SIM7600G-H 4G DTU
| ||
Overview
Feature
- 4G DTU development kit specially designed for industrial applications, which can be directly embedded for using or secondary development.
- Based on the SIM7600G-H communication module, it supports 4G/3G/2G networks in global frequency bands.
- Support GPS, Beidou, GLONASS, GALILEO, QZSS, and LBS base station positioning.
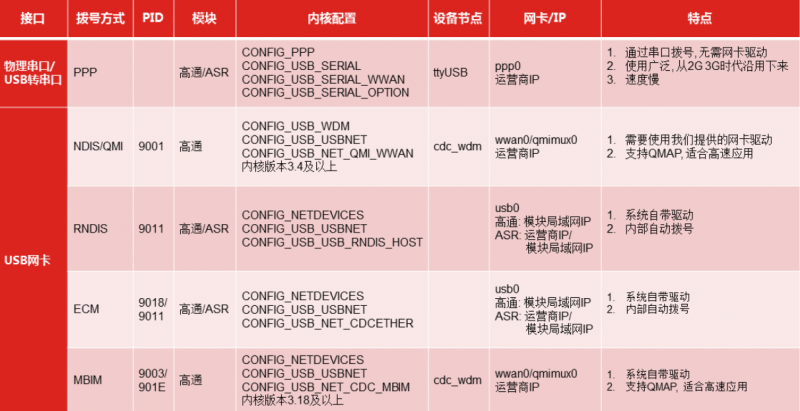
- Supports USB to 4G and UART/RS232/RS485 to 4G networking communication.
- Supports power supply in a wide voltage range of 7 ~ 36 V, which is convenient for power supply on industrial occasions.
- Onboard STM8 microcontroller, can be used as a hardware watchdog, automatically power off and restart when DTU works abnormally.
- Various on-board protection circuits, anti-static, anti-surge, etc., the communication is stable and safe.
- Support baud rate range: 300bps ~ 4Mbps (default is 115200bps).
- Support AT command control (based on 3GPP TS 27.007, 27.005 and V.25TER command set).
- Aluminum case, oxidized dull polish surface, CNC numerical control opening processing, rugged & elegant.
Specification
| Working Frequency | |
| 4G | LTE-FDD: B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B7, B8, B12, B13, B18, B19, B20, B25, B26, B28, B66
LTE-TDD: B34, B38, B39, B40, B41 |
| 3G | UMTS/HSDPA/HSPA+: B1, B2, B4, B5, B6, B8, B19 |
| 2G | GSM/GPRS/EDGE: 850, 900, 1800, 1900 MHz |
| GNSS | GPS, Beidou, GLONASS, GALILEO, QZSS |
| Applicable Area | Used globally |
| Data Transmission | |
| 4G (LTE Cat-4) | 150Mbps(DL) / 50Mbps(UL) |
| 3G (HSPA+) | 42Mbps(DL) / 5.76Mbps(UL) |
| 2G (EDGE) | 236.8Kbps(DL) / 236.8Kbps(UL) |
| Software Function | |
| Communication Protocol | TCP, IP, IPV4, IPV6, multi-PDP, FTP, FTPS, HTTP, HTTPS, DNS (send and receive control through AT instructions, can provide the module Open Linux SDK for secondary development) |
| Support System | Windows/Linux etc. |
| Hardware Description | |
| Serial Communication Interface | RS232: Interface form: DB9 female port Interface protection: TVS tube protection, surge and electrostatic protection |
|---|---|
| RS485: Interface form: terminal block (A, B) Interface protection: provide 600W lightning protection, surge protection and 15KV electrostatic protection (reserved 120R balance resistance pad) | |
| TTL(UART): Working level: 3.3V or 5V Interface form: terminal block (TXD, RXD, GND) | |
| Baud Rate Of Serial Communication | The value ranges from 300bps to 921600bps. The default value is 115200bps |
| The USB interface | Operating level: 5V Port type: Micro USB |
| Power Interface | Port type: 7 to 36V wiring terminals or 12V DC ports
Interface protection: Schottky diode protection, anti-reverse connection protection |
| Hardware Protection | Built-in MCU, hardware watchdog function to ensure no downtime; industrial grade aluminum alloy shell |
| Operating Voltage | 7 ~ 36V DC |
| Working Current | Idle current: 10 ~ 30mA @12V
Transmit current: 80 ~ 450mA @12V (depending on network conditions) |
| Indicator Light | PWR (power supply), RXD/TXD (serial port transceiver), NET (network), LINK (customizable) |
| Button | Reset button |
| SIM Card | Standard SIM card (1.8V/3V) |
| Antenna Interface | MAIN LTE, AUX LTE, GNSS |
| Operating Temperature | -40℃ ~ 80℃ |
Quick test
Hardware test environment
Hardware preparation
The accessories required for the quick test are as follows:
- Standard configuration (after purchase, there will be the following accessories):
SIM7600G-H 4G DTU host × 1 High gain LTE main antenna (about 3 meters) × 1 High Gain Paddle LTE Auxiliary Antenna × 1 GPS antenna × 1 Serial cable male to female direct connection (about 1.5 meters) × 1 USB cable type A male to micro-B male (about 1.2 meters) × 1 12V 1A power supply × 1
- Hardware that need to be prepared separately:
computer × 1 USB TO RS232/485/TTL × 1 4G card (or 4G-enabled mobile phone card) × 1
Hardware connection
In order to facilitate direct access to the computer test, we recommend to buy:USB TO RS232/485/TTL
The schematic diagram of DTU test hardware connection is as follows::

DTU startup and restart
Connect the hardware according to the picture above and insert the 4G card (standard SIM card).
- Power-on: After the power supply is powered on, the NET network light is on or blinks, indicating that the power is successfully started.
| The serial number | Indicator/button | Functional specifications |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PWR | The red light is on indicates the power is on |
| 2 | TXD | Blinking blue: Data is being transmitted |
| 3 | RXD | Blinking blue: Data is being received |
| 4 | NET | The green indicator blinks indicates the network is normal |
| 5 | LINK | User - defined LED for secondary development |
| 6 | RESET | Reset button |
- Restart: Press the RESET button to restart the device.
Software testing environment
The following test takes Windows 10 as an example. Before the test, install the driver, configure DTU parameters on the host computer, and then use the serial debugging assistant to perform transparent transmission test. The TCP/UDP server for transparent transmission can be a self-built server or a test server.
Driver installation
Used for the first time, you need to install SIM7600X 4G DTU driver
- Insert the USB port of 4G DTU into a Windows PC (Windows 10 as an example below)
- Open Device Manager - > Other Devices - > "SimTech,Incorporated" - > Update the driver - > Browse my computer for driver software - > Select a path to save the driver file based on your system - > Installation complete.
- Install all identified devices according to the above method, and the driver installation effect is as follows:
Common AT instruction
| The command | Show | The return value |
|---|---|---|
| AT | the AT test instruction | OK |
| ATE | ATE1 set echo echo ATE0 closed |
OK |
| The AT + CGMI | query module manufacturers | OK |
| AT + CGMM | query module type | OK |
| The AT + CGSN | query product serial number | OK |
| AT + CSUB | query module version and chip | OK |
| The AT + CGMR | query firmware version serial number | OK |
| AT + IPREX | Settings module hardware serial port baud rate | + IPREX: OK |
| AT + CRESET | reset module | OK |
| AT + CSQ | network signal quality query, return signal value | + CSQ: 13 of 17 OK |
| AT+CPIN? | to track the status of SIM card, return to READY, said SIM card can identify normal | + CPIN: READY |
| AT+COPS? | to query the current operator, will return after normal network operators information | + COPS: OK |
| AT+CREG? | to track the status of network registration | + CREG: OK |
| AT+CPSI? | query UE system information | |
| AT + CNMP | network mode selection command: 2: Automatic 13: GSM only 38: LTE only 48: Any modes but LTE ... |
OK |
For more AT commands, see SIM7500_SIM7600 Series_AT Command manual_v1.07
GNSS control instance
- Plug in the GPS antenna, and place the receiver tag face down in the open air,(Note that rainy weather cannot be tested) you need to wait about 1 minute before receiving the location signal.
- Detailed test instructions and screenshots are as follows:
AT+CGPS=1 // Open GPS AT+CGPSINFO // Prints GPS information to the serial port AT+CGPS=0 // Turn off GPS
4G Internet Access
Windows Internet Access
hardware connection
NDIS dial-up Internet access
- At present, when using Windows 10 operating system, you can connect to 4G DONGLE module (equipped with 4G card of China Mobile/Telecom/Unicom). After installing the driver, most computers will automatically connect to the Internet.
- If WINdows cannot access the Internet, you need to manually start NDIS dialing, open SIM7600 AT port, and send the command:
AT$QCRMCALL=1,1+enter

At this point, the NDIS dialing takes effect, and the computer can connect to the network; if the dialing command returns an error, send the following command to set the NDIS dialing mode and then dial again:
AT+CUSBPIDSWITCH=9001,1,1
RNDIS Dial-Up Internet
In addition, dial-up Internet access using RNDIS is also possible:
- After the device installed SIM card and antenna, connect the USB port to computer, then connect the power supply.
- Refer to the above to install the USB driver
- Open the serial port assistant, find the serial port number corresponding to the AT serial port, and send the AT command to check whether it is registered on the network:
AT+CPSI?
- If you have successfully registered on the network, then send the AT command to enable USB dial-up Internet access:
AT+CUSBPIDSWITCH=9011,1,1
- If the transmission is successful, the DTU will return OK and reboot automatically.
- And then you can find that there are some unrecognized devices in the Device Manager on the computer, such as RNDIS (with exclamation mark).
- Right-click the 'RNDIS', search "Update Divers" and select "Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer", then select "Network adapters" from the device list.
- Select "Microsoft" in the manufacturer list of the Network adapters window, and then select "Remote NDIS Compatible Device" in the list on the right, which is the remote NDIS compatible device.
Click 'Next' and wait for the installation to finish, the RNDIS Kitl device will be installed successfully. And then you can see that the PC can access the Internet via DTU.
PPP dial-up
If the NDIS or RNDIS dial-up cannot access the Internet, you can also use PPP dial-up. The operation steps are as follows:
- Network and Internet Settings -> Set up a new connection -> Connect to the Internet -> Dial up (D) -> Dial a phone number (D): *99# (others are empty by default) -> Connection -> Register -> Connected to the Internet
Raspberry Pi Raspbian Internet Operation
1.Hardware Connection
2.Environment Configuration
The Raspberry Pi Raspbian system has built-in drivers for SIM7600X, so there is no need to install additional drivers. However, some configuration is required to enable 4G networking. Common networking methods are as follows:
- Raspberry Pi RNDIS dial-up Internet- (the easiest way to operate)
- Raspberry Pi PPP dial-up- (the operation is relatively simple)
- Raspberry Pi NDIS dial-up Internet access
Jetson Nano Internet Operation
1.Hardware connection
The hardware connection diagram is as follows:

2.Environment configuration
The Ubuntu system of Jetson Nano does not have the driver module file of simcom for the wwan0 network port by default, so you need to compile and install the driver module. For details, see:
- RNDIS dial-up Internet access - (the easiest operation)
Other Linux Internet Operations
1. Hardware connection
Connect SIM7600X 4G DONGLE to the hardware USB interface of the corresponding Linux platform.
2. Driver installation
First, you can use the command to check whether the system can recognize the driver normally. If the driver cannot be recognized normally, you need to install the driver manually. For details, see:
Resource
Documentation
Program
Software
- SIM7600 drive
- SIM7600 Serial Debug Assistant
- GPS debugging tool
- TCP test tools
- Unicode conversion software
Datasheet
- SIM7500_SIM7600 Series_AT Command Manual_V3.00.pdf
- SIM7600G(-H)_SIM7600NA(-H)_Hardware_Design_V1.08.pdf
- SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_TCPIP_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7500_SIM7600 Series_FTP(S)_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7500_SIM7600 Series_Compatibility_With_SIM800_HTTP_ATC_V1.00.pdf
- SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SSL_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_MQTT_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7500_SIM7600_SIM7800 Series_SMS_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7500_SIM7600 Series_GNSS_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7100_SIM7500_SIM7600 Series_LBS_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7500_SIM7600 Series_Linux NDIS_driver_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7600 Series_Open Linux_Development Guide_V2.00.pdf
- SIM7600 Series_Open Linux UART-SPI_Application Note_V2.00.pdf
For more module information, please visit SIMCom official website: SIM7600G-H
FAQ
In this case, it may be that you have not successfully connected to the network, you can follow the steps below to troubleshoot:
1. First check the hardware connection:
- Check if the MAIN antenna is connected properly;
- Whether the connected SIM card can communicate and surf the Internet normally on mobile phones and other devices:
- If the Raspberry Pi is connected, whether the module enters airplane mode;
2. After confirming that there is no problem with the hardware, the software can use these instructions:
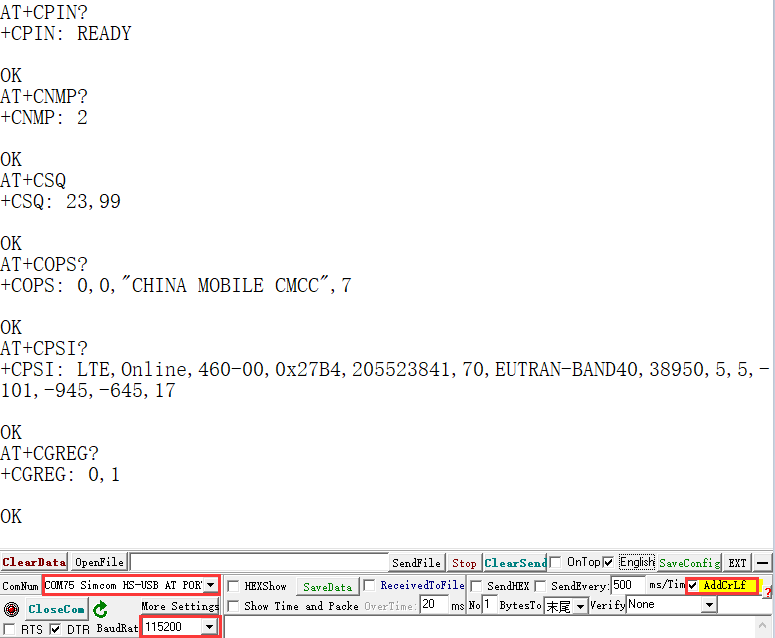
- Check if the sim card is in good contact: AT+CPIN?
- Check if the network mode setting is correct: AT+CNMP?
- Check the signal quality of the current environment: AT+CSQ
- Check carrier access:AT+COPS?
- Check internet connection:AT+CPSI?
- Check for successful registration to the network: AT+CGREG?
{{{5}}}
ATE1
{{{5}}}
- Open the Raspberry Pi terminal and input the following commands:
sudo raspi-config Select Interfacing Options -> Serial to turn off shell access and turn on the hardware serial port
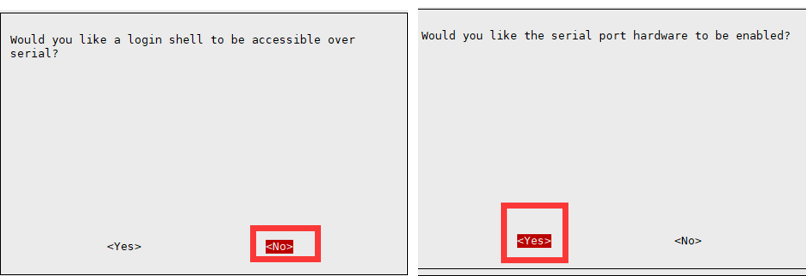
Raspberry Pi 2B/zero, the user serial device number is ttyAMA0; you can use the following command line to confirm that serial0 is the selected serial device number, as follows:
ls -l /dev/serial*
{{{5}}}
Set up as below:
AT+CGDCONT=1, "IPV6", "APN" //Switch to IPV6, different operators APN is different, pay attention to distinguish the settings AT+CGDCONT=1, "IP", "APN" //Switch back to IPV4
{{{5}}}
- Under normal circumstances, SIM7600X has already dialed automatically when it is connected to the Windows system, no need to repeat the dialing, the repeated dialing will return NO CARRIER
- If you still cannot dial up, please use the following command to change to the Windows default dial-up mode
AT+CUSBPIDSWITCH=9001,1,1
- The display is turned off and the mobile network is not enabled, you can ignore it and go online directly;
- You can also install the driver SIM7600X dial-up Driver to update the network card
- After installing the driver, the network card shows that it is enabled
- Generally, the default configuration of SIM7600 is to automatically select the network standard, and it is likely to choose 2G Internet access; if you need to force the use of 4G mode, you need to enter the following AT command configuration:
AT+CNMP=38 //Fixed 4G LTE, if there is no local 4G coverage, you may not be able to register to the network
- If 4G has been fixed and the speed is still not ideal, it may be a frequency band problem;
AT+CNBP? //Backup the current band (the returned band information can be copied to Notepad, etc.)
AT+CNBP=0x0002000000400183,0x000001E000000000,0x0000000000000021 //After returning to OK, measure the speed
AT+CNBP=0x0002000004400180,0x000001E000000000,0x000000000000003F //If the speed doesn't improve, try this
Positioning Commands
AT+CGPSNMEA=197119
Or you can use the following commands to obtain the position information.
AT+CGPSINFOCFG=10,31
{{{5}}}

For more detailed steps, please refer to the following link.
SIM7600X gets the latitude and longitude in units, we commonly use degrees as the unit, please see below for more details.
{{{5}}}
Common commands for the LBS base station positioning function of SIM7600X are as follows:
AT+CLBS=? //View the range of parameters that can be set AT+CNETSTART//Open the network; if it fails to open the network, you can use the command AT+CNETSTOP to close and then open AT+CLBS=1 //Get the current latitude and longitude AT+CLBS=2 //Get the detailed address
Calling SMS
The VOLTE function can be enabled with the following command:
at+voltesetting=1 at+cnv=/nv/item_files/modem/mmode/ue_usage_setting,1,01,1
The VOLTE function can be disabled with the following command:
at+voltesetting=0 at+cnv=/nv/item_files/modem/mmode/ue_usage_setting,0,01,1
Note: The difference between Volte calls and regular phone calls: The network of Microsoft calls goes on a packet-switched Internet network. And ordinary phone calls take the circuit-switched (PSTN network) communication network. There is a fundamental difference between the two. By the time of 4G LTE, the packet network can control the delay to low enough, and ordinary phones can make calls directly through VOLTE with the packet network. However, in places where the network is poor, circuit-switched networks are still inseparable.
{{{5}}}
SIM7600X makes a call and the phone answers ATD131xxxxx816. Record SIM7600 and phone sound to module memory E disk (record to memory card read D) AT+CREC=3, "e:/rec.wav" End recording AT+CREC=0 Play sound to the phone side to listen AT+CCMXPLAYWAV="E:/rec.wav",1 Play sound to SIM7600 AT+CCMXPLAYWAV="E:/rec.wav",2 End playback AT+CCMXSTOPWAV
{{{5}}}
If the short message is stored in the SIM card, the limit is generally 50. You can use the command: AT+CPMS? make an inquiry.
AT+CSCA="+8613800755500"
The command should be added + enter to return OK.
{{{5}}}
- Confirming that the SIM7600X is registered to the network and that the SIM card can send and receive SMS messages properly on devices such as cell phones;
- Setting the correct SMS center number;
- Initialize the SMS settings with the following command:
AT+CSCS="IRA" AT+CSMP=17,167,0,0
{{{5}}}
Hardware FAQ
This problem is generally caused by poor contact between the SIM card and the SIM card holder of the module.
- Confirm whether the frequency band supported by the IoT card covers the frequency band supported by the module.
- APN is not set, please use the following command to configure APN.
- Note: Different operators' APNs is different, here the APN is changed to the corresponding operator.
- It may be blocked, high traffic (real-name IoT) cards are going to be machine card binding, and can only be used on a device (the State Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Ministry of Public Security, issued to the operator must be so); you can let the IoT card operator check the status of the card and unlock the next.
{{{5}}}
Using a USB 5V power supply, after successful networking, the current is generally in the range of 50~300mA, and the average is about 150mA (for reference only, depending on the network environment and networking status.
Open at the same time, average: 110~170mA
- Frequency: 700m 800m 900m 1710-1920M 2010-2100M 2300-2400M 2500-2690M-5800MHZ
- Gain: 9dbi ± 0.7dbi
1) The AUX auxiliary antenna is a diversity antenna, the main antenna signal is not good enough to receive the signal with the receiving antenna, and the physical location is not the same, there is always a better, diversity antenna connected to the bandwidth and rate sensitivity will be increased by about 20%.
2) No diversity antenna can make the receiver obtain a maximum of not more than 3db diversity gain, but the diversity does not line any transmitting function, so to connect to the main antenna, transmit the signal to the base station registered to the network, the auxiliary antenna will only work.
{{{5}}}
1) /dev/ttyUSB0-diag port for output developing messages 2) /dev/ttyUSB1- NMEA port for GPS NMEA data output 3) /dev/ttyUSB2-AT port for AT commands 4) /dev/ttyUSB3-Modem port for ppp-dial 5) /dev/ttyUSB4-Audio port
{{{5}}}
echo "4" > /sys/class/gpio/export echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio4/direction echo "0" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio4/value echo "6" > /sys/class/gpio/export echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio6/direction echo "0" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio6/value
{{{5}}}
{{{5}}}
System Firmware
- Make sure your system kernel is above 5.4. Do not use sudo update to upgrade the Raspberry Pi to the latest version, otherwise, the kernel version will be upgraded to a version higher than the current firmware and will not be recognized.
- It is recommended to use the more convenient RNDIS dial
- You can burn the latest Raspberry Pi Raspbian system and reconfigure the NDIS dial-up
- Or use the image that has been configured with the driver NDIS dial-up self-starting Raspbian system image (driver installed)
The new driver may not be compatible with some WIN7 systems, you can try the old driver:
- SIM7600 old driver
- SIM7600 new driver
- 1. Download the driver.
- 2. Connect the 4G HAT to a Windows computer as shown in the hardware connection diagram above (Windows 10 OS is used as an example below)
- 3. Make sure the module has been powered on properly: refer to the previous section "Switching on and off the module"
- 4. Open Device Manager->Other Devices->"SimTech, Incorporated "-> Update Driver -> Browse My Computer to find the driver file -> According to the system, select the path where the driver file is stored -> Installation is complete.
- 5. Install all the recognized devices and drivers:
You can refer to two ways, the detailed steps refer to the following:
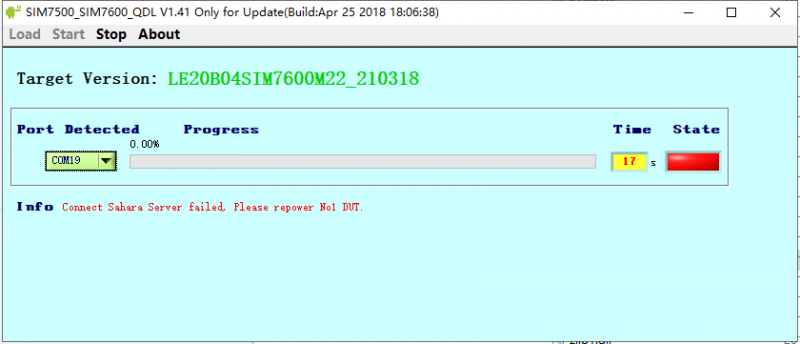
1. Pay attention to check the device manager, the upgrade process will prompt the new device inserted, and the first upgrade will not have a device driver;
2. Pay attention to the USB cable, the USB cable rate is high during the upgrade process, so you need to choose a better quality USB cable to avoid poor contact.
3. Need to run the upgrade tool with administrator privilege (SIM7500_SIM7600_QDL V1.41 only for Update).
4. Uninstall and reinstall the update tool (SIM7500_SIM7600_QDL V1.41 only for Update).
{{{5}}}
Demo Code
Question:When executing the chmod 777 sim7600_4G_hat_init command, an error is reported: "chmod: cannot access 'sim7600_4G_hat_init': No such file or directory"How to deal with it?

Please confirm that there is a sim7600_4G_hat_init file in the current path
The general operation is: download the sample program, after decompression, rename the c folder under the Raspberry folder to SIM7600X, and then copy the entire SIM7600X folder to the Raspberry Pi /home/pi directory,
Enter the command line into the /home/pi/SIM7600X directory, and then execute the chmod 777 sim7600_4G_hat_init command.
Support
Technical Support
If you need technical support or have any feedback/review, please click the Submit Now button to submit a ticket, Our support team will check and reply to you within 1 to 2 working days. Please be patient as we make every effort to help you to resolve the issue.
Working Time: 9 AM - 6 PM GMT+8 (Monday to Friday)