for CM4 version with antenna WP_DIS: Prevent EEPROM from being rewritten | |
| 19 | IO-VREF selection | CM4 IO logic voltage switching 3.3V or 1.8V | |
| 20 | FAN Power Supply Selection | Optional 5V or 12V voltage to drive the fan | |
| 21 | RTC interrupt pin switch | PI-RUN: RTC trigger interrupt CM4 restart GN-EN: RTC trigger interrupt CM4 power off D4: RTC trigger interrupt D4 pin | |
| 22 | RTC/FAN I2C bus selection | SDA0/SCL0: shared by I2C-10 and CSI/DSI GPIO3/2: shared by I2C-1 and 40PIN |
User Guide
Note
Do not plug or unplug any device while it is powered on.
Image Programming
- Write Image for Compute Module Boards eMMC version
- Write Image for Compute Module Boards Lite version
RTC FAN
Fan
As shown in the figure, switch the FAN voltage according to the position of the resistor, and the default is 12V.

The fan PWM pin is controlled by GPIO18.
RTC
RTC chip: PCF85063A
Default I2C: I2C1
I2C address: 0x51
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
#Add at the end
dtparam=i2c_arm=on
dtoverlay=i2c-rtc,pcf85063a
#Add # in front of dtparam=audio=on
#dtparam=audio=on
#Save and exit, restart
sudo reboot
Hwclock
Synchronize system clock -> hardware clock.
sudo hwclock -w
Synchronize hardware clock -> system clock.
sudo hwclock -s
#Need to close the network, or close the network time, otherwise it will be changed back.
Set the hardware clock time:
sudo hwclock --set --date="9/8/2021 16:45:05"
View hardware clock.
sudo hwclock -r
Show version information.
sudo hwclock --verbose
CSI DSI
Configuration file
CSI and DSI are disabled by default. When using the camera and DSI, it will occupy three I2C devices: I2C-10, I2C-11, and I2C-0.
- Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo apt-get install p7zip-full -y wget https://files.waveshare.com/upload/7/75/CM4_dt_blob.7z 7z x CM4_dt_blob.7z -O./CM4_dt_blob sudo chmod 777 -R CM4_dt_blob cd CM4_dt_blob/ # If using two cameras and DSI1, please execute: sudo dtc -I dts -O dtb -o /boot/dt-blob.bin dt-blob-disp1-double_cam.dts # When using any DSI, there is no image output on HDMI1. Even if you do not connect a DSI screen, as long as the corresponding file is compiled, there will be no output on HDMI1. # To restore it, simply delete the corresponding dt-blob.bin file: sudo rm -rf /boot/dt-blob.bin #Execution is complete, power off and reboot CM4
New Version (Bullseye)
Camera Config
-
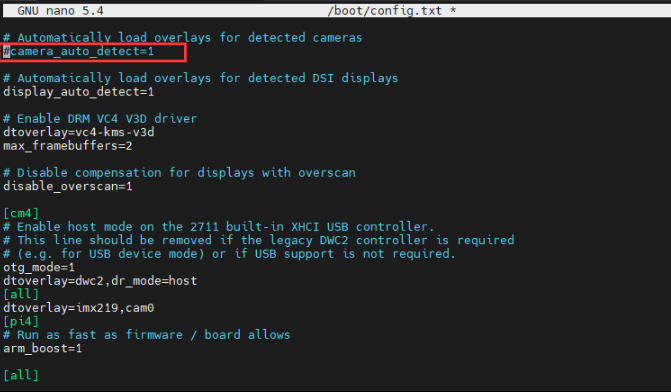
Execute the following commands to edit "/boot/config.txt" file.
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
- Block or remove the automatic camera detection statement:
-
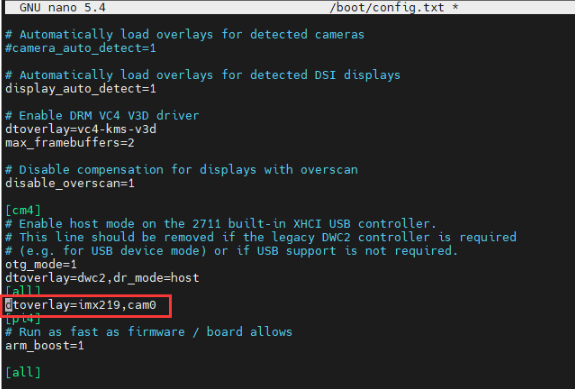
Add the driver of the camera you are using, here I take IMX219 as an example and connect it to CAM0, and attach the adapter.
Model CAM0 Set Sentence CAM1 Set Sentence OV9281 dtoverlay=ov9281,cam0 dtoverlay=ov9281,cam1 IMX290/IMX327 dtoverlay=imx290,clock-frequency=37125000,cam0 dtoverlay=imx290,clock-frequency=37125000,cam1 IMX378 dtoverlay=imx378,cam0 dtoverlay=imx378,cam1 IMX219 dtoverlay=imx219,cam0 dtoverlay=imx219,cam1 IMX477 dtoverlay=imx477,cam0 dtoverlay=imx477,cam1 IMX708 dtoverlay=imx708,cam0 dtoverlay=imx708,cam1 - If you are using the official Raspberry Pi camera and only one camera is connected, there is no need to set the config file. If it is not an official camera, set the "dtoverlay" statement without the "cam" suffix.
- CM4-NANO - only CAM0 is used, so you only need to add "dtoverlay=imx219,cam0".
5. Ctrl+x to exit the editor.
6. Reboot the Raspberry Pi.
sudo reboot
Camera Test
- Enter the camera detection command, you can see that the camera is detected by now.
libcamera-hello --list-cameras
- Display the camera screen on the desktop.
- Taking photos.
libcamera-jpeg -o test.jpg
- Record a video of 10s.
libcamera-vid -t 10000 -o test.h264
Other Commands:
libcamera-hello -t
Check whether the camera is detected:
libcamera-hello --list-cameras
Open the corresponding cameras:
libcamera-hello --camera 1 libcamera-hello --camera 0
Take a photo:
libcamera-jpeg -o test.jpg #Add --camera to specify a camera
Old Version (Buster)
Camera Config
-
1. Execute the following command to enter the Raspberry Pi configuration.
- Test the recording function:
- Where -t 10000 means recording for 10 seconds, users can adjust according to their own needs.
- Please refer to CSI.
sudo raspi-config
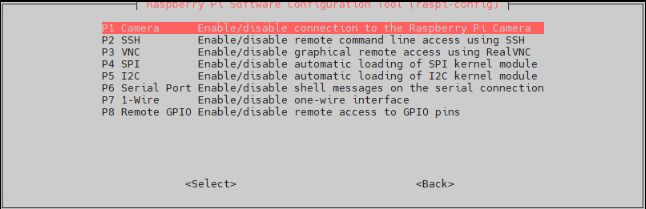
2. Choose Interfacing Options and enter.

3. Choose Camera:
4. Choose to enable the camera interface.

5. The system prompts as follows:

6. Back to the main interface, select Finish.
7. Reboot the system.

Camera Test
raspistill -o image.jpg
raspivid -o video.h264 -t 10000
Openwrt
Openwrt has high customization and scalable performance. Openwrt is becoming more and more popular at present. Compared with commonly used wireless routers, OpenWrt's modifiable firmware allows us to customize router functions according to our own needs, such as single-arm routing, automatic Define routing policies, QoS, intranet penetration, etc.
Note: Openwrt system will not provide any technical support if there is any problem during use. Only the following tutorials and images are provided, and no additional technical support other than hardware is provided.
Image
If the board used does not have USB3.0, only USB 2.0, and the USB2.0 cannot work, try adding "otg_mode=1" at the end of config.txt.
Compiled without configuration
Link: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1KccdLCYQ88Pcm0pp77e3k50qTOSgi_nK/view?usp=share_link
Configured
Link: https://drive.google.com/file/d/17THOPlBPD-BZZJS9_1JpFUj3MW7_fBh0/view?usp=share_link
Openwrt Configuration
The OpenWrt image configured above supports CM4 onboard Wifi and the driver of RTL8153. You can make CM4 into a smart router. Here is a tutorial on how to install Openwrt on the Raspberry Pi to realize the wireless router function, so that the devices in the LAN can access the Internet through the wireless router, and realize the intelligent management of the LAN. The overall network topology is shown below.

After booting up correctly, log in to the system:
The computer is connected to the ETH0 port, and then directly ssh remote login or web page login.
The configured system default IP is: 192.168.14.1
The default IP of the system without configuration is: 192.168.1.1
Account: root without password.


CM4_Openwrt
Raspberry Pi OpenWrt Tutorial 1: System Compilation and Configuration
Raspberry Pi OpenWrt Tutorial 2: Build a Portable Raspberry Pi 4G Wireless Router
If you think the network port is not enough, you can buy USB 3.2 Gen1 TO Gigabit ETH RTL8153 expansion network port, if any ETH/USB HUB HAT RTL8152 can also expand the 100M Ethernet port and support it.
Resources
Manual
Schematic Diagram
3D Drawing
Demo
Software
FAQ
a) Check whether dtparam -audio - on is blocked in /boot/config.txt.
b) Check if the /boot/dt-blob.bin file exists, if it is unusable, please delete it.
{{{5}}}
Question:Where can I obtain an E-KEY slot memory board that fits your CM4-DUAL-ETH-WIFI6-BASE board?
The E key of CM4-DUAL-ETH-WIFI6-BASE is for WIFI, not NVME or SSD.
{{{5}}}
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)