10.1inch HDMI LCD (New RTD2660 Version) User Manual
Features
- 10.1inch IPS screen,1024×600 high resolution
- Resistive touch control
- Compatible and Direct-connect with any revision of Raspberry Pi (If you are using a Raspberry Pi Zero / Zero 2 W, an additional HDMI cable is required)
- Supports Raspberry Pi OS / Ubuntu / Kali and Retropie systems.
- Also works as a computer monitor, in this case, touch panel is unavailable and HDMI cable is required
- HDMI interface for displaying, no I/Os required (however, the touch panel still needs I/Os)
- OSD menu, supports brightness/contrast ratio adjustable manually.
Getting Started
Hardware Connection
1. Connect the GPIO interface
Raspberry Pi leads out 40 GPIO pins, while the screen leads out 26 pins. When connecting, pay attention to the corresponding pins and Raspberry Pi pins.
2. Connect the HDMI connector to the HDMI port of the screen and the Pi.
Note: Raspberry Pi Zero / Zero 2 W needs an additional HDMI cable for connection.
Software Setting
This LCD can support Raspberry Pi OS / Ubuntu / Kali / Retropie systems.
Please download the latest version of the image on the Raspberry Pi official website.
1) Download the compressed file to the PC, and unzip it to get the .img file.
2) Connect the TF card to the PC, use SDFormatter software to format the TF card.
3) Open the Win32DiskImager software, select the system image downloaded in step 1, and click ‘Write’ to write the system image.
4) After the image has finished writing, open the config.txt file in the root directory of the TF card, add the following code at the end of config.txt, then save and quit the TF card safely.
hdmi_group=2 hdmi_mode=87 hdmi_cvt 1024 600 60 6 0 0 0 dtoverlay=ads7846,cs=1,penirq=25,penirq_pull=2,speed=50000,keep_vref_on=0,swapxy=0,pmax=255,xohms=150,xmin=200,xmax=3900,ymin=200,ymax=3900
5) Insert the TF card into the Raspberry Pi, power on the Raspberry Pi, and wait for more than 10 seconds to display normally. But the touch is abnormal at that time, and the touch needs to be calibrated as the following steps.
Touch calibration
The display can be calibrated via xinput-calibrator.
1. Execute the following command to install the relevant software:
sudo apt-get install xserver-xorg-input-evdev xinput-calibrator
If the execution fails, you can check here#Some possible problems
2. Execute the following commands:
sudo cp -rf /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/10-evdev.conf /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/45-evdev.conf sudo nano /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/99-calibration.conf
Add the following code to 99-calibration.conf:
Section "InputClass"
Identifier "calibration"
MatchProduct "ADS7846 Touchscreen"
Option "Calibration" "117 3992 3743 156"
Option "SwapAxes" "1"
Option "EmulateThirdButton" "1"
Option "EmulateThirdButtonTimeout" "1000"
Option "EmulateThirdButtonMoveThreshold" "300"
EndSection
3. After reboot, touch will work normally under normal circumstances. But for different resistance screens, the accuracy of using the default calibration parameters may not be very suitable.
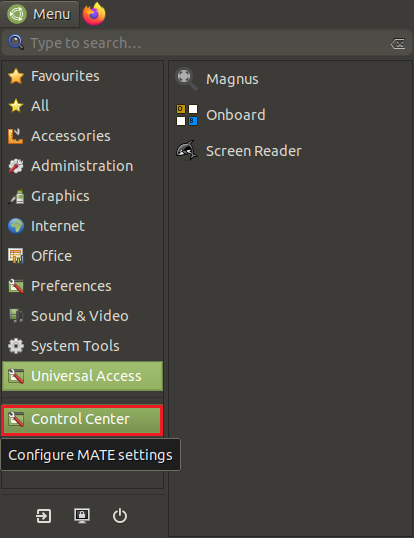
You can perform touch calibration by clicking the Raspberry Pi icon on the taskbar, selecting Preferences -> Calibrate Touchscreen, and following the displayed prompts.
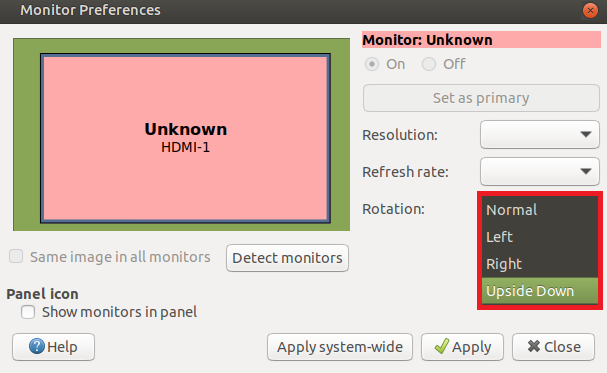
4. After calibration, the following data will be displayed. If you want to save these touch values, you can replace the data in the red circle with the data in the corresponding position in 99-calibration.conf.
Screen orientation settings
First check whether the KMS or FKMS driver is loaded on the system you are using.
Check method: In /boot/config.txt, check whether the line dtoverlay=vc4-kms-v3d or dtoverlay=vc4-fkms-v3d is turned on.
With KMS or FKMS driver loaded
Use the following command for display rotation:
sudo nano /etc/xdg/lxsession/LXDE-pi/autostart #Enter the command corresponding to the display rotation angle at the end of the autostart file, and it will take effect after rebooting the system. #0: rotate 0 degrees; 1: rotate 270 degrees; 2: rotate 180 degrees; 3: rotate 90 degrees xrandr -o 1
No KMS or FKMS driver loaded
Use the following command for display rotation:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt #Enter the command corresponding to the display rotation angle at the end of the config.txt file, and it will take effect after rebooting the system. #0: rotate 0 degrees; 1: rotate 90 degrees; 2: rotate 180 degrees; 3: rotate 270 degrees display_rotate=3
Ubuntu display rotation
First check whether the KMS or FKMS driver is loaded on the system you are using.
Check method: In /boot/firmware/config.txt, check whether the line dtoverlay=vc4-kms-v3d or dtoverlay=vc4-fkms-v3d is turned on.
With KMS or FKMS driver loaded
Use the following methods for display rotation.
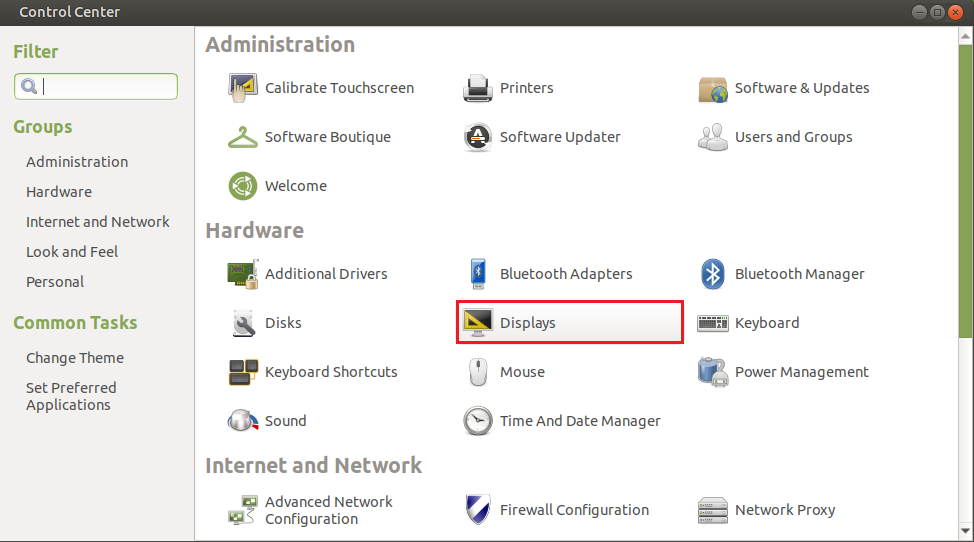
Note: For different versions of Ubuntu systems, the interface may be different. Generally, you can find the Displays application and rotate it.
Execute the command to rotate the Ubuntu login interface. If the Ubuntu login interface is not opened, this step can be omitted:
#For 32-bit systems, execute the following command, replace your_user with the currently logged in user name sudo cp /home/<your_user>/.config/monitors.xml /var/lib/lightdm/.config #For 64-bit systems, execute the following command, replace your_user with the currently logged in user name sudo cp /home/<your_user>/.config/monitors.xml /var/lib/gdm3/.config sudo chown gdm:gdm /var/lib/gdm3/.config/monitors.xml
Execute the following command to rotate the command line display during startup:
sudo nano /boot/firmware/cmdline.txt #Add the following code at the end to rotate the command line #rotate 0 degrees fbcon=rotate:0 video=HDMI-A-1:640x480M@60,rotate=0 #Rotate 90 degrees fbcon=rotate:3 video=HDMI-A-1:640x480M@60,rotate=90 #rotate 180 degrees fbcon=rotate:2 video=HDMI-A-1:640x480M@60,rotate=0 #rotate 270 degrees fbcon=rotate:1 video=HDMI-A-1:640x480M@60,rotate=270
No KMS or FKMS driver loaded
Rotation is relatively simple, just use the following command to display rotation:
sudo nano /boot/firmware/config.txt #Enter the command corresponding to the display rotation angle at the end of the config.txt file, and it will take effect after rebooting the system. #0: rotate 0 degrees; 1: rotate 90 degrees; 2: rotate 180 degrees; 3: rotate 270 degrees display_rotate=3
Add touch rotation parameter
sudo nano /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/99-calibration.conf #Modify the relevant command line in the 99-calibration.conf file, and it will take effect after rebooting the system. The following are the default calibration parameters. If you need to use specific calibration parameters, please pay attention to the order of the Calibration parameter values. #touch rotate 0 degrees: Option "Calibration" "117 3992 3743 156" Option "SwapAxes" "1" #touch rotate 90 degrees: Option "Calibration" "39 3789 97 3970" Option "SwapAxes" "0" #touch rotate 180 degrees: Option "Calibration" "3967 97 97 3782" Option "SwapAxes" "1" #touch rotate 270 degrees: Option "Calibration" "3795 73 3964 94" Option "SwapAxes" "0"
Interface
| PIN NO. | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 1, 17 | 3.3V | Power positive (3.3V power input) |
| 2, 4 | 5V | Power positive (5V power input) |
| 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16, 18, 24 | NC | NC |
| 6, 9, 14, 20, 25 | GND | Ground |
| 19 | TP_SI | SPI data input of Touch Panel |
| 21 | TP_SO | SPI data output of Touch Panel |
| 22 | TP_IRQ | Touch Panel interrupt, low level while the Touch Panel detects touching |
| 23 | TP_SCK | SPI clock of Touch Panel |
| 26 | TP_CS | Touch Panel chip selection, low active |
KEYS
- Power: turn on/off the back light. If you needn't use the LCD for a long time, you can turn off the back light with this button to reduce the comsuption
- Menu: Menu button. Press this button to open the OSD menu, and used as "OK" button as well.
- Up/Left: Direction button
- Down/Right: Direction button
- Return: Return button. Press to return.
Some possible problems
Touch jitter so obvious, how to solve it?
De-jitter parameters can be set to solve the problem of touch jitter, but at the cost of sacrificing a part of the sensitivity.
Since the ads7846.dtbo provided by Raspberry Pi by default has no de-jitter parameters, you can increase the de-jitter parameters by modifying and replacing ads7846.dtbo
Specifically, the anti-shake function can be added in the following method:
1.Execute the following command:
wget https://www.waveshare.net/w/upload/2/29/Ads7846_waveshare.zip unzip Ads7846_waveshare.zip cd ads7846_waveshare sudo cp ads7846_waveshare.dtbo /boot/overlays/
2.Execute the following command:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt #Comment out the following line: #dtoverlay=ads7846,cs=1,penirq=25,penirq_pull=2,speed=50000,keep_vref_on=0,swapxy=0,pmax=255,xohms=150,xmin=200,xmax=3900,ymin=200,ymax =3900 #Add the following command at the end of the config.txt file, it will take effect after rebooting the system. dtoverlay=ads7846_waveshare
Related reference documents:ads7846-overlay.dts ads7846.txt
The installation of xserver-xorg-input-evdev and xinput-calibrator in Ubuntu system reports an error, so the touch cannot be used normally. How to solve it?
Note: The Ubuntu system may not be able to access the default source due to network problems in some regions, resulting in an installation error.
Solution 1, update the source:
1. Execute the command to view the current version:
lsb_release -c -s
For example, after execution, the system version may be: groovy
2. Execute the commands:
#backup the original source sudo mv /etc/apt/syntaxhighlights.list /etc/apt/syntaxhighlights.list.old sudo nano /etc/apt/syntaxhighlights.list
Add the following code and save:
#If your system version is not groovy, please replace the following groovy with the version name obtained in step 1 deb http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ groovy universe main deb http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ groovy-security main universe deb http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ groovy-updates main universe
3. Execute the command to update:
sudo apt-get update
4. After the update is complete, run #Touch calibration again.
If the above source fails, the following methods can be used:
Solution 2, directly find the download address of the two applications, download and install directly
For 32-bit systems, execute the following commands:
wget http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/x/xserver-xorg-input-evdev/xserver-xorg-input-evdev_2.10.6-2_armhf.deb sudo dpkg -i xserver-xorg-input-evdev_2.10.6-2_armhf.deb wget wget http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian/pool/main/x/xinput-calibrator/xinput-calibrator_0.7.5+git20140201-1+b2_armhf.deb sudo dpkg -i xinput-calibrator_0.7.5+git20140201-1+b2_armhf.deb
For 64-bit systems, execute the following commands:
wget http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/x/xserver-xorg-input-evdev/xserver-xorg-input-evdev_2.10.6-2_arm64.deb sudo dpkg -i xserver-xorg-input-evdev_2.10.6-2_arm64.deb wget http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian/pool/main/x/xinput-calibrator/xinput-calibrator_0.7.5+git20140201-1+b2_arm64.deb sudo dpkg -i xinput-calibrator_0.7.5+git20140201-1+b2_arm64.deb
The installation of xserver-xorg-input-evdev and xinput-calibrator in Kali system reports an error, so the touch cannot be used normally. How to solve it?
Note: The Kali system may not be able to access the default source due to network problems in some regions, resulting in an installation error.
Solution 1, update the source:
1. Execute sudo su to obtain administrator privileges. The default password is kali.
2. Execute the command:
wget -q -O - https://archive.kali.org/archive-key.asc | apt-key add
3. Execute the command to modify the source:
nano /etc/apt/syntaxhighlights.list
Comment out the original source and modify it to:
deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-free
Save and exit.
4. Execute the command to update:
apt-get update --fix-missing
5. After the update is complete, run #Touch calibration again.
If the above source fails, the following methods can be used:
Solution 2, directly find the download address of the two applications, download and install directly
For 32-bit systems, execute the following commands:
wget http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/x/xserver-xorg-input-evdev/xserver-xorg-input-evdev_2.10.6-2_armhf.deb sudo dpkg -i xserver-xorg-input-evdev_2.10.6-2_armhf.deb wget wget http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian/pool/main/x/xinput-calibrator/xinput-calibrator_0.7.5+git20140201-1+b2_armhf.deb sudo dpkg -i xinput-calibrator_0.7.5+git20140201-1+b2_armhf.deb
For 64-bit systems, execute the following commands:
wget http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/x/xserver-xorg-input-evdev/xserver-xorg-input-evdev_2.10.6-2_arm64.deb sudo dpkg -i xserver-xorg-input-evdev_2.10.6-2_arm64.deb wget http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/debian/pool/main/x/xinput-calibrator/xinput-calibrator_0.7.5+git20140201-1+b2_arm64.deb sudo dpkg -i xinput-calibrator_0.7.5+git20140201-1+b2_arm64.deb